Abstract
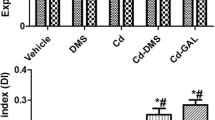
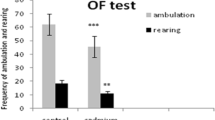
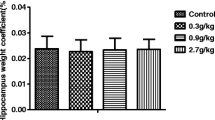
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic metal and classified as a carcinogen whose exposure could affect the function of the central nervous system. There are studies that suggest that Cd promotes neurodegeneration in different regions of the brain, particularly in the hippocampus. It is proposed that its mechanism of toxicity maybe by an oxidative stress pathway, which modifies neuronal morphology and causes the death of neurons and consequently affecting cognitive tasks. However, this mechanism is not yet clear. The aim of the present work was to study the effect of Cd administration on recognition memory for 2, 3 and 4 months, neuronal morphology and immunoreactivity for caspase-3 and 9 in rat hippocampi. The results show that the administration of Cd decreased recognition memory. Likewise, it caused the dendritic morphology of the CA1, CA3 and dentate gyrus regions of the hippocampus to decrease with respect to the time of administration of this heavy metal. In addition, we observed a reduction in the density of dendritic spines as well as an increase in the immunoreactivity of caspase-3 and 9 in the same hippocampal regions of the animals treated with Cd. These results suggest that Cd affects the structure and function of the neurons of the hippocampus, which contribute to the deterioration of recognition memory. Our results suggest that the exposure to Cd represents a critical health problem, which if not addressed quickly, could cause much more serious problems in the quality of life of the human population, as well as in the environment in which they develop.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richter E, Hecht F, Schnellbacher N, Ternes TA, Wick A, Wode F, Coors A (2015) Assessing the ecological long-term impact of wastewater irrigation on soil and water based on bioassays and chemical analyses. Water Res 84:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.07.013
Shi Y, Xie H, Cao L, Zhang R, Xu Z, Wang Z, Deng Z (2017) Effects of Cd- and Pb-resistant endophytic fungi on growth and phytoextraction of Brassica napus in metal-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(1):417–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7693-y
Sharma VK, McDonald TJ, Sohn M, Anquandah GAK, Pettine M, Zboril R (2017) Assessment of toxicity of selenium and cadmium selenium quantum dots. Chemosphere 188:403–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.130
Agency for toxic substances and disease registry-CDC (2012) https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov
Rafati Rahimzadeh M, Rafati Rahimzadeh M, Kazemi S, Moghadamnia AA (2017) Cadmium toxicity and treatment: an update. Casp J Intern Med 8(3):135–145. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.8.3.135
Huang Y, Feng F, Chen ZG, Wu T, Wang ZH (2018) Green and efficient removal of cadmium from rice flour using natural deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem 244:260–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.060
Rinaldi M, Micali A, Marini H, Adamo EB, Puzzolo D, Pisani A, Trichilo V, Altavilla D, Squadrito F, Minutoli L (2017) Cadmium, organ toxicity and therapeutic approaches: a review on brain, kidney and testis damage. Curr Med Chem 24(35):3879–3893. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170801101448
Richter P, Faroon O, Pappas RS (2017) Cadmium and cadmium/zinc ratios and tobacco-related morbidities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(10):E1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101154
Kwong RW, Andrés JA, Niyogi S (2011) Effects of dietary cadmium exposure on tissue-specific cadmium accumulation, iron status and expression of iron-handling and stress-inducible genes in rainbow trout: influence of elevated dietary iron. Aquat Toxicol 102(1–2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.12.010
Wang B, Du Y (2013) Cadmium and its neurotoxic effects. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/898034
Xu MY, Wang P, Sun YJ, Yang L, Wu YJ (2017) Joint toxicity of chlorpyrifos and cadmium on the oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in neuronal cells. Food Chem Toxicol 103:246–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.03.013
Liu LL, Li CM, Zhang ZW, Zhang JL, Yao HD, Xu SW (2014) Protective effects of selenium on cadmium-induced brain damage in chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 158(2):176–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-9919-5
Yang XF, Fan GY, Liu DY, Zhang HT, Xu ZY, Ge YM, Wang ZL (2015) Effect of cadmium exposure on the histopathology of cerebral cortex in juvenile mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 165(2):167–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0246-2
Yan Y, Bian JC, Zhong LX, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Liu ZP (2012) Oxidative stress and apoptotic changes of rat cerebral cortical neurons exposed to cadmium in vitro. Biomed Environ Sci 25(2):172–181
Chow ES, Hui MN, Lin CC, Cheng SH (2008) Cadmium inhibits neurogenesis in zebrafish embryonic brain development. Aquat Toxicol 87(3):157–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.01.019
Kim W, Yim HS, Yoo DY, Jung HY, Kim JW, Choi JH, Yoon YS, Kim DW, Hwang IK (2016) Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract ameliorates cadmium-induced impairment in memory and hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 16(1):452
Peng Q, Bakulski KM, Nan B, Park SK (2017) Cadmium and Alzheimer’s disease mortality in U.S. adults: updated evidence with a urinary biomarker and extended follow-up time. Environ Res 157:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.05.011
Notarachille G, Arnesano F, Calò V, Meleleo D (2014) Heavy metals toxicity: effect of cadmium ions on amyloid beta protein 1–42. Possible implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Biometals 27(2):371–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9719-6
Treviño S, Andrade-García A, Herrera Camacho I, León-Chavez BA, Aguilar-Alonso P, Flores G, Brambila E (2015) Chronic cadmium exposure lead to inhibition of serum and hepatic alkaline phosphatase activity in wistar rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 29(12):587–594. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21732
Vidal B, Vázquez-Roque RA, Gnecco D, Enríquez RG, Floran B, Díaz A, Flores G (2017) Curcuma treatment prevents cognitive deficit and alteration of neuronal morphology in the limbic system of aging rats. Synapse https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.21952
Treviño S, Vázquez-Roque RA, López-López G, Perez-Cruz C, Moran C, Handal-Silva A, González-Vergara E, Flores G, Guevara J, Díaz A (2017) Metabolic syndrome causes recognition impairments and reduced hippocampal neuronal plasticity in rats. J Chem Neuroanat 82:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2017.02.007
Flores G, Barbeau D, Quirion R, Srivastava LK (1996) Decreased binding of dopamine D3 receptors in limbic subregions after neonatal bilateral lesion of rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 16:2020–2026
Gibb R, Kolb B (1998) A method for vibratome sectioning of Golgi–Cox stained whole rat brain. J Neurosci Methods 79:1–4
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain atlas. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego
Kolb B, Forgie M, Gibb R, Gorny G, Rowntree S (1998) Age, experience and the changing brain. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 22:143–159
Sholl A, Uttley AM (1953) Pattern discrimination and the visual cortex. Nature 171:387–388
Diaz A, Treviño S, Vázquez-Roque R, Venegas B, Espinosa B, Flores G, Fernández-G JM, Montaño LF, Guevara J (2017) The aminoestrogen prolame increases recognition memory and hippocampal neuronal spine density in aged mice. Synapse. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.21987
Antunes M, Biala G (2012) The novel object recognition memory: neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn Process 13(2):93–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.21987
Akinyemi AJ, Oboh G, Fadaka AO, Olatunji BP, Akomolafe S (2017) Curcumin administration suppress acetylcholinesterase gene expression in cadmium treated rats. Neurotoxicology 62:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2017.05.004
Shukla A, Shukla GS, Srimal RC (1996) Cadmium-induced alterations in blood-brain barrier permeability and its possible correlation with decreased microvessel antioxidant potential in rat. Hum Exp Toxicol 15(5):400–405
Favorito R, Monaco A, Grimaldi MC, Ferrandino I (2017) Effects of cadmium on the glial architecture in lizard brain. Eur J Histochem 61(1):2734. https://doi.org/10.4081/ejh.2017.2734
Larner SF, Wang J, Goodman J, Altman MBO, Xin M, Wang KKW (2017) In vitro neurotoxicity resulting from exposure of cultured neural cells to several types of nanoparticles. J Cell Death 10:11796707–17694523. https://doi.org/10.1177/1179670717694523
Batool Z, Agha F, Ahmad S, Liaquat L, Tabassum S, Khaliq S, Anis L, Sajid I, Emad S, Perveen T, Haider S (2017) Attenuation of cadmium-induced decline in spatial, habituation and recognition memory by long-term administration of almond and walnut supplementation: role of cholinergic function. Pak J Pharm Sci 30(1 uppl):273–279
Wu Z, Yin X, Bañuelos GS, Lin ZQ, Liu Y, Li M, Yuan L (2016) Indications of selenium protection against cadmium and lead toxicity in oilseed rape. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01875
Lukawski K, Nieradko B, Sieklucka-Dziuba M (2005) Effects of cadmium on memory processes in mice exposed to transient cerebral oligemia, 27(4):575–584
Culbreth ME, Harrill JA, Freudenrich TM, Mundy WR, Shafer TJ (2012) Comparison of chemical-induced changes in proliferation and apoptosis in human and mouse neuroprogenitor cells. Neurotoxicology 33(6):1499–1510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2012.05.012
Vahter M, Akesson A, Lidén C, Ceccatelli S, Berglund M (2007) Gender differences in the disposition and toxicity of metals. Environ Res 104(1):85–95
Mahdavi S, Khodarahmi P, Roodbari NH (2017) Effects of cadmium on Bcl-2/Bax expression ratio in rat cortex brain and hippocampus. Hum Exp Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327117703687
Fern R, Black JA, Ransom BR, Waxman SG (1996) Cd(2+)-induced injury in CNS white matter. J Neurophysiol 76(5):3264–3273
Rai NK, Ashok A, Rai A, Tripathi S, Nagar GK, Mitra K, Bandyopadhyay S (2013) Exposure to As, Cd and Pb-mixture impairs myelin and axon development in rat brain, optic nerve and retina. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 273(2):242–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.05.003
Ben P, Zhang Z, Zhu Y, Xiong A, Gao Y, Mu J, Yin Z, Luo L (2016) l-Theanine attenuates cadmium-induced neurotoxicity through the inhibition of oxidative damage and tau hyperphosphorylation. Neurotoxicology 57:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2016.09.010
Amara S, Douki T, Garrel C, Favier A, Ben Rhouma K, Sakly M, Abdelmelek H (2011) Effects of static magnetic field and cadmium on oxidative stress and DNA damage in rat cortex brain and hippocampus. Toxicol Ind Health 27(2):99–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233710381887
Pak EJ, Son GD, Yoo BS (2014) Cadmium inhibits neurite outgrowth in differentiating human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Int J Toxicol 33(5):412–418. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091581814550338
Abdalla FH, Schmatz R, Cardoso AM, Carvalho FB, Baldissarelli J, de Oliveira JS, Rosa MM, Gonçalves Nunes MA, Rubin MA, da Cruz IB, Barbisan F, Dressler VL, Pereira LB, Schetinger MR, Morsch VM, Gonçalves JF, Mazzanti CM (2014) Quercetin protects the impairment of memory and anxiogenic-like behavior in rats exposed to Cd: possible involvement of the acetylcholinesterase and Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activities. Physiol Behav 135:152–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.06.008
Kotelnikova SV, Sokolova NG, Kotelnikov AV (2008) Lipid peroxidation in various organs and tissues of albino rats with cadmium in toxication in winter and summer. Bull Exp Biol Med 146(3):291–302
Del Pino J, Zeballos G, Anadon MJ, Capo MA, Díaz MJ, García J, Frejo MT (2014) Higher sensitivity to cadmium induced cell death of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: a cholinesterase dependent mechanism. Toxicology 325:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2014.09.004
Del Pino J, Zeballos G, Anadón MJ, Moyano P, Díaz MJ, García JM, Frejo MT (2016) Cadmium-induced cell death of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons mediated by muscarinic M1 receptor blockade, increase in GSK-3β enzyme, β-amyloid and tau protein levels. Arch Toxicol 90(5):1081–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1540-7
Karri V, Schuhmacher M, Kumar V (2016) Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, As and MeHg) as risk factors for cognitive dysfunction: a general review of metal mixture mechanism in brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 48:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.09.016
Luo T, Yuan Y, Yu Q, Liu G, Long M, Zhang K, Bian J, Gu J, Zou H, Wang Y, Zhu J, Liu X, Liu Z (2017) PARP-1 overexpression contributes to cadmium-induced death in rat proximal tubular cells via parthanatos and the MAPK signalling pathway. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04555-2
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Dr. Francisco Ramos Collazo for his help with the animal care. ST, JG, EB, AM-R, AHS, GF, AD acknowledge the “Sistema Nacional de Investigadores” of Mexico for membership. Thanks to Professor Thomas Edwards PhD., for editing the English language text.
Funding
Funding for this study was provided by grants from VIEP-BUAP Grant (No. DIFA-NAT17-I) to AD, (No. TEMS-NAT17-I) to ST and PAPIIT-UNAM (IN214117) to JG. None of the funding institutions had any further role in the study design, the collection of data, analyses, and interpretation of data, writing of the report or in the decision to submit the paper for publication and interpretation of data, writing of the report or the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AD and ST designed the study and wrote the protocol. GP, UPR, RV-R, and AM-R performed the experiments. AD, ST, GF, EB, JG managed the literature searches and analysis, AHS undertook the statistical analysis. AD and ST wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All contributing authors have approved the final manuscript. JLMP participated in the managed the literature searches and analysis and undertook the statistical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pulido, G., Treviño, S., Brambila, E. et al. The Administration of Cadmium for 2, 3 and 4 Months Causes a Loss of Recognition Memory, Promotes Neuronal Hypotrophy and Apoptosis in the Hippocampus of Rats. Neurochem Res 44, 485–497 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-02703-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-02703-2