Abstract
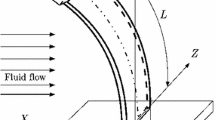
We investigate the effectiveness of linear and nonlinear time-delay feedback controls to suppress high amplitude oscillations of an elastically mounted square cylinder undergoing galloping oscillations. A representative model that couples the transverse displacement and the aerodynamic force is used. The quasi-steady approximation is used to model the galloping force. A linear analysis is performed to investigate the effect of linear time-delay controls on the onset speed of galloping and natural frequencies. It is demonstrated that a linear time-delay control can be used to delay the onset speed of galloping. The normal form of the Hopf bifurcation is then derived to characterize the type of the instability (supercritical or subcritical) and to determine the effects of the linear and nonlinear time-delay parameters on their outputs near the bifurcation. The results show that the nonlinear time-delay control can be efficiently implemented to significantly reduce the galloping amplitude and suppress any dangerous behavior by converting any subcritical Hopf bifurcation into a supercritical one.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, S.S.: Flow-Induced Vibration of Circular Cylindrical Structures. Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, Washington, DC (1987)
Chang, W.K., Pilipchuk, V., Ibrahim, R.A.: Fluid flow-induced nonlinear vibration of suspended cables. Nonlinear Dyn. 14, 377–406 (1997)
Paidoussis, M.P.: Fluid-Structure Interactions: Slender Structures and Axial Flow, vol. 1. Academic Press, London (1998)
Paidoussis, M.P., Price, S.J., de Langre, E.: Fluid Structure Interactions: Cross-Flow-Induced Instabilities. Cambridge University Press, New York (2011)
Wang, L., Dai, H.L., Han, Y.Y.: Cross-flow-induced instability and nonlinear dynamics of cylinder arrays with consideration of initial axial load. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 1043–1051 (2012)
Li, F.M.: Active aeroelastic flutter suppression of a supersonic plate with piezoelectric material. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 51, 190–203 (2012)
Berryman, J.G.: Combining analysis of random elastic polycrystals with poroelasticity for granular composites having orthotropic porous grains and fluid-filled pores. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 72, 11–21 (2013)
Paak, M., Paidoussis, M.P., Misra, A.K.: Nonlinear dynamics and stability of cantilevered circular cylindrical shells conveying fluid. J. Sound Vib. 332, 3474–3498 (2013)
Ghayesh, M.H., Paidoussis, M.P., Amabili, M.: Nonlinear dynamics of cantilevered extensible pipes conveying fluid. J. Sound Vib. 332, 6405–6418 (2013)
Wang, L.: Flutter instability of supported pipes conveying fluid subjected to distributed follower force. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 25, 46–52 (2012)
Keber, M., Wiercigroch, M.: Dynamics of a vertical riser with weak structural nonlinearity excited by wakes. J. Sound Vib. 315, 685–699 (2008)
Dai, H.L., Wang, L., Qian, Q., Ni, Q.: Vortex-induced vibrations of pipes conveying fluid in the subcritical and supercritical regimes. J. Fluids Struct. 39, 322–334 (2013)
Dai, H.L., Wang, L., Qian, Q., Ni, Q.: Vortex-induced vibrations of pipes conveying pulsating fluid. Ocean Eng. 77, 12–24 (2014)
Fan, C.C., Syu, J.W., Pan, M.C., Tsao, W.C.: Study of start-up vibration response for oil whirl, oil whip and dry whip. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 25, 3102–3115 (2011)
Blevins, R.D.: Flow-Induced Vibrations. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York (1990)
Den Hartog, J.P.: Mechanical Vibrations. McGraw-Hill, New York (1956)
Naudascher, E., Rockwell, D.: Flow-Induced Vibrations: An Engineering Guide. Dover, New York (1994)
Alonso, G., Meseguer, J., Prez-Grande, I.: Galloping stabilities of two-dimensional triangular cross-sectional bodies: a systematic approach. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 95, 928–940 (2007)
Wang, L., Liu, W.B., Dai, H.L.: Aeroelastic galloping response of square prisms: the role of time-delayed feedbacks. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 75, 79–84 (2014)
Barrero-Gil, A., Alongso, G., Sanz-Andres, A.: Energy harvesting from transverse galloping. J. Sound Vib. 329, 2873–2883 (2010)
Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M.R., Nayfeh, A.H.: Power harvesting from transverse galloping of square cylinder. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1355–1363 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Yan, Z., Hajj, M.R.: Temperature impact on the performance of galloping-based piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 055026 (2013)
Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M.R., Nayfeh, A.H.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from transverse galloping of bluff bodies. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 015014 (2013)
Abdelkefi, A., Yan, Z., Hajj, M.R.: Performance analysis of galloping-based piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters with different cross-section geometries. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 25, 246–256 (2014)
Yang, Y., Zhao, L., Tang, L.: Comparative study of tip cross-sections for efficient galloping energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 064105 (2013)
Mehmood, A., Abdelkefi, A., Akhtar, I., Nayfeh, A.H., Nuhait, A., Hajj, M.R.: Linear and nonlinear active feedback controls for vortex-induced vibrations of circular cylinders. J. Vib. Control. (2012). doi:10.1177/1077546312469425
Bert, C.W., Egle, D.M., Wilkins, D.J.: Optimal design of a non-linear dynamic absorber. J. Sound Vib. 137, 347–352 (1990)
Lee, Y.S., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A., et al.: Passive nonlinear targeted energy transfer and its applications to vibration and absorption: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-body Dyn. 222, 77 (2008)
Gendelman, V., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A., McFarland, D.M.: Asymptotic analysis of passive nonlinear suppression of aeroelastic instabilities of a rigid wing in subsonic flow. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 70, 1655–1677 (2010)
Gendelman, V., Starosvetsky, Y., Feldman, M.: Attractors of harmonically forced linear oscillator with attached nonlinear energy sink: description of response regimes. Nonlinear Dyn. 51, 31–46 (2008)
Abdelkefi, A., Ghommem, M.: Model reduction of nonlinear aeroelastic systems experiencing Hopf bifurcation. J Model. Simul. Identif. Control 1, 57–77 (2013)
Masoud, Z., Nayfeh, A.H.: Sway reduction on container cranes using delayed feedback controller. Nonlinear Dyn. 34, 347–358 (2003)
Masoud, Z., Nayfeh, A.H., Nayfeh, N.A.: Sway reduction on quay-side container cranes using delayed feedback controller: simulations and experiments. J. Vib. Control. 11, 1103 (2005)
Nayfeh, A.H., Nayfeh, N.A.: Time-delay feedback control of lathe cutting tools. J. Vib. Control. 18, 1106 (2012)
Parkinson, G.V., Smith, J.D.: The square prism as an aeroelastic nonlinear oscillator. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 17, 225–239 (1964)
Nayfeh, A.H., Nayfeh, N.A.: Analysis of the cutting tool on a lathe. Nonlinear Dyn. 63, 395–416 (2011)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support provided by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-11-0183) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST (2013TS034, 2014YQ007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, H.L., Abdelkefi, A., Wang, L. et al. Control of cross-flow-induced vibrations of square cylinders using linear and nonlinear delayed feedbacks. Nonlinear Dyn 78, 907–919 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1485-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1485-z