Abstract
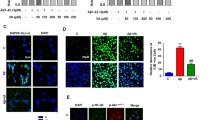
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a progressive neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system, is the most common cause of senile dementia. This study aimed to investigate whether amentoflavone (AF), a biflavonoid compound, could exert neuroprotective activities against AD. The AD model was established by the intracranial injection of amyloid-beta (Aβ) in rat models. The effect of AF on cognitive function was examined using the Morris water maze test. Cell survival and apoptosis in the hippocampal region in an animal model were detected using Nissl staining and a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferased UTP nick-end labeling assay, respectively. The levels of oxidant enzymes were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Signaling molecule expressions were examined by western blotting. Our results showed that AF significantly attenuated Aβ-induced deficits in neurological functions as well as neuronal cell death and apoptosis in the hippocampal region. Moreover, our findings revealed that AF increased nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) expression and translocation and activated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling. In a cellular model of AD established by exposing PC12 cells to Aβ, our results provided further evidence that the neuroprotective activities of AF were mediated by modulating Nrf2 through AMPK/glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta signaling. AF exerts a protective effect against Aβ1–42-induced neurotoxcicity by inducing Nrf2 antioxidant pathways via AMPK signaling activation, which provided experimental evidence that AF might provide a clinical benefit to patients with AD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu Z, Yan J, Jiang W, Yao XG, Chen J, Chen L, Li C, Hu L, Jiang H, Shen X (2013) Arctigenin effectively ameliorates memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease model mice targeting both beta-amyloid production and clearance. J Neurosci 33:13138–13149
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R, Hansen LA, Katzman R (1991) Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 30:572–580
Choi SM, Kim BC, Cho YH, Choi KH, Chang J, Park MS, Kim MK, Cho KH, Kim JK (2014) Effects of flavonoid compounds on beta-amyloid-peptide-induced neuronal death in cultured mouse cortical neurons. Chonnam Med J 50:45–51
Marcus DL, Thomas C, Rodriguez C, Simberkoff K, Tsai JS, Strafaci JA, Freedman ML (1998) Increased peroxidation and reduced antioxidant enzyme activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 150:40–44
Zheng L, Kagedal K, Dehvari N, Benedikz E, Cowburn R, Marcusson J, Terman A (2009) Oxidative stress induces macroautophagy of amyloid beta-protein and ensuing apoptosis. Free Radical Biol Med 46:422–429
Behl C, Holsboer F (1998) Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and antioxidant neuroprotection. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 66:113–121
Peng QL, Buz’Zard AR, Lau BH (2002) Pycnogenol protects neurons from amyloid-beta peptide-induced apoptosis. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 104:55–65
Andersen JK (2004) Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: cause or consequence?. Nature Med 10(7):S18
Butterfield DA, Perluigi M, Sultana R (2006) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease brain: new insights from redox proteomics. Eur J Pharmacol 545:39–50
Aliev G, Obrenovich ME, Reddy VP, Shenk JC, Moreira PI, Nunomura A, Zhu X, Smith MA, Perry G (2008) Antioxidant therapy in Alzheimer’s disease: theory and practice. Mini Rev Med. Chem. 8:1395–1406
Lin YH, Liu AH, Wu HL, Westenbroek C, Song QL, Yu HM, Ter Horst GJ, Li XJ (2006) Salvianolic acid B, an antioxidant from Salvia miltiorrhiza, prevents Abeta(25–35)-induced reduction in BPRP in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:593–599
Sun YX, Xu AH, Yang Y, Li J (2015) Role of Nrf2 in bone metabolism. J Biomed Sci 22:101
Khodagholi F, Eftekharzadeh B, Maghsoudi N, Rezaei PF (2010) Chitosan prevents oxidative stress-induced amyloid beta formation and cytotoxicity in NT2 neurons: involvement of transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biochem 337:39–51
Kanninen K, Heikkinen R, Malm T, Rolova T, Kuhmonen S, Leinonen H, Yla-Herttuala S, Tanila H, Levonen AL, Koistinaho M, Koistinaho J (2009) Intrahippocampal injection of a lentiviral vector expressing Nrf2 improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:16505–16510
Choudhry F, Howlett DR, Richardson JC, Francis PT, Williams RJ (2012) Pro-oxidant diet enhances beta/gamma secretase-mediated APP processing in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 33:960–968
Eftekharzadeh B, Maghsoudi N, Khodagholi F (2010) Stabilization of transcription factor Nrf2 by tBHQ prevents oxidative stress-induced amyloid beta formation in NT2N neurons. Biochimie 92:245–253
Ji HF, Li XJ, Zhang HY (2009) Natural products and drug discovery. Can thousands of years of ancient medical knowledge lead us to new and powerful drug combinations in the fight against cancer and dementia? EMBO Rep 10:194–200
Vauzour D, Vafeiadou K, Rodriguez-Mateos A, Rendeiro C, Spencer JP (2008) The neuroprotective potential of flavonoids: a multiplicity of effects. Genes Nutr 3:115–126
Tian HY, Li ZX, Li HY, Wang HJ, Zhu XW, Dou ZH (2013) Effects of 14 single herbs on the induction of caspase-3 in tumor cells: a brief review. Chin J Integr Med 19:636–640
Coulerie P, Nour M, Maciuk A, Eydoux C, Guillemot JC, Lebouvier N, Hnawia E, Leblanc K, Lewin G, Canard B, Figadere B (2013) Structure-activity relationship study of biflavonoids on the dengue virus polymerase DENV-NS5 RdRp. Planta Med 79:1313–1318
Erdogan-Orhan I, Altun ML, Sever-Yilmaz B, Saltan G (2011) Anti-acetylcholinesterase and antioxidant assets of the major components (salicin, amentoflavone, and chlorogenic acid) and the extracts of Viburnum opulus and Viburnum lantana and their total phenol and flavonoid contents. J Med Food 14:434–440
Lee CW, Na Y, Park NH, Kim HS, Ahn SM, Kim JW, Kim HK, Jang YP (2012) Amentoflavone inhibits UVB-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression through the modulation of AP-1 components in normal human fibroblasts. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:1137–1147
Tarallo V, Lepore L, Marcellini M, Dal Piaz F, Tudisco L, Ponticelli S, Lund FW, Roepstorff P, Orlandi A, Pisano C, De Tommasi N, De Falco S (2011) The biflavonoid amentoflavone inhibits neovascularization preventing the activity of proangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factors. J Biol Chem 286:19641–19651
Shin DH, Bae YC, Kim-Han JS, Lee JH, Choi IY, Son KH, Kang SS, Kim WK, Han BH (2006) Polyphenol amentoflavone affords neuroprotection against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage via multiple mechanisms. J Neurochem 96:561–572
Lan Z, Xie G, Wei M, Wang P, Chen L (2017) The protective effect of epimedii folium and curculiginis rhizoma on Alzheimer’s disease by the inhibitions of NF-kappaB/MAPK pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Oncotarget 8:43709–43720
Blokland A, Geraerts E, Been M (2004) A detailed analysis of rats’ spatial memory in a probe trial of a Morris task. Behav Brain Res 154:71–75
Sun Z, Yu JT, Jiang T, Li MM, Tan L, Zhang Q, Tan L (2013) Genome-wide microRNA profiling of rat hippocampus after status epilepticus induced by amygdala stimulation identifies modulators of neuronal apoptosis. PLoS One 8:e78375
Han Y, Yang X, Zhao N, Peng J, Gao H, Qiu X (2016) Alpinumisoflavone induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating miR-370/PIM1 signaling. Am J Cancer Res 6:2755–2771
Stein C, Hopfeld J, Lau H, Klein J (2015) Effects of ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761, donepezil and their combination on central cholinergic function in aged rats. J Pharm Pharm Sci 18:634–646
Kansanen E, Kuosmanen SM, Leinonen H, Levonen AL (2013) The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: mechanisms of activation and dysregulation in cancer. Redox Biol 1:45–49
Song JS, Kim EK, Choi YW, Oh WK, Kim YM (2016) Hepatocyte-protective effect of nectandrin B, a nutmeg lignan, against oxidative stress: role of Nrf2 activation through ERK phosphorylation and AMPK-dependent inhibition of GSK-3beta. Toxicol Appl Pharm 307:138–149
Zeng Z, Xu J, Zheng W (2017) Artemisinin protects PC12 cells against beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis through activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Redox Biol 12:625–633
Zhou J, Chao G, Li Y, Wu M, Zhong S, Feng Z (2016) Activation of NRF2/ARE by isosilybin alleviates Abeta25-35-induced oxidative stress injury in HT-22 cells. Neurosci Lett 632:92–97
Thapa A, Chi EY (2015) Biflavonoids as potential small molecule therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 863:55–77
Woodruff-Pak DS (2008) Animal models of Alzheimer’s disease: therapeutic implications. J Alzheimer’s Dis 15:507–521
Chauhan V, Chauhan A (2006) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Pathophysiology 13:195–208
Lauderback CM, Hackett JM, Keller JN, Varadarajan S, Szweda L, Kindy M, Markesbery WR, Butterfield DA (2001) Vulnerability of synaptosomes from apoE knock-out mice to structural and oxidative modifications induced by A beta(1–40): implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 40:2548–2554
Wan L, Nie G, Zhang J, Luo Y, Zhang P, Zhang Z, Zhao B (2011) Beta-Amyloid peptide increases levels of iron content and oxidative stress in human cell and Caenorhabditis elegans models of Alzheimer disease. Free Radical Biol Med 50:122–129
Sandberg M, Patil J, D’Angelo B, Weber SG, Mallard C (2014) NRF2-regulation in brain health and disease: implication of cerebral inflammation. Neuropharmacology 79:298–306
Dumont M, Wille E, Calingasan NY, Tampellini D, Williams C, Gouras GK, Liby K, Sporn M, Nathan C, Flint Beal M, Lin MT (2009) Triterpenoid CDDO-methylamide improves memory and decreases amyloid plaques in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 109:502–512
Kim HV, Kim HY, Ehrlich HY, Choi SY, Kim DJ, Kim Y (2013) Amelioration of Alzheimer’s disease by neuroprotective effect of sulforaphane in animal model. Amyloid 20:7–12
Amin FU, Shah SA, Kim MO (2017) Vanillic acid attenuates Abeta1-42-induced oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mice. Sci Rep 7:40753
Hardie DG (2007) AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:774–785
Byun SJ, Son Y, Pae HO (2014) Cytoprotective effect of beta-lapachone by inducing heme oxygenase-1 expression and AMP-activated protein kinase activation in human endothelial cells. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci 18:949–958
Vingtdeux V, Davies P, Dickson DW, Marambaud P (2011) AMPK is abnormally activated in tangle- and pre-tangle-bearing neurons in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Acta Neuropathol 121:337–349
Ma T, Chen Y, Vingtdeux V, Zhao H, Viollet B, Marambaud P, Klann E (2014) Inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase signaling alleviates impairments in hippocampal synaptic plasticity induced by amyloid beta. J Neurosci 34:12230–12238
Greco SJ, Hamzelou A, Johnston JM, Smith MA, Ashford JW, Tezapsidis N (2011) Leptin boosts cellular metabolism by activating AMPK and the sirtuins to reduce tau phosphorylation and beta-amyloid in neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 414:170–174
Chiang MC, Cheng YC, Chen SJ, Yen CH, Huang RN (2016) Metformin activation of AMPK-dependent pathways is neuroprotective in human neural stem cells against Amyloid-beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Exp Cell Res 347:322–331
Inestrosa NC, Varela-Nallar L, Grabowski CP, Colombres M (2007) Synaptotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease: the Wnt signaling pathway as a molecular target. IUBMB Life 59:316–321
Hooper C, Killick R, Lovestone S (2008) The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 104:1433–1439
Xu M, Dong Y, Wan S, Yan T, Cao J, Wu L, Bi K, Jia Y (2016) Schisantherin B ameliorates Abeta1-42-induced cognitive decline via restoration of GLT-1 in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Physiol Behav 167:265–273
Wu L, Feng X, Li T, Sun B, Khan MZ, He L (2017) Risperidone ameliorated Abeta1-42-induced cognitive and hippocampal synaptic impairments in mice. Behav Brain Res 322:145–156
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (zr2014hl034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Li, B., Cheng, G. et al. Amentoflavone Ameliorates Aβ1–42-Induced Memory Deficits and Oxidative Stress in Cellular and Rat Model. Neurochem Res 43, 857–868 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2489-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2489-8