Abstract
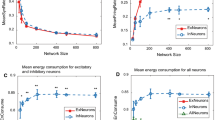
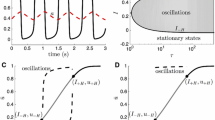
Spontaneous periodic up and down transitions are considered to be a significant phenomenon that is characteristic of slow-wave sleep. We studied a neural network model of spontaneous up and down transitions based on our former study of a single-neuron model. We expanded the model by using two types of neurons—excitatory and inhibitory neurons—and redefining the connecting function between two neurons instead of assuming a constant connection, so that the model is closer to the in vivo network. Using this model, we studied the relationship between the transitions and network parameters such as size, structure and the ratio of excitatory to inhibitory neurons. We found that the network parameters have little impact on these spontaneous periodic up and down transitions. However, the intrinsic currents were found to play a leading role in the process. Then, we studied the transitions in the presence of stimulation and found that the addition of stimulation did have an effect on the network transitions. Through the observation and analysis of the findings, we have tried to explain the dynamics of up and down transitions and to lay the foundation for future work on the role of these transitions in cortex activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parga, N., Abbott, L.F.: Network model of spontaneous activity exhibiting synchronous transitions between up and down states. Front. Neurosci. 1(1), 57 (2007)
Anderson, J., Lampl, I., Reichova, I., Carandini, M., Ferster, D.: Stimulus dependence of two-state fluctuations of membrane potential in cat visual cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 3(6), 617–621 (2000)
Lampl, I., Reichova, I., Ferster, D.: Synchronous membrane potential fluctuations in neurons of the cat visual cortex. Neuron 22(2), 361–374 (1999)
Steriade, M., Nuñez, A., Amzica, F.: Intracellular analysis of relations between the slow (1 Hz) neocortical oscillation and other sleep rhythms of the electroencephalogram. J. Neurosci. 13(8), 3266–3283 (1993)
Petersen, C.C., Hahn, T.T., Mehta, M., Grinvald, A., Sakmann, B.: Interaction of sensory responses with spontaneous depolarization in layer 2/3 barrel cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100(23), 13638–13643 (2003)
Araki, O.: Computer simulations of synchrony and oscillations evoked by two coherent inputs. Cogn. Neurodyn. 7(2), 133–141 (2013)
Ma, J., Hu, B., Wang, C., Jin, W.: Simulating the formation of spiral wave in the neuronal system. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(1), 73–83 (2013)
Wang, G., Jin, W., Wang, A.: Synchronous firing patterns and transitions in small-world neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(3), 1453–1458 (2015)
Zhou, J., Wu, Q., Xiang, L.: Impulsive pinning complex dynamical networks and applications to firing neuronal synchronization. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(3), 1393–1403 (2012)
Liu, Y., Wang, R., Zhang, Z., Jiao, X.: Analysis of stability of neural network with inhibitory neurons. Cogn. Neurodyn. 4(1), 61–68 (2010)
Gu, H., Pan, B., Li, Y.: The dependence of synchronization transition processes of coupled neurons with coexisting spiking and bursting on the control parameter, initial value, and attraction domain. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(3), 1191–1210 (2015)
Njap, F., Claussen, J.C., Moser, A., Hofmann, U.G.: Modeling effect of GABAergic current in a basal ganglia computational model. Cogn. Neurodyn. 6(4), 333–341 (2012)
Zheng, C., Zhang, T.: Alteration of phase-phase coupling between theta and gamma rhythms in a depression-model of rats. Cogn. Neurodyn. 7(2), 167–172 (2013)
Wang, Q., Zheng, Y., Ma, J.: Cooperative dynamics in neuronal networks. Chaos Solions Fractals 56(7), 19–27 (2013)
Perc, M.: Spatial coherence resonance in excitable media. Phys. Rev. E 72(1), 016207 (2005)
Gosak, M., Marhl, M., Perc, M.: Spatial coherence resonance in excitable biochemical media induced by internal noise. Biophys. Chem. 128(2), 210–214 (2007)
Perc, M., Gosak, M., Marhl, M.: Periodic calcium waves in coupled cells induced by internal noise. Chem. Phys. Lett. 437(1), 143–147 (2007)
DiFrancesco, D.: Pacemaker mechanisms in cardiac tissue. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55(1), 455–472 (1993)
Lüthi, A., McCormick, D.A.: H-current: properties of a neuronal and network pacemaker. Neuron 21(1), 9–12 (1998)
Pape, H.C.: Queer current and pacemaker: the hyperpolarization-activated cation current in neurons. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 58(1), 299–327 (1996)
Dickson, C.T., Magistretti, J., Shalinsky, M.H., Fransén, E., Hasselmo, M.E., Alonso, A.: Properties and role of Ih in the pacing of subthreshold oscillations in entorhinal cortex layer II neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 83(5), 2562–2579 (2000)
Wilson, A., Cowan, J.D.: Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons. Biophys. J. 12(1), 1–24 (1972)
Compte, A., Sanchez-Vives, M.V., McCormick, D.A., Wang, X.J.: Cellular and network mechanisms of slow oscillatory activity (1 Hz) and wave propagations in a cortical network model. J. Neurophysiol. 89, 2707–2725 (2003)
Holcman, D., Tsodyks, M.: The emergence of up and down states in cortical networks. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2, 174–181 (2006)
Yang, Z., Wang, Q., Danca, M.F., Zhang, J.: Complex dynamics of compound bursting with burst episode composed of different bursts. Nonlinear Dyn. 70(3), 2003–2013 (2012)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics of collective behaviors of network of neurons. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58, 2038–2045 (2015)
Xu, X., Wang, R.: Neurodynamics of up and down transitions in a single neuron. Cogn. Neurodyn. 8(6), 509–515 (2014)
Xu, X., Wang, R.: Neurodynamics of up and down transitions in network model. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2013, 9 (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/486178
Wang, R., Zhang, Z., Chen, G.: Energy coding and energy functions for local activities of the brain. Neurocomputing 73(1), 139–150 (2009)
Wang, R., Zhang, Z., Chen, G.: Energy function and energy evolution on neuronal populations. Neural Netw. IEEE Trans. 19(3), 535–538 (2008)
Wang, R., Zhang, Z.: Energy coding in biological neural networks. Cogn. Neurodyn. 1(3), 203–212 (2007)
Wang, Q.Y., Murks, A., Perc, M., Lu, Q.S.: Taming desynchronized bursting with delays in the Macaque cortical network. Chin. Phys. B 20(4), 040504 (2011)
Loewenstein, Y., Mahon, S., Chadderton, P., Kitamura, K., Sompolinsky, H., Yarom, Y., Häusser, M.: Bistability of cerebellar Purkinje cells modulated by sensory stimulation. Nat. Neurosci. 8(2), 202–211 (2005)
Koch, C., Segev, I.: Methods in neuronal modeling: from ions to networks. MIT Press, Cambridge (1998)
Destexhe, A., Mainen, Z.F., Sejnowski, T.J.: Synthesis of models for excitable membranes, synaptic transmission and neuromodulation using a common kinetic formalism. J. Comput. Neurosci. 1(3), 195–230 (1994)
Bazhenov, M., Timofeev, I., Steriade, M., Sejnowski, T.J.: Potassium model for slow (2–3 Hz) in vivo neocortical paroxysmal oscillations. J. Neurophysiol. 92(2), 1116 (2004)
Ermentrout, T.J., Terman, D.H.: Mathematical foundations of neuroscience. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Li, C.Y., Poo, M.M., Dan, Y.: Burst spiking of a single cortical neuron modifies global brain state. Science 324(5927), 643–646 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11232005) and The Ministry of Education Doctoral Foundation (No. 20120074110020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Ni, L. & Wang, R. A neural network model of spontaneous up and down transitions. Nonlinear Dyn 84, 1541–1551 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2587-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2587-y