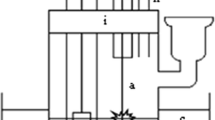
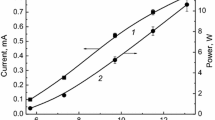
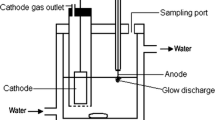
Abstract
Decomposition of aqueous dichlorophenols and trichlorophenols was investigated by means of contact glow discharge electrolysis. With the decay of chlorophenols (CPs), the amount of total organic carbon (TOC) in water also decreased smoothly, indicating that carbon atoms of benzene nucleus could be eventually converted to inorganic carbons. And, it was found that chlorine atoms in the CPs were released as chloride ions. As the by-products, oxalate and formate were formed. The chlorine derivatives of 1,4-hydroquinone and 1,4-benzoquinone were detected as the primary intermediates in the initial stage of decomposition of each of CPs. The decay of both CPs and TOC obeyed the first-order rate law, respectively. The apparent rate constants for the decay of CPs increased with the decrease in pKa values of CPs, while those for the decay of TOC were substantially unaffected.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hickling A, Ingram MD (1964) Trans Faraday Soc 60:783
Hickling A (1971) In: Bockris JOM, Conway BE (eds) Modern aspects of electrochemistry, vol 6. Butterworths, London, p 329
Sengupta SK, Singh OP (1991) J Electroanal Chem 301:189
Gangal U, Srivastava M, Sen Gupta SK (2009) J Electrochem Soc 156:131
Gangal U, Srivastava M, Sen Gupta SK (2010) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30(2):299
Wang X, Zhou M, Jin X (2012) Electrochim Acta 83:501
Almubarak MA, Wood A (1977) J Electrochem Soc 124:1356
Bullock AT, Gavin DL, Ingram MD (1980) J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 76:648
Sengupta SK, Singh OP (1994) J Electroanal Chem 369:113
Sengupta SK, Singh R, Srivastava AK (1998) J Electrochem Soc 145:2209
Sengupta SK, Singh R, Srivastava AK (1998) Indian J Chem 37:558
Mazzocchin GA, Bontempelli G, Magno F (1973) J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 42:243
Liu YJ (2009) J Hazard Mater 166:1495
Gong JY, Wang J, Xie WJ, Cai WM (2008) J Appl Electrochem 38:1749
Jin XL, Wang XY, Zhang HM, Xia Q, Wei DB, Yue JJ (2010) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30:429
Tezuka M, Iwasaki M (1997) Denki Kagaku 65:1057
Tezuka M, Iwasaki M (1999) Plasma Ions 1:23
Tezuka M, Iwasaki M (2001) Thin Solid Films 386:204
Amano R, Tomizawa S, Tezuka M (2004) Electrochemistry 72:836
Amano R, Tezuka M (2006) Water Res 40:1857
Tomizawa S, Tezuka M (2007) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 27:486
Yang HM, An BG, Wang SY, Li LX, Jin WJ, Li LH (2013) J Environ Sci 25(6):1
Yang HM, Matsumoto Y, Tezuka M (2009) J Environ Sci 21(Suppl 1):S142
Yang HM, Tezuka M (2011) J Phys D Appl Phys 44:155203
Yang HM, Tezuka M (2011) J Environ Sci 23:1044
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51308276) and the Youth Science Foundation of University of Science and Technology Liaoning (Grant No. 2012QN02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Caixia & Tezuka, M. Plasma-Induced Decomposition of Dichlorophenols and Trichlorophenols in Water by Means of Anodic Contact Glow Discharge Electrolysis. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 33, 1043–1052 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9481-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9481-5