Abstract
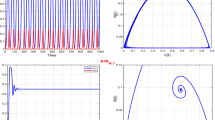
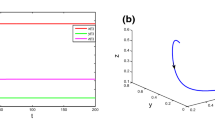
In this paper we have discussed about the dynamics of three species (two preys and one predator) delayed predator–prey model with cooperation among the preys against predation. We accept that the rate of change of density of population relies on the growth, death and in addition intra-species competition for the predators. The growth rate for preys is thought to be logistic. Delays are taken just in the growth components for each of the species. With this model we have demonstrated that the system has permanence. Taking the delays as the bifurcation parameter, the stability of the interior equilibrium point has been discussed analytically and numerically. Critical value of the delay is obtained where the Hopf-bifurcation happens. In presence of delay by constructing a Lyapunov function local asymptotic stability of the positive equilibrium point is discussed.


































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfred, J.: Lotka, elements of physical biology (baltimore: Williams and wilkins,); vito volterra. Variazioni e fluttuazioni del numero dindividui in specie animali conviventi (1925)
Arino, J., Wang, L., Wolkowicz, G.S.: An alternative formulation for a delayed logistic equation. J. Theor. Biol. 241(1), 109–119 (2006)
Begon, M., Harper, J.L., Townsend, C.R., et al.: Ecology. Individuals, Populations and Communities. Blackwell, New York (1986)
Castro, R., Sierra, W., Stange, E.: Bifurcations in a predator–prey model with general logistic growth and exponential fading memory. Appl. Math. Model. 45, 134–147 (2017)
Chen, F.: The permanence and global attractivity of Lotka–Volterra competition system with feedback controls. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 7(1), 133–143 (2006)
Chen, F.: Permanence of a discrete n-species food-chain system with time delays. Appl. Math. Comput. 185(1), 719–726 (2007)
Chen, F., You, M.: Permanence for an integrodifferential model of mutualism. Appl. Math. Comput. 186(1), 30–34 (2007)
Choudhury, S.R.: On bifurcations and chaos in predator–prey models with delay. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2(4), 393–409 (1992)
Dhar, J., Jatav, K.S.: Mathematical analysis of a delayed stage-structured predator–prey model with impulsive diffusion between two predators territories. Ecol. Complex. 16, 59–67 (2013)
Elettreby, M.: Two-prey one-predator model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 39(5), 2018–2027 (2009)
Fan, Y.H., Li, W.T.: Permanence for a delayed discrete ratio-dependent predator–prey system with holling type functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 299(2), 357–374 (2004)
Goh, B.: Stability in models of mutualism. Am. Nat. 113(2), 261–275 (1979)
Greenhalgh, D., Khan, Q.J., Pettigrew, J.S.: An eco-epidemiological predator–prey model where predators distinguish between susceptible and infected prey. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 40(1), 146–166 (2017)
Hou, Z.: On permanence of Lotka–Volterra systems with delays and variable intrinsic growth rates. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 14(2), 960–975 (2013)
Hu, H., Teng, Z., Jiang, H.: On the permanence in non-autonomous Lotka–Volterra competitive system with pure-delays and feedback controls. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 10(3), 1803–1815 (2009)
Hugie, D.M.: Applications of Evolutionary Game Theory to the Study of Predator–Prey Interactions. Simon Fraser University, Burnaby (1999)
Hutchinson, G.E.: Circular causal systems in ecology. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 50(4), 221–246 (1948)
Keshet, E.L.: Mathematical Models in Biology. McGraw-Hill, New York (1988)
Kingsland, S.: The refractory model: the logistic curve and the history of population ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 57(1), 29–52 (1982)
Kot, M.: Elements of Mathematical Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Kundu, S., Maitra, S.: Stability and delay in a three species predator–prey system. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1751, p. 020004. AIP Publishing (2016)
Kuniya, T., Nakata, Y.: Permanence and extinction for a nonautonomous seirs epidemic model. Appl. Math. Comput. 218(18), 9321–9331 (2012)
Li, C.H., Tsai, C.C., Yang, S.Y.: Analysis of the permanence of an sir epidemic model with logistic process and distributed time delay. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17(9), 3696–3707 (2012)
Liao, X., Zhou, S., Chen, Y.: Permanence and global stability in a discrete n-species competition system with feedback controls. Nonlinear Ana. Real World Appl. 9(4), 1661–1671 (2008)
Liu, M., Bai, C.: Optimal harvesting of a stochastic mutualism model with Lévy jumps. Appl. Math. Comput. 276, 301–309 (2016)
Liu, S., Chen, L.: Necessary-sufficient conditions for permanence and extinction in Lotka–Volterra system with distributed delays. Appl. Math. Lett. 16(6), 911–917 (2003)
Lynch, S.: Dynamical Systems with Applications Using MATLAB. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Ma, J., Zhang, Q., Gao, Q.: Stability of a three-species symbiosis model with delays. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(1), 567–572 (2012)
MacLean, M., Willard, A.: The logistic curve applied to Canada’s population. Can. J. Econ. Polit. Sci. 3(02), 241–248 (1937)
Muroya, Y.: Permanence and global stability in a Lotka–Volterra predator–prey system with delays. Appl. Math. Lett. 16(8), 1245–1250 (2003)
Pearl, R., Reed, L.J.: The logistic curve and the census count of i930. Science 72(1868), 399–401 (1930)
Saha, T., Bandyopadhyay, M.: Dynamical analysis of a delayed ratio-dependent prey–predator model within fluctuating environment. Appl. Math. Comput. 196(1), 458–478 (2008)
Teng, Z., Zhang, Y., Gao, S.: Permanence criteria for general delayed discrete nonautonomous n-species kolmogorov systems and its applications. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(2), 812–828 (2010)
Verhulst, P.F.: Notice sur la loi que la population suit dans son accroissement. Correspondance mathématique et physique publiée par a. Quetelet 10, 113–121 (1838)
Xu, C., Wu, Y.: Dynamics in a Lotka–Volterra predator–prey model with time-varying delays. In: McKibben, M. (ed.) Abstract and Applied Analysis, vol. 2013. Hindawi Publishing Corporation, Cairo, Egypt (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/956703
Zhao, J., Jiang, J.: Average conditions for permanence and extinction in nonautonomous Lotka–Volterra system. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 299(2), 663–675 (2004)
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous referee for valuable suggestions. The first author is thankful to DST, New Delhi, India, for its financial support under INSPIRE fellowship, without which this research would not have been possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundu, S., Maitra, S. Dynamical behaviour of a delayed three species predator–prey model with cooperation among the prey species. Nonlinear Dyn 92, 627–643 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4079-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4079-3