Abstract
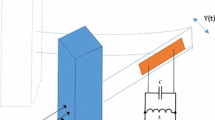
An energy harvester is proposed to concurrently harness energy from base and galloping excitations. This harvester consists of a triangular cross-sectional tip mass attached to a multilayered piezoelectric cantilever beam and placed in an incompressible flow and subjected to a harmonic base excitation in the cross-flow direction. A coupled nonlinear-distributed-parameter model is developed representing the dynamics of the transverse degree of freedom and the generated voltage. The galloping force and moment are modeled by using a nonlinear quasi-steady approximation. Under combined loadings and when the excitation frequency is away from the global natural frequency of the harvester, the response of the harvester mainly contains these two harmonic frequencies. Thus, the harvester’s response is generally aperiodic and is either periodic with large period (i.e., period-\(n\)), or quasi-periodic, or chaotic. To characterize the harvester’s response under a combination of vibratory base excitations and aerodynamic loading, we use modern methods of nonlinear dynamics, such as phase portraits, power spectra, and Poincaré sections. A further analysis is then performed to determine the effects of the wind speed, frequency excitation, base acceleration, and electrical load resistance on the performance of the harvester under separate loadings.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muralt, P.: Ferroelectric thin films for micro-sensors and actuators: a review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 10, 136–146 (2000)
Roundy, S., Wright, P.K.: A piezoelectric vibration-based generator for wireless electronics. Smart Mater. Struct. 13, 1131 (2005)
Karami, A., Inman, D.J.: Powering pacemakers from heartbeat vibrations using linear and nonlinear energy harvesters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 042901 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Ghommem, M.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from morphing wing motions for micro air vehicles. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 3, 052001 (2013)
Karami, A., Inman, D.J.: Equivalent damping and frequency change for linear and nonlinear hybrid vibrational energy harvesting systems. J. Sound Vib. 330, 5583–5597 (2012)
El-hami, M., Glynne-Jones, P., White, N.M., et al.: Design and fabrication of a new vibration-based electromechanical power generator. Sens. Actuators A 92, 335–342 (2001)
Roundy, S., Wright, P.K., Rabaey, J.: A study of low level vibrations as a power source for wireless sensor nodes. Comput. Commun. 26, 1131–1144 (2003)
Wang, L., Yuan, F.G.: Vibration energy harvesting by magnetostrictive material. Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 045009 (2008)
Anton, S.R., Sodano, H.A.: A review of power harvesting using piezoelectric materials (2003–2006). Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 1–21 (2007)
Abdelkefi, A.: Global nonlinear analysis of piezoelectric energy harvesting from ambient and aeroelastic vibrations. PhD Dissertation. Virginia Tech. (2012)
Inman, D.J., Grisso, B.L.: Towards autonomous sensing. Smart Structures and Materials Conference. SPIE, 61740T (2006)
Stanton, S.C., McGehee, C.C., Mann, B.P.: Nonlinear dynamics for broadband energy harvesting: Investigation of a bistable piezoelectric inertial generator. Physica D. 239, 640–653 (2010)
Masana, R., Daqaq, M.F.: Electromechanical modeling and nonlinear analysis of axially loaded energy harvesters. J. Vib. Acoust. 133, 011007 (2011)
Abdelkefi, A., Nayfeh, A.H., Hajj, M.R.: Global nonlinear distributed-parameter model of parametrically excited piezoelectric energy harvesters. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 1147–1160 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Barsallo, N.: Comparative modeling of low-frequency piezomagnetoelastic energy harvesters. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. (2014). doi:10.1177/1045389X14523860
Erturk, A., Vieira, W.G.R., De Marqui, C., Inman, D.J.: On the energy harvesting potential of piezoaeroelastic systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 184103 (2010)
De Marqui, C., Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: Piezoaeroelastic modeling and analysis of a generator wing with continuous and segmented electrodes. Journal of Intelligent Material Syst. Struct. 21, 983–993 (2010)
Bryant, M., Garcia, E.: Modeling and testing of a novel aeroelastic flutter energy harvester. J. Vib. Acoust. 133, 011010 (2011)
Abdelkefi, A., Nayfeh, A.H., Hajj, M.R.: Modeling and analysis of piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 925–939 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M.R., Nayfeh, A.H.: Sensitivity analysis of piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 23, 1523–1531 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Nuhait, A.: Modeling and performance analysis of cambered wing-based piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 095029 (2013)
Mann, B.P., Sims, N.D.: Energy harvesting from the nonlinear oscillations of magnetic levitation. J. Sound Vib. 319, 515–530 (2009)
Litak, G., Friswell, M.I., Adhikari, S.: Magnetopiezoelastic energy harvesting driven by random excitations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 214103 (2010)
Daqaq, M.F.: Transduction of a bistable inductive generator driven by white and exponentially correlated Gaussian noise. J. Sound Vib. 330, 2554–2564 (2011)
Abdelkefi, A., Najar, F., Nayfeh, A.H., Ben Ayed, S.: An energy harvester using piezoelectric cantilever beams undergoing coupled bending-torsion vibrations. Smart Mater. Struct. 20, 115007 (2011)
Abdelkefi, A., Nayfeh, A.H., Hajj, M.R., Najar, F.: Energy harvesting from a multifrequency response of a tuned bendingtorsion system. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 075029 (2012)
Ben Ayed, S., Abdelkefi, A., Najar, F., Hajj, M.R.: Design and performance of variable-shaped piezoelectric energy harvesters. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 25, 174–186 (2014)
Abdelkefi, A., Nayfeh, A.H., Hajj, M.R.: Design of piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters. Nonlinear Dyn. 68, 519–530 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Nayfeh, A.H., Hajj, M.R.: Enhancement of power harvesting from piezoaeroelastic systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 68, 531–541 (2012)
Akaydin, H.D., Elvin, N., Andrepoulos, Y.: Energy harvesting from highly unsteady fluid flows using piezoelectric materials. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 21, 1263–1278 (2010)
Akaydin, H.D., Elvin, N., Andrepoulos, Y.: The performance of a self-excited fluidic energy harvester. Smart Mater. Struct. 21, 025007 (2012)
Dai, H.L., Abdelkefi, A., Wang, L.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from concurrent vortex-induced vibrations and base excitations. Nonlinear Dyn. (2014). doi:10.1007/s11071-014-1355-8
Mehmood, A., Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M.R., Nayfeh, A.H., Akhtar, I., Nuhait, A.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from vortex-induced vibrations of circular cylinder. J. Sound Vib. 332, 4656–4667 (2013)
Mackowski, A.W., Williamson, C.H.K.: An experimental investigation of vortex-induced vibration with nonlinear restoring forces. Phys. Fluids. 25, 087101 (2013)
Sirohi, J., Mahadik, R.: Piezoelectric wind energy harvester for low-power sensors. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 22, 2215–2228 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M.R., Nayfeh, A.H.: Power harvesting from transverse galloping of square cylinder. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1377–1388 (2012)
Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M.R., Nayfeh, A.H.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from transverse galloping of bluff bodies. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 015014 (2013)
Abdelkefi, A., Yan, Z., Hajj, M.R.: Modeling and nonlinear analysis of piezoelectric energy harvesting from transverse galloping. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 025016 (2013)
Abdelkefi, A., Yan, Z., Hajj, M.R.: Nonlinear dynamics of galloping-based piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 222, 1483–1501 (2013)
Abdelkefi, A., Yan, Z., Hajj, M.R.: Performance analysis of galloping-based piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters with different cross-section geometries. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 25, 246–256 (2014)
Yang, Y.W., Zhao, L.Y., Tang, L.H.: Comparative study of tip cross-sections for efficient galloping energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 064105 (2013)
Zhao, L.Y., Tang, L.H., Yang, Y.W.: Comparison of modeling methods and parametric study for a piezoelectric wind energy harvester. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 125003 (2013)
Jung, H.J., Lee, S.W.: The experimental validation of a new energy harvesting system based on the wake galloping phenomenon. Smart Mater. Struct. 20, 055022 (2011)
Abdelkefi, A., Scanlon, J.M., McDowell, E., Hajj, M.R.: Performance enhancement of piezoelectric energy harvesters from wake galloping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 033903 (2013)
Abdelkefi, A., Hasanyan, A., Montgomery, J., Hall, D., Hajj, M.R.: Incident flow effects on the performance of piezoelectric energy harvesters from galloping vibrations. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 4, 022002 (2014)
Bibo, A., Daqaq, M.F.: Energy harvesting under combined aerodynamic and base excitations. J. Sound Vib. 332, 5086–5102 (2013)
Bibo, A., Daqaq, M.F.: Investigation of concurrent energy harvesting from ambient vibrations and wind using a single piezoelectric generator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 243904 (2013)
Yan, Z., Abdelkefi, A., Hajj, M.R.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from hybrid vibrations. Smart Mater. Struct. 23, 025026 (2014)
Barrero-Gil, A., Alonso, G., Sanz-Andres, A.: Energy harvesting from transverse galloping. J. Sound Vib. 329, 2873–2883 (2010)
Naudascher, E., Rockwell, D.: Flow-induced vibrations, an engineering guide. Dover Publications, New York (1994)
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.M.: Nonlinear oscillations. Wiley, New York (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Abdelkefi, A. Nonlinear characterization of concurrent energy harvesting from galloping and base excitations. Nonlinear Dyn 77, 1171–1189 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1369-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1369-2