Abstract
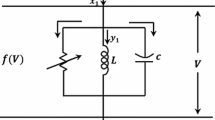
In this paper, to research the relationship between network synchronous dynamics and the optimal coupling mode, we have constructed the coupled network structure with the Hindmarsh–Rose (HR) neuron cells as the unit and found out the optimal coupling matrix, by using the chaos ant swarm optimization (CASO) algorithm. Some typical coupled networks from all the coupled configurations are selected for analysis. Furthermore, to further verify the results of the optimization algorithm, a network of 42 cell units is constructed and the synchronization behavior is compared in both the optimization and non-optimized coupling topology. Our results indicate that proper coupling matrix of HR neural network could be obtained by means of CASO algorithm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osipov, G.V., Kurths, J., Zhou, C.: Synchronization in Oscillatory Networks. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Wang, Q.Y., Zheng, Y.H., Ma, J.: Cooperative dynamics in neuronal networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 56, 19–27 (2013)
Wei, D.Q., Luo, X.S., Zhang, B.: Chaos synchronization of brushless DC motors based on LaSalle invariance principle. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(8), 1733–1738 (2012)
Wang, Q.Y., Chen, G.R., Perc, M.: Synchronous bursts on scale-free neuronal networks with attractive and repulsive coupling. PLoS One 6(1), e15851,1-10 (2011)
Tang, J., Ma, J., Yi, M., Xia, H., Yang, X.Q.: Delay and diversity-induced synchronization transitions in a small-world neuronal network. Phys. Rev. E. 83, 046207-1-4 (2011)
Zhang, J.Q., Chen, H.S., Wang, M.S.: Enhanced synchronization of intercellular calcium oscillations by noise contaminated signals. Commun. Theor. Phys. 50, 903–906 (2008)
Wang, M.S., Hou, Z.H., Xin, H.W.: Optimal network size for Hodgkin–Huxley neurons. Phys. Lett. A 334, 93–97 (2005)
Chen, H.S., Zhang, J.Q., Liu, J.Q.: Enhancement of neuronal coherence by diversity in coupled Rulkov-map models. Phys. A 387, 1071–1076 (2008)
Zhang, J.Q., Wang, C.D., Wang, M.S., Huang, S.F.: Firing patterns transition induced by system size in coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neural system. Neurocomputing 74, 2961–2966 (2011)
Wang, Q.Y., Zhang, H.H., Chen, G.R.: Stimulus-induced transition of clustering firings in neuronal networks with information transmission delay. Eur. Phys. J. B. 86(7), 1–7 (2013)
Neefs, P.J., Steur, E., Nijmeijer, H.: Network complexity and synchronous behavior—an experimental approach. Int. J. Neural Syst. 20, 233–243 (2010)
Wang, Q.Y., Perc, M., Duan, Z.S., Chen, G.R.: Impact of delays and rewiring on the dynamics of small-world neuronal networks with two types of coupling. Phys. A. 389, 3299–3306 (2010)
Xu, B., Gong, Y.B., Wang, L., Wu, Y.A.: Multiple synchronization transitions due to periodic coupling strength in delayed Newman-Watts networks of chaotic bursting neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 72, 79–86 (2013)
Yu, Q.: Time delay and long-range connection induced synchronization transitions in Newman–Watts small-world neuronal networks. PLoS One 9, e96415 (2014)
Zheng, Y.G., Wang, Z.H.: Time delay included different synchronization patterns in repulsively coupled chaotic oscillators. Chaos 22, 043127-1-6 (2012)
Yao, C.G., Yi, M., Shuai, J.W.: Time delay included different synchronization patterns in repulsively coupled chaotic oscillators. Chaos 23, 033140-1-7 (2013)
Ma, J., Zhang, A.H., Xia, Y.F., Zhang, L.P.: Optimize design of adaptive synchronization controllers and parameter observers in different hyperchaotic systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 215, 3318–3326 (2010)
Dahasert, N., Öztürk, İ., Kiliç, R.: Experimental realizations of the HR neuron model with programmable hardware and synchronization applications. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 2343–2358 (2012)
Rosin, D.P., Rontani, D., Gauthier, D.J., Schöll, E.: Control of synchronization patterns in neural-like Boolean networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 104102-1-4 (2013)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.M.: A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 221, 87–102 (1984)
dos Santos Coelho, L., de Andrade Bernert, D.L.: A modified ant colony optimization algorithm based on differential evolution for chaotic synchronization. Exp. Syst. Appl. 37, 4198–4203 (2010)
Li, L.X., Yang, Y.X., Peng, H.P., Wang, X.D.: Parameters identification of chaotic systems via chaotic ant swarm. Chaos Soliton Fractals 28, 1204–1211 (2006)
Socha, K., Dorigo, M.: Ant colony optimization for continuous domains. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 185, 1155–1173 (2008)
Li, Y.Y., Wen, Q.Y., Li, L.X., Peng, H.P.: Hybrid chaotic ant swarm optimization. Chaos Soliton Fractals 42, 880–889 (2009)
Liu, L.Z., Zhang, J.Q., Xu, G.X., Liang, L.S., Huang, S.F.: A modified chaotic ant swarm optimization algorithm. Acta Phys. Sin 62, 170501-1-6 (2013)
Li, Y.Y., Wen, Q.Y., Li, L.X.: Modified chaotic ant swarm to function optimization. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 16, 58–63 (2009)
Wan, M., Wang, C., Li, L., Yang, Y.: Chaotic ant swarm approach for data clustering. Appl. Soft Comput. 12, 2387–2393 (2012)
Liu, L.Z., Zhang, J.Q., Xu, G.X., Liang, L.S., Wang, M.S.: A chaotic secure communication method based on chaos systems partial series parameter estimation. Acta Phys. Sin 63, 010501-1-6 (2014)
Li, L.X., Peng, H.P., Yang, Y.X., Wang, X.D.: Parameter estimation for Lorenz chaotic systems based on chaotic ant swarm algorithm. Acta Phys. Sin 56, 51–55 (2007)
Mikkelsen, K., Imparato, A., Torcini, A.: Emergence of slow collective oscillations in neural networks with spike-timing dependent plasticity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 208101 (2013)
Han, F., Wiercigroch, M., Fang, J.A., Wang, Z.J.: Excitement and synchronization of small-world neuronal networks with short-term synaptic plasticity. Int. J. Neural Syst. 21, 415–425 (2011)
Li, L.X., Peng, H.P., Yang, Y.X.: T-S fuzzy system design by chaotic ant swarm algorithm. Acta Phys. Sin 57, 703–708 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science and special Found for the Theoretical Physics of China (21103002, 11047017), the Natural Science Funds of Anhui Province of China (No. 1508085MA15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Huang, S., Pang, S. et al. Optimizing calculations of coupling matrix in Hindmarsh–Rose neural network. Nonlinear Dyn 84, 1303–1310 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2569-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2569-0