Abstract
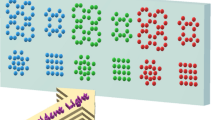
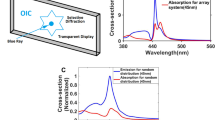
Nanoparticles based transparent display is one of the most successful methods to realize transparent monitors. Also, an array of nanoparticles, especially aperiodic arrangements, plays an important role in this case. Normally, when one talks about nanoparticles, the spherical morphology appears in mind, in which it is possible to implement different morphology for nanoparticles. In this paper, six different classes of morphologies with various arrangements, such as periodic array and deterministic aperiodic arrays, have been investigated to propose a high-performance transparent display. We compare different morphologies of Si–SiO2 nanoparticles at RGB (Red, Green, Blue) wavelengths in different types of arrays to find the highest scattering cross-section. Our calculations and figure of merit depending on the optical properties of nanoparticles, such as the resonance wavelength, the extinction, scattering and absorption cross-section, and the scattering to absorption ratio (SAR). We will show that in the proposed structures, there are suitable parameters to provide higher scattering cross-section as well as narrow bandwidth in which that is equivalent to introduce the maximum transparency and contrast ratio of transparent monitor. We use the Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) numerical method to simulate and calculate the deterministic aperiodic and periodic arrays of nanoparticles. Finally, we obtain the absorption and scattering cross-sections for six classes of nanoparticles: Cube, Sphere, Disk, Oblate ellipse, Prolate ellipse, and Pyramid into aperiodic and periodic arrays.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma, R., Baillot, Y., Behringer, R., Feiner, S., Julier, S., MacIntyre, B.: Recent advances in augmented reality. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 21(6), 34–47 (2001)
Ballisti, R., Hafner, C.: The multiple multipole method(MMP) in electro-and magnetostatic problems. IEEE Trans. Mag. 19, 2367–2370 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.1983.1062871
Bohren, C.F., Huffman, D.R.: Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. Wiley, New Jersey (2008)
Chen, H.W., Lee, J.H., Lin, B.Y., Chen, S., Wu, S.T.: Liquid crystal display and organic light-emitting diode display: present status and future perspectives. Light Sci. Appl. 7, 17168 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2017.168
Dallapiccola, R., Gopinath, A., Stellacci, F., Negro, L.D.: Quasi-periodic distribution of plasmon modes in two-dimensional Fibonacci arrays of metal nanoparticles. Opt. Soc. Am. 16(8), 5544–5555 (2008)
Dolatyari, M., Jafari, A., Rostami, A., Klein, A.: Transparent display using a quasi-array of Si-SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles. Nat. Sci. Rep. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38771-9
Downing, E., Hesselink, L., Ralston, J., Macfarlane, R.: A three-color, solid-state, three-dimensional display. Science 273, 1185–1189 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.273.5279.1185
Ekroll, V., Faul, F.: Transparency perception: the key to understanding simultaneous color contrast. J. Opt. Soc. of Am. A 30(3), 342–352 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.30.000342
Forestiere, C., Miano, G., Boriskina, S.V., Negro, L.D.: The role of nanoparticle shapes and deterministic aperiodicity for the design of nanoplasmonic arrays. Opt Soc. Am. 17(12), 9648–9661 (2009)
Gatoo, M.A., Naseem, S., Arfat, M.Y., Qasim, AMDKh, Zubair, S.: Physicochemical properties of nanomaterials: implication in associated toxic manifestations. Hindawi Publishing Corporation, London (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/498420
Gopinah, A., Boriskina, S.V., Reinhard, B.M., Negro, L.D.: Deterministic aperiodic arrays of metal nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering(SERS). Opt. Soc. Am. 17(5), 3741–3753 (2009)
Honcapie-Ramos, J.D., Roscher, S., Buschel, W., Kister, U., Dachselt, R., Irani, P.: CAR: contact augmented reality with transparent-display mobile devices. ACM (2014). https://doi.org/10.1145/2611009.2611014
Hsu, C.W., Zhen, B., Qiu, W., Shapira, O., Delacy, B.G., Joannppoulos, J.D., Solacic, M.: Transparent displays enabled by resonant nanoparticle scattering. Nat Commun. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4152
Jain, P.K., Lee, K.S., El-Sayed, I.H., El-Sayed, M.A.: Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. Am. Chem. Soc. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7238–7248 (2006)
Karar, V., Ghost, S.: Attention tunneling: effects of limiting the field of view due to beam combiner frame of a head-up display. J Disp. Technol. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/JDT.2014.2311159
Kateb, M., Safarian, S., Kolahdouz, M., Fathipour, M., Ahmadi, V.: ZnO-PEDOT core-shell nanowires: an ultrafast, high contrast and transparent electrochromic display. ELSEVIER, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2015.10.014
Kim, B.H., Park, S.C.: Optical system design for a Head-up display using aberration analysis of an off-axis two-mirror system. J. Opt. Soc. Korea (2016). https://doi.org/10.3807/JoSK.2016.20.4.481
Kim, H., Seo, Y.J., Yang, B., Chu, H.Y.: Black perception in a transparent OLED display. Opt. Express (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.25.003954
Kondorskiy, A.D., Lam, N.T., Lebedev, V.S.: Absorption and scattering of light by silver and gold nanodisks and nano prisms. J. Russ. Laser Res. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-018-9689-1
Lechner, M.D.: Influence of mie scattering on nanoparticles with different particle sizes and shapes: photometry and analytical ultracentrifugation with absorption optics, original scientific paper UDC 54-72:535.342:543.48. J. Serb Chem. Soc. 70(3), 361–369 (2005)
Lee, J.Y., Hong, H.G., Kim, Y.J.: Design and fabrication of semi-transparent screen using micro patterns and metal coating for head-up display, The Japan society of applied physics, 18th Microoptics Conference Tokyo Japan (2014)
Li, C.C., Tseng, H.Y., Liao, H.C., Chen, H.M., Hsieh, T., Lin, S.A., Jau, H.C., Wu, Y.C., Hsu, Y.L., Hsu, W.H., Lin, T.H.: Enhanced image quality of OLED transparent display by cholesteric liquid crystal back-panel. Opt. Express (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.25.029199
Liu, S., Sun, P., Wang, C., Zheng, Z.: Color waveguide transparent screen using lens array holographic optical element. ELSEVIER, Opt. Commun. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom
Loke, V.L.Y., Menguc, M.P., Nieminen, T.A.: Discrete-dipole approximation with surface interaction: a computational toolbox for MATLAB. ELSEVIER J. Quant. Spect. Rad. Trans. 112, 1711–1725 (2011)
Macia, E.: The role of aperiodic order in science and technology Inst. Phys. Publ. 69, 397–441 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/69/2/R03
Mahajan, S.M., Khedkar, S.B., Kasav, S.M.: Head-Up display techniques in cars. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Innov. Technol. 4(2), 119–124 (2015)
Merkus, H.G.: Particle size measurement fundamentals, practice, quality. Springer, Berlin (2009). (ISBN 978-1-4020-9015-8)
Mishchenko, M.I., Travis, L.D., Mackowski, D.W.: T-matrix computations of light scattering by nano spherical particles: a review. ELSEVIER, J. Quant. Spect. Rad. Trans. 55(5), 535–575 (1996)
Negro, L.D., Boriskina, S.V.: Deterministic aperiodic nanostructures for photonics and plasmonic applications. Laser Photon. Rev. 6(2), 178–218 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.201000046
Negro, L.D., Feng, N.N., Gopinath, A.: Electromagnetic coupling and plasmon localization in deterministic aperiodic arrays. J. Opt. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/1464-4258/10/6/064013
Numata, Y., Okuyama, k., Nakahara, T., Nakamura, T., Mizuno, M., Sugiyama, H., Nomura, S., Takeuchi, S., Oue, Y., Kato, H., Ito, S., Hasegawa, A., Ozaki, T., Douyou, M., Imai, T., Takizawa, K., Matsushima, S.: Highly transparent LCD using a new scattering-type liquid crystal with field sequential color edge light, IEEE, 24th International workshop on active–matrix flat panel displays and devices, Kyoto, Japan, 2017
Okumura, H., Shinohara, K.: Human attention and fatigue for AR Head-Up display. IEEE Int. Symp. Mixed Augment. Real. Adj. Proc. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMAR-Adjunct
Palik, E.D.: Handbook of optical constants of solids, author and subject indices for volumes I, II, and III. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1998)
Piliarik, M., Kvasnicka, P., Galler, N., Krem, J.R., Homola, J.: Local refractive index sensitivity of plasmonic nanoparticles. Optic. Soc. Am. 19(10), 9213–9220 (2011)
Purcell, E.M., Pennypacker, C.R.: Scattering and absorption of light by nonspherical dielectric grains. Astrophys. J. 186, 705–714 (1973)
Qin, Z., Xie, J., Lin, F.C., Huang, Y.P., Shieh, H.P.D.: Evaluation of a transparent display’s pixel structure regarding the subjective quality of diffracted see-through images. IEEE Photon. J. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2722000
Raghuwanshi, M., Kumar, G.V.P.: Plasmonic nanowires arranged in Fibonacci number chain: extinction angle-dependent optical properties. AIP Adv. 3, 022112 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4791766
Ramaccia, D., Arcieri, S., Toscano, A., Bilotti, F.: Core-shell super-spherical nanoparticles for LSPR based sensing platforms. IEEE J. Select. Topics Quantum Electron. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2016.2615851
Rostami, A., Matloub, S.: Waveguiding properties of photonic quasicrystal heterostructures based on envelope approximation, IOP publishing. J. Opt. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8978/12/11/115503
Rostami, A., Haddadpour, A., Nazari, F., Alipour, H.: Proposal for an ultra-compact tunable wavelength-division-multiplexing optical filter based on quasi-2D photonic crystals, IOP publishing. J. Opt. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8978/12/1/015405
Schebarchov, D., Auguie, B., Ru, E.C.L.: Simple accurate approximations for the optical properties of metallic nanospheres and nanoshells PCCP. Phys. Chem. 15, 4233–4242 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP44124E
Schneider, J.B., Wagner, C.L., Ramahi, O.M.: Implementation of transparent sources in FDTD simulations. IEEE Trans. Antenna Prop. (1998). https://doi.org/10.1109/8.18570
Sun, X.D., Liu, J.Q.: Light-emitting material integrated into a substantially transparent substrate, the United States Patent Application Publication, 6,986,581, (2006)
Tsujimura, T.: OLED display fundamentals and applications, 2nd edn. Wiley, New Jersy (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119187493
Vardeny, Z.V., Nahata, A., Agrawal, A.: Optics of photonic quasicrystals. Nat. Photon. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/NPHOTON.2012.343
Wiesner, C.A., Ruf, M., Sirim, D., Klinker, G.: Visualization of the electronic horizon in Head-up displays. IEEE Int. Symp. Mixed Augment. Real. Adjunct Proc. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMAR-Adjunct
Yang, L., Xu, X., Yuan, Y., Li, Z., He, S.: Meter-scale transparent conductive circuits based on silver nanowire networks for rigid and flexible transparent light-emitting diode screens. Opt. Mater. Express (2019). https://doi.org/10.1364/OME9.004483
Yurkin, M.A., Hoekstra, A.G., Brock, R.S., Lu, J.Q.: Systematic comparison of the discrete dipole approximation and the finite difference time domain method for large dielectric scatterers. Optic. Soc. Am. 15(26), 17902–17911 (2007)
Zou, S., Schatz, G.C.: Narrow plasmonic/photonic extinction and scattering line shapes for one and two-dimensional silver nanoparticle arrays. J. Chem. Phys. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1826036
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seyyedi, M., Rostami, A. & Matloub, S. Effect of morphology of nanoparticles on performance of transparent display. Opt Quant Electron 52, 308 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02417-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02417-2