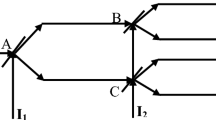
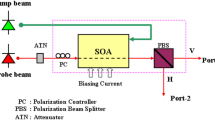
Abstract
Addition of binary coded decimal (BCD) data is very important in optical computing and optical signal processing. In this article the author proposes a method of developing all-optical frequency encoded BCD adder exploiting frequency conversion and polarization switching action of semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA). Frequency encoded BCD data offer more advantages over conventionally encoded data in terms of less probability of bit errors and greater reliability. Again efficient frequency conversion and faster switching action of SOA with good on-off contrast ratio makes the scheme attractive.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awwal, A.A.S., Karim, M.A.: Microprocessor design using polarization encoded optical shadow casting. Appl. Opt. 29(14), 2107–2112 (1990)
Connelly, M.J.: Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2002)
Floyd, T.L., Jain, R.P.: Digital fundamentals. In: Pearson Education, Eighth Edition, Chapter-2, ISBN 978-81-7758-763-0 (2009)
Garai, S.K.: A novel all-optical frequency encoded method to develop Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) using semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE/OSA J. Light Wave Technol. 29(23), 3506–3514 (2011)
Garai, S.K.: A novel method of developing all optical trinary JK, D-type and T-type flip-flops using semiconductor optical amplifiers. Appl. Opt. 51(11), 1757–1764 (2012)
Garai, S.K.: A novel method of developing all optical frequency encoded Fredkin Gates. Opt. Commun. (Elsevier) 313C, 441–447 (2014)
Garai, S.K.: All-optical quaternary logic gates: an extension of binary logic gates. Opt. Laser Technol. 67(C), 125–136 (2015)
Gayen, D.K., Bhattacharyya, A., Pal, R.K., Roy, J.N.: All-optical binary coded decimal (BCD) adder with the help of terahertz optical asymmetric demultiplexer. In: Computing in Science and Engineering (ISSN: 1521-961), (99), pp. 1–4 (2009)
Jung, Y. J., Leeb, S., Park, N.: All-optical 4-bit Gray code to binary coded decimal converter. In: Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6890, pp. 68900S-(1–10) (2008)
Jung, Y.J., Son, C.W., Jhon, Y.M., Lee, S., Park, N.: One-level simplification method for all-optical combinational logic circuits. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 20(10), 800–802 (2008)
Liu, Y., Hill, M.T., Tangdiongga, E., de Waardt, H., Calabretta, N., Khoe, G.D., Dorren, H.J.S.: Wavelength conversion using nonlinear polarization rotation in a single semiconductor optical amplifier. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 15(01), 90–92 (2003)
Mandal, S., Mandal, D., Garai, S.K.: An all-optical method of developing data communication system with error detection circuit. Opt. Fiber Technol. (Elsevier) 20(2), 120–129 (2014)
Michel, H.E., Awwal, A.A.S.: Artificial neural networks using complex numbers and phase encoded weights. Appl. Opt. 49(10), B71–B82 (2010)
Mukhopadhyay, S., Das, D.N., Pahari, N.: An optical method for the addition of binary data by non-linear material. Appl. Opt. (USA) 43(33), 6147–6150 (2004)
Tanida, J., Ichioka, Y.: OPALS: optical parallel array logic system. Appl. Opt. 25(10), 1565–1570 (1986)
Toyohiko, Y.: Optical space-variant logic gate based on spatial encoding technique. Opt. Lett. 11(4), 260–262 (1986)
Vorreau, P., Marculescu, A., Wang, J., Böttger, G., Sartorius, B., Bornholdt, C., Slovak, J., Schlak, M., Schmidt, C., Tsadka, S., Freude, W., Leuthold, J.: Cascadability and regenerative properties of SOA all-optical DPSK wavelength converters. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 18(18), 1970–1972 (2006)
Yang, X., Weng, Q., Hu, W.: High-speed all-optical switches based on cascaded SOAs’. In: Garai, S.K. (eds.) Selected Topics on Optical Amplifiers in Present Scenario, Chap-2. InTech Publisher (2012)
Zaghloul, Y.A., Zaghloul, A.R.M.: Unforced polarization based optical implementation of Binary logic. Opt. Express 14(16), 7252–7269 (2006)
Zhihong, Li, Guifang, Li: Ultrahigh-speed reconfigurable logic gates based on four-wave mixing in a semiconductor optical amplifier. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 18(12), 1341–1343 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garai, S.K. An all-optical frequency encoded BCD data addition. Opt Quant Electron 48, 49 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-015-0285-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-015-0285-0