Abstract
In 1948, Hodgkin identified three firing patterns of a single neuron in response to increasing the external DC input. In this work, we investigated the responses of a single neuron with an autapse based on a modified Morris–Lecar neuron model, which can exhibit the three types of firing patterns by changing only one parameter. An excitatory autapse was found to enhance the firing frequency, but an inhibitory autapse suppressed neuron firing. With excitatory autaptic feedback, the firing of a Class-1 neuron could be switched to that of a Class-2 neuron, and a Class-3 neuron could exhibit a Class-2 firing pattern. The sustained response frequency of the Class-2 neuron transferred from that of Class-3 is only dependent on the autaptic time delay, and the frequency decays gradually with increased the delay time.







Similar content being viewed by others
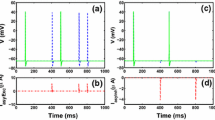
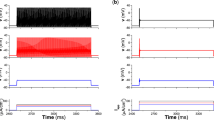
References
Abbott, L.F.: Lapicque’s introduction of the integrate-and-fire model neuron (1907). Brain Res. Bull. 50, 303–304 (1999)
Morris, C., Lecar, H.: Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 35(1), 193–213 (1981)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500–544 (1952)
Suresh, R., Senthilkumar, D.V., Lakshmanan, M., et al.: Emergence of a common generalized synchronization manifold in network motifs of structurally different time-delay systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 93, 235–245 (2016)
Hettiarachchi, I.T., Lakshmanan, S., Bhatti, A., et al.: Chaotic synchronization of time-delay coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neurons via nonlinear control. Nonlinear Dyn. 86, 1249–1262 (2016)
Yamakou, E.M., Inack, E.M., Kakmeni, F.M.M.: Ratcheting and energetic aspects of synchronization in coupled bursting neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 83, 541–554 (2016)
Kim, S.Y., Lim, W.: Dynamical responses to external stimuli for both cases of excitatory and inhibitory synchronization in a complex neuronal network. Cogn. Neurodyn. 11, 395–413 (2017)
Panaggio, M.J., Abrams, D.M.: Chimera states: coexistence of coherence and incoherence in networks of coupled oscillators. Nonlinearity 28(3), R67 (2015)
Hizanidis, J., Kanas, V.G., Bezerianos, A., et al.: Chimera states in networks of nonlocally coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neuron models. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24(03), 1450030 (2014)
Vogels, T.P., Abbott, L.F.: Gating multiple signals through detailed balance of excitation and inhibition in spiking networks. Nat. Neurosci. 12(4), 483 (2009)
Wang, L.F., Jia, F., Liu, X.Z., et al.: Temperature effects on information capacity and energy efficiency of Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Chin. Phys. Lett. 32(10), 108701 (2015)
Ju, H., Hines, M.L., Yu, Y.: Cable energy function of cortical axons. Sci. Rep. 6, 29686 (2016)
Christoph, J., Chebbok, M., Richter, C., et al.: Electromechanical vortex filaments during cardiac fibrillation. Nature 555(7698), 667 (2018)
Jalife, J.: The tornadoes of sudden cardiac arrest. Nature 555, 597–598 (2018)
Tateno, T., Harsch, A., Robinson, H.P.C.: Threshold firing frequency–current relationships of neurons in rat somatosensory cortex: type 1 and type 2 dynamics. J. Neurophysiol. 92(4), 2283–2294 (2004)
Yu, L.C., Ma, J., Zhang, G.Y., et al.: Suppression of spiral waves by voltage clamp techniques in a conductance-based cardiac tissue model. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25(7), 2706 (2008)
Wu, X.Y., Ma, J.: The formation mechanism of defects, spiral wave in the network of neurons. PLoS ONE 8(1), e55403 (2013)
Zhang, J., Tang, J., Ma, J., et al.: The dynamics of spiral tip adjacent to inhomogeneity in cardiac tissue. Physica A 491, 340–346 (2018)
Prescott, S.A., De Koninck, Y., Sejnowski, T.J.: Biophysical basis for three distinct dynamical mechanisms of action potential initiation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 4(10), e1000198 (2008)
Huang, C., Sun, W., Zheng, Z., et al.: Hopf bifurcation control of the M–L neuron model with type I. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(2), 755–766 (2017)
Hodgkin, A.L.: The local electric changes associated with repetitive action in a non-medullated axon. J. Physiol. 107(2), 165–181 (1948)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Dynamical Systems in Neuroscience. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (2007)
Tateno, T., Robinson, H.P.C.: Rate coding and spike-time variability in cortical neurons with two types of threshold dynamics. J. Neurophysiol. 95(4), 2650–2663 (2006)
Sadeghi, S., Valizadeh, A.: Synchronization of delayed coupled neurons in presence of inhomogeneity. J. Comput. Neurosci. 36(1), 55–66 (2014)
Esfahani, Z.G., Valizadeh, A.: Zero-lag synchronization despite inhomogeneities in a relay system. PLoS ONE 9(12), e112688 (2014)
Wang, H.T., Wang, L.F., Yu, L.C., et al.: Response of Morris–Lecar neurons to various stimuli. Phys. Rev. E 83(2), 021915 (2011)
Wang, H.T., Chen, Y., Chen, Y.: First-spike latency in Hodgkin’s three classes of neurons. J. Theor. Biol. 328, 19–25 (2013)
Wang, C.N., Guo, S.L., Xu, Y., et al.: Formation of autapse connected to neuron and its biological function. Complexity 2017, 5436737 (2017)
Xu, Y., Ying, H.P., Jia, Y., et al.: Autaptic regulation of electrical activities in neuron under electromagnetic induction. Sci. Rep. 7, 43452 (2017)
Qin, H.X., Ma, J., Wang, C.N., et al.: Autapse-induced target wave, spiral wave in regular network of neurons. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57(10), 1918–1926 (2014)
Ma, J., Song, X.L., Tang, J., et al.: Wave emitting and propagation induced by autapse in a forward feedback neuronal network. Neurocomputing 167, 378–389 (2015)
Wang, L., Wang, H., Yu, L., et al.: Role of axonal sodium-channel band in neuronal excitability. Phys. Rev. E 85(5), 052901 (2011)
Kole, M.H.P., Stuart, G.J.: Signal processing in the axon initial segment. Neuron 73(2), 235–247 (2012)
Van der Loos, H.: Neuronal circuitry and its development. Perspect. Brain Res. 45, 259–278 (1976)
Yin, L., Zheng, R., Ke, W., et al.: Autapses enhance bursting and coincidence detection in neocortical pyramidal cells. Nat. Commun. 9(1), 4890 (2018)
Song, S., Miller, K.D., Abbott, L.F.: Competitive Hebbian learning through spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 3(9), 919 (2000)
Song, X., Wang, H., Chen, Y.: Coherence resonance in an autaptic Hodgkin–Huxley neuron with time delay. Nonlinear Dyn. 94(1), 141 (2018)
Wang, H.T., Wang, L.F., Chen, Y., et al.: Effect of autaptic activity on the response of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Chaos 24(3), 033122 (2014)
Yilmaz, E., Ozer, M., Baysal, V., et al.: Autapse-induced multiple coherence resonance in single neurons and neuronal networks. Sci. Rep. 6, 30914 (2016)
Yilmaz, E., Ozer, M.: Delayed feedback and detection of weak periodic signals in a stochastic Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Physica A 421, 455–462 (2015)
Wang, H.T., Chen, Y.: Response of autaptic Hodgkin–Huxley neuron with noise to subthreshold sinusoidal signals. Physica A 462, 321–329 (2016)
Wang, H.T., Sun, Y.J., Li, Y.C., et al.: Influence of autapse on mode-locking structure of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron under sinusoidal stimulus. J. Theor. Biol. 358, 25–30 (2014)
Wang, H.T., Ma, J., Chen, Y., et al.: Effect of an autapse on the firing pattern transition in a bursting neuron. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19(9), 3242–3254 (2014)
Wang, H.T., Chen, Y.: Firing dynamics of an autaptic neuron. Chin. Phys. B 24(12), 128709 (2015)
Guo, D., Chen, M., Perc, M., et al.: Firing regulation of fast-spiking interneurons by autaptic inhibition. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 114(3), 30001 (2016)
Zhao, Z., Jia, B., Gu, H.G.: Bifurcations and enhancement of neuronal firing induced by negative feedback. Nonlinear Dyn. 86(3), 1549–1560 (2016)
Zhao, Z., Gu, H.G.: Transitions between classes of neuronal excitability and bifurcations induced by autapse. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 6760 (2017)
Connelly, W.M., Lees, G.: Modulation and function of the autaptic connections of layer V fast spiking interneurons in the rat neocortex. J. Physiol. 588, 2047–2063 (2009)
Ermentrout, G.B., Terman, D.H.: Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience. Springer, New York (2010)
Sterratt, D., Graham, B., Gillies, A., et al.: Principles of Computational Modelling in Neuroscience. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2011)
Smeal, R.M., Ermentrout, G.B., White, J.A.: Phase-response curves and synchronized neural networks. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 365(1551), 2407–2422 (2010)
Wang, L.F., Wang, H.T., Yu, L.C., et al.: Spike-threshold variability originated from separatrix-crossing in neuronal dynamics. Sci. Rep. 6, 31719 (2016)
Wu, S.D., Zhang, Y.S., Cui, Y., et al.: Heterogeneity of synaptic input connectivity regulates spike-based neuronal avalanches. Neural Netw. 110, 95–103 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.10.017
Guo, D.Q., Wu, S.D., Chen, M.M., et al.: Regulation of irregular neuronal firing by autaptic transmission. Sci. Rep. 6, 2609 (2016)
Hashemi, M., Valizadeh, A., Azizi, Y.: Effect of duration of synaptic activity on spike rate of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron with delayed feedback. Phys. Rev. E 85(2), 021917 (2012)
Kalat, J.W.: Biological Psychology. Cengage Learning, Wadsworth (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China with Grant No. 11675008 (YC), Grant No. 21434001 (YC) and Grant No. 11447027 (HTW). HTW acknowledges in addition supports from Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China with Grant No. 2016JQ1037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All the authors declare that there are no any conflict with the publication of this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Wang, H. & Chen, Y. Autapse-induced firing patterns transitions in the Morris–Lecar neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn 96, 2341–2350 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04925-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04925-7


