Abstract
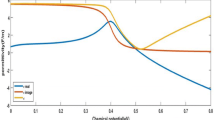
In this paper, a graphene–dielectric–graphene modulator with a dual-ring resonator structure is designed. To achieve the dynamic modulation of the light intensity, the modulator is combined with the selective frequency filtering characteristic of the dual-ring resonator and the electrically tunable characteristic of the graphene. The finite element method is used to study the radius of the ring, the dielectric material, the wavelength and the chemical potential of graphene. The simulation results show that when the incident wavelength is 1580 nm, the chemical potential drops from 0.854 to 0.834 eV, for a 5 μm-long graphene light modulator, the extinction ratio of the modulator reaches 7.56 dB. Compare the previously proposed graphene light modulator, the device can not only be combined with the high extinction ratio and small size, but also has the high speed modulation rate, which is of great significance for large-scale production and integration of optoelectronic devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gardes, F.Y., Thomson, D.J., Emerson, N.G., Reed, G.T.: 40 Gb/s silicon photonics modulator for TE and TM polarisations. Opt. Express 19(12), 11804–11814 (2011)
Hao, R., Jin, J., Wei, X., Jin, X., Zhang, X., Li, E.: Recent developments in graphene-based optical modulators. Front. Optoelectron. 7(3), 277–292 (2014)
Huang, L., Gao, B., Hartland, G., Kelly, M., Xing, H.L.: Ultrafast relaxation of hot optical phonons in monolayer and multilayer graphene on different substrates. Surf. Sci. 605(17), 1657–1661 (2011)
Liu, M., Yin, X., Ulin-Avila, E., Geng, B., Zentgraf, T., Ju, L.: A graphene-based broadband optical modulator. Nature 474(7349), 64–67 (2011)
Grigorenk, A.N., Polini, M., Novoselov, K.S.: Graphene plasmonics. Nat. Photo 6(11), 749–758 (2012)
Brownson, D.A.C., Banks, C.E.: The electrochemistry of CVD graphene: progress and prospects. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(23), 8264 (2012)
Stauber, T., Peres, N.M.R., Geim, A.K.: Optical conductivity of graphene in the visible region of the spectrum. Phys Rev B 78(8), 085432 (2008)
Ye, Jianting, Monica, F.C., Mikito, K., Saverio, R., Seiji, L., Hongtao, Y.: Accessing the transport properties of graphene and its multilayers at high carrier density. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108(32), 13002–13006 (2011)
Efetov, D.K., Kim, P.: Controlling electron-phonon interactions in graphene at ultrahigh carrier densities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 256805 (2010)
Jablan, M., Buljan, H., Soljacic, M.: Plasmonics in graphene at infrared frequencies. Phys. Rev. 80(24), 245435.1–245435.7 (2009)
Alexander, Y.Z., Fei, Y., Jason, C.R., Ertugrul, C.: Cavity-enhanced mid-infrared absorption in perforated graphene. J. Nanophoton. 8(4), 083888 (2014)
Zhan, S., Li, H., Cao, G., He, Z., Li, B., Yang, H.: Slow light based on plasmon-induced transparency in dual-ring resonator-coupled mdm waveguide system. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 47(20), 205101 (2014)
Yun, B., Hu, G., Cui, Y.: Theoretical analysis of a nanoscale plasmonic filter based on a rectangular metal–insulator–metal waveguide. J. Phys. D Appl. 43(38), 385102 (2010)
Hosseini, A., Massoud, Y.: Nanoscale surface plasmon based resonator using rectangular geometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(18), 1811021–1811023 (2007)
Li, B., Li, H., Zeng, L., Zhan, S., Cao, G., He, Z.: Tunable filter and optical buffer based on dual plasmonic ring resonators. J. Mod. Opt. 62(3), 186–194 (2015)
Hao, R., Du, W., Chen, H., Jin, X., Yang, L., Li, E.: Ultra-compact optical modulator by graphene induced electro-refraction effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(6), 061116 (2013)
Dionne, J.A., Sweatlock, L.A., Atwater, H.A., Polman, A.: Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Phys. Rev. B 73(3), 035407 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province Grant (No: F2017501088) in China, the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province Grant (No: F2017203316) in China and the Hebei Province Higher Education Science and Technology Research Project (QN2019061) in China: Research on Biosensor Based on Diamond Thin Film Microring Resonator Structure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Guo, Z., Li, X. et al. Graphene light modulator based on dual-ring resonator structure. Opt Quant Electron 52, 302 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02419-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02419-0