Abstract
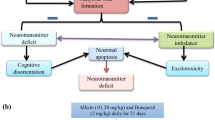
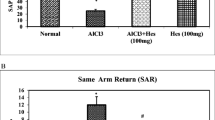
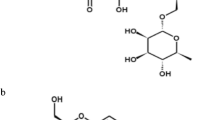
The present study was aimed to evaluate the protective effect of hesperidin (Hes) on aluminium chloride (AlCl3) induced neurobehavioral and pathological changes in Alzheimeric rats. Intraperitonial injection of AlCl3 (100 mg/kg body weight) for 60 days significantly elevated the levels of aluminium (Al), activity of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and protein expressions of amyloid precursor protein (APP), β amyloid (Aβ1–42), β and γ secretases as compared to control group in hippocampus and cortex of rat brain. Hes administration orally along with AlCl3 injection for 60 days, significantly revert the Al concentration, AChE activity and Aβ synthesis-related molecules in the studied brain regions. Our results showed that aluminum exposure was significantly reduced the spontaneous locomotor and exploratory activities in open field test and enhanced the learning and memory impairments in morris water maze test. The behavioral impairments caused by aluminum were significantly attenuated by Hes. The histopathological studies in the hippocampus and cortex of rat brain also supported that Hes (100 mg/kg) markedly reduced the toxicity of AlCl3 and preserved the normal histoarchitecture pattern of the hippocampus and cortex. From these results, it is concluded that hesperidin can reverse memory loss caused by aluminum intoxication through attenuating AChE activity and amyloidogenic pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 May 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03616-x
References
Cam JA, Bu GJ (2006) Modulation of beta-amyloid precursor protein trafficking and processing by the low density lipoprotein receptor family. Mol Neurodegener 8:1–13
Ribes D, Colomina MT, Vicens P, Domingo JL (2008) Effects of oral aluminum exposure on behavior and neurogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 214:293–300
Akila R, Stollery BT, Riihimaki V (1999) Decrements in cognitive performance in metal inert gas welders exposed to aluminium. Occup Environ Med 56:632–639
Drago D, Folin M, Baiguera S, Tognon G, Ricchelli F, Zatta P (2007) Comparative effects of Abeta(1–42)-Al complex from rat and human amyloid on rat endothelial cell cultures. J Alzheimers Dis 11:33–44
Zaky A, Mohammad B, Moftah M, Kandeel KM, Bassiouny AR (2013) Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is a key modulator of aluminum-induced neuroinflammation. BMC Neurosci 14:26
Gulya K, Rakonczay Z, Kasa P (1990) Cholinotoxic effects of aluminium in rat brain. J Neurochem 54:1020–1026
Rakonczay Z, Horváth Z, Juhász A, Kálmán J (2005) Peripheral cholinergic disturbances in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Biol Interact 157–158:233–238
Standridge JB (2004) Pharmacotherapeutic approaches to the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 2:119–132
Espín JC, García-Conesa MT, Tomás-Barberán FA (2007) Nutraceuticals: facts and fiction. Phytochemistry 68:2986–3008
Spencer JP (2007) The interactions of flavonoids within neuronal signalling pathways. Genes Nutr 2:257–273
Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B, Denisova NA, Bielinski D, Martin A, McEwen JJ, Bickford PC (1999) Reversals of age-related declines in neuronal signal transduction, cognitive, and motor behavioral deficits with blueberry, spinach, or strawberry dietary supplementation. J Neurosci 19:8114–8121
Gaur V, Aggarwal A, Kumar A (2011) Possible nitric oxide mechanism in the protective effect of hesperidin against ischemic reperfusion cerebral injury in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 49:609–618
Salem HRA, El-Raouf AA, Saleh EM, Shalaby KAF (2012) Influence of hesperidin combined with Sinemet on genetical and biochemical abnormalities in rats suffering from Parkinson’s disease. Life Sci J 9:930–945
Dimpfel W (2006) Different anticonvulsive effects of hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin on electrical activity in the rat hippocampus in-vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol 58:375–379
Kumar P, Kumar A (2010) Protective effect of hesperidin and naringin against 3-nitropropionic acid induced Huntington’s like symptoms in rats: possible role of nitric oxide. Behav Brain Res 206:38–46
Raza SS, Khan MM, Ahmad A, Ashafaq M, Khuwaja G, Tabassum R, Javed H, Siddiqui MS, Safhi MM, Islam F (2011) Hesperidin ameliorates functional and histological outcome and reduces neuroinflammation in experimental stroke. Brain Res 1420:93–105
Ikemura M, Sasaki Y, Giddings JC, Yamamoto J (2012) Preventive effects of hesperidin, glucosyl hesperidin and naringin on hypertension and cerebral thrombosis in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Phytother Res 26:1272–1277
Viswanatha GL, Shylaja H, Sandeep Rao KS, Santhosh Kumar VR, Jagadeesh M (2012) Hesperidin ameliorates immobilization-stress-induced behavioral and biochemical alterations and mitochondrial dysfunction in mice by modulating nitrergic pathway. ISRN Pharmacol 479–570
Abdel-Aal RA, Assi AA, Kostandy BB (2011) Rivastigmine reverses aluminum-induced behavioral changes in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 659:169–176
Fernagut PO, Diguet E, Stefanova N, Biran M, Wenning GK, Canioni P, Bioulac B, Tison F (2002) Subacute systemic 3-nitropropionic acid intoxication induces a distinct motor disorder in adult C57Bl/6 mice: behavioural and histopathological characterisation. Neuroscience 114:1005–1017
Sethi P, Jyoti A, Singh R, Hussain E, Sharma D (2008) Aluminium-induced electrophysiological, biochemical and cognitive modifications in the hippocampus of aging rats. Neurotoxicology 29:1069–1079
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water maze procedure for studing spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
RajaSankar S, Manivasagam T, Surendran S (2009) Ashwagandha leaf extract: a potential agent in treating oxidative damage and physiological abnormalities seen in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 454:11–15
Erazi H, Sansar W, Ahboucha S, Gamrani H (2010) Aluminum affects glial system and behavior of rats. C R Biol 333:23–27
Hartmann M, Heumann R, Lessmann V (2001) Synaptic secretion of BDNF after high-frequency stimulation of glutamatergic synapses. EMBO J 20:5887–5897
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Annida B, Menon VP (2007) Protective effect of hesperidin on nicotine induced toxicity in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 45:194–202
Sakamoto T, Ogasawara Y, Ishii K, Takahashi H, Tanabe S (2004) Accumulation of aluminum in ferritin isolated from rat brain. Neurosci Lett 366:264–267
Abubakar MG, Taylor A, Ferns GAA (2004) Regional accumulation of aluminium in the rat brain is affected by dietary vitamin E. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18:53–59
Roskams AJ, Connor JR (1990) Aluminum access to the brain: a role for transferrin and its receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9024–9027
Kaur A, Gill KD (2006) Possible peripheral markers for chronic aluminium toxicity in Wistar rats. Toxicol Ind Health 22:39–46
Crapper DR, Krishnan SS, Dalton AJ (1973) Brain aluminum distribution in Alzheimer’s disease and experimental neurofibrillary degeneration. Science 180:511–513
Pavun LA, Dimitricmarkovic JM, Durdevic PT, Jelikic-Stankov MD, Dikanovic DB, Ciric AR, Malesev DL (2012) Development and validation of a fluorometric method for the determination of hesperidin in human plasma and pharmaceutical forms. J Serb Chem Soc 77:1625–1640
Shagirtha K, Pari L (2011) Hesperetin, a citrus flavonone, protects potentially cadmium induced oxidative testicular dysfunction in rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:2105–2111
Kuntic V, Filipovic I, Vujic Z (2011) Effects of rutin and hesperidin and their Al(III) and Cu(II) complexes on in vitro plasma coagulation assays. Molecules 16:1378–1388
Amberla K, Nordberg A, Viitanen M, Winblad B (2009) Long-term treatment with tacrine (THA) in Alzheimers disease evaluation of neuropsychological data. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 149:55–57
Zheng H, Youdim MB, Fridkin M (2009) Site-activated multifunctional chelator with acetylcholinesterase and neuroprotective-neurorestorative moieties for Alzheimer’s therapy. J Med Chem 52:4095–4098
Zatta P, Zambenedetti P, Bruna V, Filippi B (1994) Activation of acetylcholinesterase by aluminium(III): the relevance of the metal species. NeuroReport 5:1777–1780
Kakkar V, Kaur IP (2011) Evaluating potential of curcumin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in aluminium induced behavioural, biochemical and histopathological alterations in mice brain. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2906–2913
Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H (2006) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 368:387–403
Wilkinson DG, Francis PT, Schwam E, Payne-Parrish J (2004) Cholinesterase inhibitors used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: the relationship between pharmacological effects and clinical efficacy. Drugs Aging 21:453–478
Javed H, Vaibhav K, Ahmed ME, Khan A, Tabassum R, Islam F, Safhi MM, Islam F (2014) Effect of hesperidin on neurobehavioral, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and lipid alteration in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced cognitive impairment in mice. J Neurol Sci (in press)
Young-Pearse TL, Chen AC, Chang R, Marquez C, Selkoe DJ (2008) Secreted APP regulates the function of full-length APP in neurite outgrowth through interaction with integrin beta1. Neural Dev 3:15
Tamagno E, Guglielmotto M, Aragno M, Borghi R, Autelli R, Giliberto L, Muraca G, Danni O, Zhu XW, Smith MA, Perry G, Jo DG, Mattson MP, Tabaton M (2008) Oxidative stress activates a positive feedback between the γ- and β-secretase cleavages of the β-amyloid precursor protein. J Neurochem 104:683–695
Lin R, Chen X, Li W (2008) Exposure to metal ions regulates mRNA levels of APP and BACE1 in PC12 cells: blockage by curcumin. Neurosci Lett 440:344–347
Luo HB, Yang JS, Shi XQ (2009) Tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside reduces the cognitive impairment and overexpression of amyloid precursor protein induced by aluminum exposure. Neurosci Bull. 25:391–396
Lukiw WJ, Percy ME, Kruck TP (2005) Nanomolar aluminum induces pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic gene expression in human brain cells in primary culture. J Inorg Biochem 99:1895–1898
Alexandrov PN, Zhao Y, Pogue AI, Tarr MA, Kruck TP, Percy ME, Cui JG, Lukiw WJ (2005) Synergistic effects of iron and aluminum on stress-related gene expression in primary human neural cells. J Alzheimer’s Dis 8:117–127
Ghorbani A, Nazari M, Jeddi-Tehrani M, Zand H (2012) The citrus flavonoid hesperidin induces p53 and inhibits NF-κB activation in order to trigger apoptosis in NALM-6 cells: involvement of PPARγ-dependent mechanism. Eur J Nutr 51:39–46
Nazari M, Ghorbani A, Hekmat-Doost A, Jeddi-Tehrani M, Zand H (2011) Inactivation of nuclear factor-κB by citrus flavanone hesperidin contributes to apoptosis and chemo-sensitizing effect in Ramos cells. Eur J Pharmacol 650:526–533
Kim JY, Jung KJ, Choi JS, Chung HY (2006) Modulation of the age-related nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway by hesperetin. Aging Cell 5:401–411
Cochran M, Elliott DC, Brennan P, Chawtur V (1990) Inhibition of protein kinase C activation by low concentrations of aluminium. Clin Chim Acta 194:167–172
Caporaso GL, Gandy SE, Buxbaum JD, Ramabhadran TV, Greengard P (1992) Protein phosphorylation regulates secretion of Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:3055–3059
Kawahara M, Kato M, Kuroda Y (2001) Effects of aluminum on the neurotoxicity of primary cultured neurons and on the aggregation of beta-amyloid protein. Brain Res Bull 55:211–217
Li C, Zug C, Qu H, Schluesener H, Zhang Z (2016) Hesperidin ameliorates behavioral impairments and neuropathology of transgenic APP/PS1 mice. Behav Brain Res 281:32–42
Bastianetto S, Brouillette J, Quirion R (2007) Neuroprotective effects of natural products: interaction with intracellular kinases, amyloid peptides and a possible role for transthyretin. Neurochem Res 32:1720–1725
Levites Y, Amit T, Youdim MB, Mandel S (2002) Involvement of protein kinase C activation and cell survival/cell cycle genes in green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate neuronprotective action. J Biol Chem 277:30574–30580
Acknowledgments
Financial assistance in the form of a major research project from the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
Hereby, the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest that might have influenced the views expressed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thenmozhi, A.J., Raja, T.R.W., Janakiraman, U. et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Hesperidin on Aluminium Chloride Induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Wistar Rats. Neurochem Res 40, 767–776 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1525-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1525-1