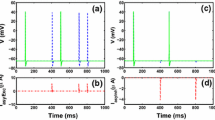
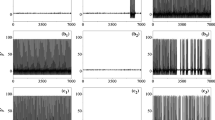
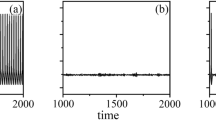
Abstract
Autapses, synapses between a neuron and itself, are believed to serve as a regulator of information processing in the nervous system. Noise, as random or unpredictable fluctuations, affects nearly all aspects of nervous function. In this work, we studied the regulatory ability of an autapse on firing behaviors of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron in response to synaptic-like signals in the presence of noise. For weak subthreshold synaptic input, the autaptic neuron produced the similar firing behavior governed by the noise in case of either determinate or random synaptic input. The critical noise intensity necessary to trigger the spike train slightly was decreased with determinate low-frequency input. Under a strong suprathreshold synaptic current, noise-induced frequency resonance and precise responses mostly occured with a high-frequency determinate input. With a random strong synaptic input, an increase in the autaptic delay led to a resonance-like response, but had no observable effects in cases with a short delay time under a low-frequency input.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Der Loos, H., Glaser, E.M.: Autapses in neocortex cerebri: synapses between a pyramidal cells axon and its own dendrites. Brain Res. 48, 355–360 (1972)
Karabelas, A.B., Purrura, D.P.: Evidence for autapses in the substantia nigra. Brain Res. 200(2), 467–473 (1980)
Shkolnik-Yarros, E.G.: Neurons and lnterneuronal Connections of the Central Visual System, pp. 154–155. Plenum Press, New York (1971)
Held, H.: Beiträge zur structur der nervenzellen und ihrer Fortsätze, Zweite Abhandlung. Arch Anat Physiol. (Lpz). Anat. Abt. 204–244 (1897)
Chan-Palay, V.: The recurrent collaterals of Purkinje cell axons: a correlated study of the rat’s cerebellar cortex with electron microscopy and the Golgi method. Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 134(2), 200–234 (1971)
Scheibel, M.E., Scheibel, A.B.: Inhibition and the Renshaw cell. A structural critique. Brain Behav. Evol. 4(1), 53–93 (1971)
DiFiglia, M., Pasik, P., Paslk, T.: A Golgi study of neuronal types in the neostriatum of monkeys. Brain Res. 114(2), 245–256 (1976)
Tamás, G., Buhl, E.H., Somogyi, P.: Massive autaptic self-innervation of GABAergic neurons in cat visual cortex. J. Neurosci. 17(16), 6352–6364 (1997)
Saada, R., Miller, N., Hurwitz, I., et al.: Autaptic excitation elicits persistent activity and a plateau potential in a neuron of known behavioral function. Curr. Biol. 19(6), 479–484 (2009)
Bacci, A., Huguenard, J.R.: Enhancement of spike-timing precision by autaptic transmission in neocortical inhibitory interneurons. Neuron 49(1), 119–130 (2006)
Jiang, M., Yang, M., Yin, L., et al.: Developmental reduction of asynchronous GABA release from neocortical fast-spiking neurons. Cereb. Cortex. 25(1), 258–270 (2015)
Jiang, M., Zhu, J., Liu, Y., et al.: Enhancement of asynchronous release from fast-spiking interneuron in human and rat epileptic neocortex. PLoS Biol. 10(5), e1001324 (2012)
Wang, H.T., Chen, Y.: Firing dynamics of an autaptic neuron. Chin. Phys. B 24(12), 128709 (2015)
Wang, H.T., Sun, Y.J., Li, Y.C., et al.: Influence of autapse self-feedback on mode-locking structure of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron under sinusoidal stimulus. J. Theor. Biol. 358, 25–30 (2014)
Wang, H.T., Ma, J., Chen, Y.L., et al.: Effect of an autapse on the firing pattern transition in a bursting neuron. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19(9), 3242–3254 (2014)
Wang, H.T., Wang, L.F., Chen, Y.L., et al.: Effect of autaptic activity on the response of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Chaos 24(3), 033122 (2014)
Hashemi, M., Valizadeh, A., Azizi, Y.: Effect of duration of synaptic activity on spike rate of a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron with delayed feedback. Phys. Rev. E. 85(2), 021917 (2012)
Yuan, Y., Liu, L.W., Liu, Y.J., et al.: Dynamical response, information transition and energy dependence in a neuron model driven by autapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 90, 2893–2902 (2017)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1569–1578 (2017)
Wang, C.N., Ma, J.: A review and guidance for pattern selection in spatiotemporal system. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32, 1830003 (2018)
Sagués, F., Sancho, J.M., García-Ojalvo, J.: Spatiotemporal order out of noise. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79(3), 829–882 (2007)
Borkowski, L.S.: Bistability and resonance in the periodically stimulated Hodgkin–Huxley model with noise. Phys. Rev. E. 83(5), 051901 (2011)
Pikovsky, A.S., Kurths, J.: Coherence resonance in a noise-driven excitable system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78(5), 775–778 (1997)
Yao, Y.G., Yi, M., Hou, D.J.: Coherence resonance induced by cross-correlated sine-Wiener noises in the FitzHugh–Nagumo neurons. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 31(28), 1750204 (2017)
Yao, Y.G., Ma, J.: Weak periodic signal detection by sine-Wiener-noise-induced resonance in the FitzHugh-Nagumo neuron. Cogn. Neurodyn. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-018-9475-3
Jothimurugan, R., Thamilmaran, K., Rajasekar, S., et al.: Multiple resonance and anti-resonance in coupled Duffing oscillators. Nonlinear Dyn. 83(4), 1803–1814 (2016)
Collins, J.J., Imhoff, T.T., Grigg, P.: Noise-enhanced information transmission in rat SA1 cutaneous mechanoreceptors via aperiodic stochastic resonance. J Neurophysiol. 76(1), 642–645 (1996)
Hänggi, P.: Stochastic resonance in biology how noise can enhance detection of weak signals and help improve biological information processing. ChemPhysChem 3(3), 285–290 (2002)
Levin, J.E., Miller, J.P.: Broadband neural encoding in the cricket cercal sensory system enhanced by stochastic resonance. Nature 380(6570), 165–168 (1996)
Wang, C.J., Yang, K.L., Qu, S.X.: Time-delay enhanced coherence resonance in a discrete neuron with noises. Chin. Phys. Lett. 31(8), 080502 (2014)
Wang, C.J., Yang, K.L., Qu, S.X.: Stochastic resonance in a discrete neuron with time delay and two different modulation signals. Phys. Scr. 89, 105001 (2014)
Bolhasani, E., Azizi, Y., Valizadeh, A.: Direct connections assist neurons to detect correlation in small amplitude noises. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 7, 108 (2013)
Bolhasani, E., Valizadeh, A.: Stabilizing synchrony by inhomogeneity. Sci. Rep. 5, 13854 (2015)
Chen, Y., Yu, L.C., Qin, S.M.: Detection of subthreshold pulses for neurons with channel noise. Phys. Rev. E 78(5), 051909 (2008)
Chen, Y.L., Yu, Y.L., Chen, Y.: Reliability of weak signals detection in neurons with noise. Sci. China: Tech. Sci. 59(3), 411–417 (2016)
Chen, Y.L., Zhang, H., Wang, H.T., et al.: The role of coincidence-detector neuron in reliability and precision of subthreshold signal detection in noise. PLoS One 8(2), e56822 (2013)
Cordo, P., Inglits, J.T., Verschueren, S., et al.: Noise in human muscle spindles. Nature 383(6603), 769–770 (1996)
Wiesenfeld, K., Moss, F.: Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: from ice ages to crayfish and SQUIDs. Nature 373(6509), 33–36 (1995)
Lee, S.G., Kim, S.: Bifurcation analysis of mode-locking structure in a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron under sinusoidal current. Phys. Rev. E. 73(4), 041924 (2006)
Wang, H.T., Chen, Y.: Response of autaptic Hodgkin–Huxley neuron with noise to subthreshold sinusoidal signals. Phys. A. 462, 321–329 (2016)
Yilmaz, E., Ozer, M., Baysal, V., et al.: Autapse-induced multiple coherence resonance in single neurons and neuronal networks. Sci. Rep. 6, 30914 (2016)
Uzun, R.: Influences of autapse and channel blockage on multiple coherence resonance in a single neuron. App. Math. Comput. 35, 203–210 (2017)
Uzun, R., Yilmaz, Z., Ozer, M.: Effects of autapse and ion channel block on the collective firing activity of Newman–Watts small-world neuronal networks. Phys. A 486, 386–396 (2017)
Guo, D.Q., Wu, S.D., Chen, M.M., et al.: Regulation of irregular neuronal firing by autaptic transmission. Sci. Rep. 6, 26096 (2016)
Guo, D.Q., Perc, M., Zhang, Y., et al.: Frequency-difference-dependent stochastic resonance in neural systems. Phys. Rev. E. 96(2), 022415 (2017)
Gianní, M., Liberti, M., Apollonio, F., et al.: Modeling electromagnetic fields detectability in a HH-like neuronal system : stochastic resonance and window behavior. Biol. Cybern. 94(2), 118–127 (2006)
Lu, L.L., Jia, Y., Liu, W.H., et al.: Mixed stimulus-induced mode selection in neural activity driven by high and low frequency current under electromagnetic radiation. Complexity 2017, 7628537 (2017)
Ge, M.Y., Jia, Y., Xu, Y., et al.: Mode transition in electrical activities of neuron driven by high and low frequency stimulus in the presence of electromagnetic induction and radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91, 515–523 (2018)
Xu, Y., Jia, Y., Ge, M.Y., et al.: Effects of ion channel blocks on electrical activity of stochastic Hodgkin–Huxley neural network under electromagnetic induction. Neurocomputing 283, 196–204 (2018)
Wang, L.F., Qiu, K., Jia, Y.: Effects of time delays in a mathematical bone model. Chin. Phys. B 26(3), 030503 (2017)
Yao, Y.G., Deng, H.Y., Ma, C.Z., et al.: Impact of bounded noise and rewiring on the formation and instability of spiral waves in a small-world network of Hodgkin–Huxley neurons. PLoS One 12(1), e0171273 (2017)
Wang, H.T., Wang, L.F., Yu, L.C., et al.: Response of Morris–Lecar neurons to various stimuli. Phys. Rev. E. 83(2), 021915 (2011)
Connelly, W.M., Lees, G.: Modulation and function of the autaptic connections of layer V fast spiking interneurons in the rat neocortex. J. Physiol. 588, 2047–2063 (2009)
Ermentrout, G.B., Terman, D.H.: Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience. Springer, New York (2010)
Sterratt, D., Graham, B., Gillies, A., et al.: Principles of Computational Modelling in Neuroscience. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2011)
Mathy, A., Ho, S.S., Davie, J.T., et al.: Encoding of oscillations by axonal bursts in inferior olive neurons. Neuron 62, 388–399 (2009)
Deleuze, C., Pazienti, A., Bacci, A.: Autaptic self-inhibition of cortical GABAergic neurons: synaptic narcissism or useful introspection? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 26, 64–71 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China with Grant Nos. 11675008, 21434001 and 11447027. HTW acknowledges in addition supports from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities with Grant No. GK201503025 and Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China with Grant No. 2016JQ1037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
All the authors declare that there are no any conflict with the publication of this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Wang, H. & Chen, Y. Coherence resonance in an autaptic Hodgkin–Huxley neuron with time delay. Nonlinear Dyn 94, 141–150 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4349-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4349-0