Abstract
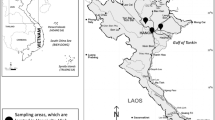
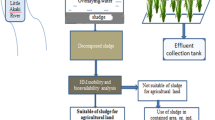
More than 80% of sewage sludge (SS) produced in Iran is landfilled with high environmental impact. The chemical properties of SS produced from wastewater plants of cites of Arak, Isfahan, Kermanshah, Rasht, Saveh, Shiraz, Sanandaj, Tehran, Takestan, and Toyserkan were studied to assess the potential beneficial effects of their application to agricultural soil as sustainable SS management. The pH and EC values, total content and water-soluble concentration of nutrients and heavy metals, their water-extractable pools were determined, and their speciation was done through the NICA–Donnan model using the Visual MINTEQ software. Relatively high contents of N, P, and physiologically active cations indicated potential beneficial effects of SS for land application in the agro-ecosystems, whereas the heavy metal content depended on the SS production site, with higher levels found in the SS of the Arak and Saveh wastewater treatment plants. The pH value was the main factor controlling the metal speciation, with Cu and Pb having the highest affinity for the organic matter, and Zn and Mn being mainly present as free ions or inorganic species. Results showed that SS from different locations in Iran differed in their main chemical properties and elemental composition and that speciation analysis could be used to predict potential beneficial and harmful effects of SS, particularly upon the modeling of metal–organic complexes by the NICA–Donnan approach. Globally, our results confirmed that while the SS produced in Iran has potential suitable chemical properties for use in agriculture, their heavy metals load should not be ignored.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggelides S, Londra P (2000) Effects of compost produced from town wastes and sewage sludge on the physical properties of a loamy and a clay soil. Bioresour Technol 71:253–259
Allison L, Richards L (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. vol 60. Soil and Water Conservative Research Branch, Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture
Allison JD, Brown DS, Novo-Gradac KJ (1991) MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2, a geochemical assessment model for environmental systems: version 3.0 user’s manual. Environmental Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency
Alvarez EA, Mochon MC, Sánchez JJ, Rodrı́guez MT (2002) Heavy metal extractable forms in sludge from wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 47:765–775
Ambily P, Jisha M (2012) Biodegradation of anionic surfactant, sodium dodecyl sulphate by Psuedomonas aeruginosa MTCC 10311. J Environ Biol 33:717
Andrés NF, Francisco MS (2008) Effects of sewage sludge application on heavy metal leaching from mine tailings impoundments. Bioresour Technol 99:7521–7530
Ashworth D, Alloway B (2008) Influence of dissolved organic matter on the solubility of heavy metals in sewage-sludge-amended soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 39:538–550
BSI P (2005) 100 specification for composted materials British Standards Institution. London, UK
Cao H, Chen J, Zhang J, Zhang H, Qiao L, Men Y (2010) Heavy metals in rice and garden vegetables and their potential health risks to inhabitants in the vicinity of an industrial zone in Jiangsu, China. J Environ Sci 22:1792–1799
Chang Z, Ambe S, Takahashi K, Ambe F (2006) A study on the metal binding of humic acid by multitracer technique. Radiochim Acta 94:37–46
Fadiran AO, Tiruneh AT, Mtshali JS (2014) Assessment of mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals in sewage sludge from Swaziland through speciation analysis. Am J Environ Protect 3:198–208
Gomes N, Landi L, Smalla K, Nannipieri P, Brookes P, Renella G (2010) Effects of Cd-and Zn-enriched sewage sludge on soil bacterial and fungal communities. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1255–1263
Gustafsson JP (2011) Visual MINTEQ 3.0 user guide KTH. Department of Land and Water Recources, Stockholm, Sweden
Hooda P (2010) Trace elements in soils. Wiley, Hoboken
Khaleel R, Reddy K, Overcash M (1981) Changes in soil physical properties due to organic waste applications: a review 1. J Environ Qual 10:133–141
Kidd P, Dominguez-Rodriguez M, Diez J, Monterroso C (2007) Bioavailability and plant accumulation of heavy metals and phosphorus in agricultural soils amended by long-term application of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 66:1458–1467
Kim K-H, Kim S-H (1999) Heavy metal pollution of agricultural soils in central regions of Korea. Water Air Soil Pollut 111:109–122
Kinniburgh DG, van Riemsdijk WH, Koopal LK, Borkovec M, Benedetti MF, Avena MJ (1999) Ion binding to natural organic matter: competition, heterogeneity, stoichiometry and thermodynamic consistency. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 151:147–166
Koopal L, Saito T, Pinheiro J, Van Riemsdijk W (2005) Ion binding to natural organic matter: general considerations and the NICA-Donnan model. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 265:40–54
Kumpiene J, Giagnoni L, Marschner B, Denys S, Mench M, Adriansen K, Vangronsveld J, Puschenreiter M, Renella G (2017) Assessment of methods for determining bioavailability of trace elements in soils: a review. Pedosphere 27:389–406
Latare A, Kumar O, Singh S, Gupta A (2014) Direct and residual effect of sewage sludge on yield, heavy metals content and soil fertility under rice–wheat system. Ecol Eng 69:17–24
Li Z (2014) Modeling precipitate-dominant clogging for landfill leachate with NICA-Donnan theory. J Hazard Mater 274:413–419
Liu J-y, Sun S-Y (2013) Total concentrations and different fractions of heavy metals in sewage sludge from Guangzhou, China. Trans Nonferr Metals Soc China 23:2397–2407
Martínez CE, McBride MB (1999) Dissolved and labile concentrations of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn in aged ferrihydrite − organic matter systems. Environ Sci Technol 33:745–750
Mateo-Sagasta J, Raschid-Sally L, Thebo A (2015) Global wastewater and sludge production, treatment and use. In: Drechsel P, Qadir M, Wichelns D (eds) Wastewater: economic asset in an urbanizing world. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 15–38
McGrath S, Chang A, Page A, Witter E (1994) Land application of sewage sludge: scientific perspectives of heavy metal loading limits in Europe and the United States. Environ Rev 2:108–118
Milne CJ, Kinniburgh DG, Tipping E (2001) Generic NICA-Donnan model parameters for proton binding by humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 35:2049–2059
Mtshali JS, Tiruneh AT, Fadiran AO (2014) Characterization of sewage sludge generated from wastewater treatment plants in Swaziland in relation to agricultural uses. Resour Environ 4:190–199
Mulvaney RL (1996) Nitrogen-inorganic forms. Methods of soil analysis part 3. Chemical Methods-SSSA Book series no. 5, Madison, WI, pp 1123–1184
Naidu R, Oliver D, McConnell S (2003) Heavy metal phytotoxicity in soils. In: Langley A, Gilbey M, Kennedy B (eds) Proceedings of the fifth national workshop on the assessment of site contamination. National environment protection council service corporation, Adelaide, SA, pp 235–241
Nikolova-Kuscu R, Powrie W, Smallman D (2013) Mechanisms of clogging in granular drainage systems permeated with low organic strength leachate. Can Geotech J 50:632–649
Nyamangara J, Mzezewa J (2001) Effect of long-term application of sewage sludge to a grazed grass pasture on organic carbon and nutrients of a clay soil in Zimbabwe. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 59:13–18
Oleszczuk P, Hollert H (2011) Comparison of sewage sludge toxicity to plants and invertebrates in three different soils. Chemosphere 83:502–509
Pakhnenko E, Ermakov A, Ubugunov L (2009) Influence of sewage sludge from sludge beds of Ulan-Ude on the soil properties and the yield and quality of potatoes. Mosc Univ Soil Sci Bull 64:175
Pedra F, Plaza C, García-Gil JC, Polo A (2008) Effects of municipal waste compost and sewage sludge on proton binding behavior of humic acids from Portuguese sandy and clay loam soils. Bioresour Technol 99:2141–2147
Pérez-Esteban J, Escolástico C, Masaguer A, Vargas C, Moliner A (2014) Soluble organic carbon and pH of organic amendments affect metal mobility and chemical speciation in mine soils. Chemosphere 103:164–171
Plaza C, Brunetti G, Senesi N, Polo A (2006) Fluorescence characterization of metal ion–humic acid interactions in soils amended with composted municipal solid wastes. Anal Bioanal Chem 386:2133–2140
Renella G, Landi L, Nannipieri P (2004) Degradation of low molecular weight organic acids complexed with heavy metals in soil. Geoderma 122:311–315
Renella G, Chaudri AM, Falloon CM, Landi L, Nannipieri P, Brookes PC (2007) Effects of Cd, Zn, or both on soil microbial biomass and activity in a clay loam soil. Biol Fertil Soils 43:751–758
Roussel J (2013) Metal behaviour in anaerobic sludge digesters supplemented with trace nutrients. University of Birmingham
Rowell DL (2014) Soil science: methods & applications. Routledge, Abingdon
Saar RA, Weber JH (1982) Fulvic acid: modifier of metal-ion chemistry. Environ Sci Technol 16:510A–517A
Sakala GM, Rowel DL, Pilbeam CJ (2004) Acid–base reactions between an acidic soil and plant residues. Geoderma 123:219–232
Sato T, Qadir M, Yamamoto S, Endo T, Zahoora A (2013) Global, regional, and country level need for data on wastewater generation, treatment, and use. Agric Water Manag 130:1–13
Ščančar J, Milačič R, Stražar M, Burica O (2000) Total metal concentrations and partitioning of Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ni and Zn in sewage sludge. Sci Total Environ 250:9–19
Schaecke W, Tanneberg H, Schilling G (2002) Behavior of heavy metals from sewage sludge in a Chernozem of the dry belt in Saxony-Anhalt/Germany. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 165:609–617
Serna M, Pomares F (1992) Nitrogen mineralization of sludge-amended soil. Bioresour Technol 39:285–290
Sumner ME, Naidu R (1998) Sodic soilsdistribution, properties, management, and environmental consequences. vol 631.416 S6
Tapia Y, Cala V, Eymar E, Frutos I, Gárate A, Masaguer A (2010) Chemical characterization and evaluation of composts as organic amendments for immobilizing cadmium. Bioresour Technol 101:5437–5443
Terry R, Nelson D, Sommers L (1979) Carbon Cycling During Sewage Sludge Decomposition in Soils 1. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43:494–499
Torri SI, Corrêa RS, Renella G, Valdecantos A, Perelomov L (2012) Biosolids soil application: why a new special on an old issue? Appl Environ Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/265783
Torri SI, Corréa RS, Renella G (2017) Biosolid application to agricultural land—a contribution to global phosphorus recycle: a review. Pedosphere 27:1–16
Usman ARA (2008) The relative adsorption selectivities of Pb, Cu, Zn, Cd and Ni by soils developed on shale in New Valley, Egypt. Geoderma 144:334–343
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Zaman M, Cameron K, Di H, Inubushi K (2002) Changes in mineral N, microbial biomass and enzyme activities in different soil depths after surface applications of dairy shed effluent and chemical fertilizer. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 63:275–290
Zhang Y, Jiang J, Maozhe C (2008) MINTEQ modeling for evaluating the leaching behavior of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash. J Environ Sci 20:1398–1402
Zhang C, Chen H, Yu Y, Wang L, Han J, Tao P (2013) Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in sludge from wastewater treatment plants and sludge disposal in Chinese coastal areas. Huan jing ke xue = Huanjing kexue 34:1345–1350
Zheng X-Y, Wang X-N, Huang X, Chen Q, Chen W, He Y-J (2013) Effects of Cu2+ on morphological structure, functional groups, and elemental composition of aerobic granular sludge. Environ Technol 34:219–224
Zhou L, Wong J (2001) Effect of dissolved organic matter from sludge and sludge compost on soil copper sorption. J Environ Qual 30:878–883
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feizi, M., Jalali, M. & Renella, G. Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal content and speciation in sewage sludge from different locations in Iran. Nat Hazards 95, 657–675 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3513-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3513-7