Abstract
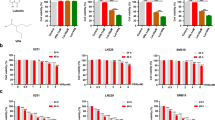
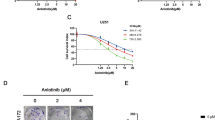
Glioblastoma shows poor response to current therapies and warrants new therapeutic strategies. We examined the efficacy of combination of valproic acid (VPA) and taxol (TX) or nanotaxol (NTX) in human glioblastoma LN18 and T98G cell lines. Cell differentiation was manifested in changes in morphological features and biochemical markers. Cell growth was controlled with down regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), phospho-Akt (p-Akt), and multi-drug resistance (MDR) marker, indicating suppression of angiogenic, survival, and multi-drug resistance pathways. Cell cycle analysis showed that combination therapy (VPA and TX or NTX) increased the apoptotic sub G1 population and apoptosis was further confirmed by Annexin V-FITC/PI binding assay and scanning electron microscopy. Combination therapy caused activation of caspase-8 and cleavage of Bid to tBid and increased Bax:Bcl-2 ratio and mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF). Upregulation of calpain and caspases (caspase-9 and caspase-3) and substrate degradation were also detected in course of apoptosis. The combination of VPA and NTX most effectively controlled the growth of LN18 and T98G cells. Therefore, this combination of drugs can be used as an effective treatment for controlling growth of human glioblastoma cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Narayana A, Leibel SA (2004) Primary and metastatic brain tumors in adults. In: Leibel SA, Phillips TL (eds) Textbook of radiation oncology. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 463–495
Bähr O, Rieger J, Duffner F, Meyermann R, Weller M, Wick W (2003) P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein mediate specific patterns of multidrug resistance in malignant glioma cell lines, but not in primary glioma cells. Brain Pathol 13:482–494
Tang R, Faussat AM, Majdak P, Perrot JY, Chaoui D, Legrand O, Marie JP (2004) Valproic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells expressing P-gp and MRP1. Leukemia 18:1246–1255
Rowinsky EK, Wright M, Monsarrat B, Lesser GJ, Donehower RC (1993) Taxol: pharmacology, metabolism and clinical implications. Cancer Surv 17:283–304
Karmakar S, Banik NL, Patel SJ, Ray SK (2007) Combination of all-trans retinoic acid and taxol regressed glioblastoma T98G xenografts in nude mice. Apoptosis 12:2077–2087
Karmakar S, Banik NL, Ray SK (2008) Combination of all-trans retinoic acid and taxol-induced differentiation and apoptosis in human glioblastoma U87MG xenografts in nude mice. Cancer 112:596–607
Prados MD, Schold SC, Spence AM, Berger MS, McAllister LD, Mehta MP, Gilbert MR, Fulton D, Kuhn J, Lamborn K, Rector DJ, Chang SM (1996) Phase II study of paclitaxel in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 14:2316–2321
Weiss RB, Donehower RC, Wiernik PH, Ohnuma T, Gralla RJ, Trump DL et al (1990) Hypersensitivity reactions from taxol. J Clin Oncol 8:1263–1268
Gallo JM, Li S, Guo P, Reed K, Ma J (2003) The effect of P-glycoprotein on Taxol brain and brain tumor distribution in mice. Cancer Res 63:5114–5117
Fellner S, Bauer B, Miller DS, Schaffri M, Fankhänel M, Spruss T et al (2002) Transport of paclitaxel (Taxol) across the blood-brain barrier in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest 110:1309–1318
Joo KM, Park K, Kong DS, Song SY, Kim MH, Lee GS et al (2008) Oral taxol chemotherapy for brain tumors: ideal combination treatment of taxol and P-glycoprotein inhibitor. Oncol Rep 19:17–23
Koziara JM, Whisman TR, Tseng MT, Mumper RJ (2006) In vivo efficacy of novel taxol nanoparticles in taxol-resistant human colorectal tumors. J Cont Rel 112:312–319
Desai N, Trieu V, Yao Z, Louie L, Ci S, Yang A et al (2006) Increased antitumor activity, intratumor taxol concentrations, and endothelial cell transport of cremophor-free, albumin-bound taxol, ABI-007, compared with cremophor-based taxol. Clin Cancer Res 12:1317–1324
Green MR, Manikhas GM, Orlov S, Afanasyev B, Makhson AM, Bhar P, Hawkins MJ (2006) Abraxane, a novel Cremophor-free, albumin-bound particle form of taxol for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 17:1263–1268
Gradishar WJ, Tjulandin S, Davidson N, Shaw H, Desai N, Bhar P, Hawkins M, O’Shaughnessy J (2005) Phase III trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound taxol compared with polyethylated castor oil-based taxol in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:7794–7803
Abe T, Hasegawa S, Taniguchi K, Yokomizo A, Kuwano T, Ono M et al (1994) Possible involvement of multidrug-resistance-associated protein (MRP) gene expression in spontaneous drug resistance to vincristine, etoposide and adriamycin in human glioma cells. Int J Cancer 58:860–864
Rieger L, Rieger J, Winter S, Streffer J, Esser P, Dichgans J, Meyermann R, Weller M (2000) Evidence for a constitutive, verapamil-sensitive, non-P-glycoprotein multidrug resistance phenotype in malignant glioma that is unaltered by radiochemotherapy in vivo. Acta Neuropathol 99:555–562
Karmakar S, Weinberg MS, Banik NL, Patel SJ, Ray SK (2006) Activation of multiple molecular mechanisms for apoptosis in human malignant glioblastoma T98G and U87MG cells treated with sulforaphane. Neuroscience 141:1265–1280
Dhandapani KM, Mahesh VB, Brann DW (2007) Curcumin suppresses growth and chemoresistance of human glioblastoma cells via AP-1 and NF-κB transcription factors. J Neurochem 102:522–538
Karmakar S, Davis KA, Choudhury SR, Deeconda A, Banik NL, Ray SK (2009) Bcl-2 inhibitor and apigenin worked synergistically in human malignant neuroblastoma cell lines and increased apoptosis with activation of extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:705–710
Roy Choudhury S, Karmakar S, Banik NL, Ray SK (2010) Synergistic efficacy of sorafenib and genistein in growth inhibition by down regulating angiogenic and survival factors and increasing apoptosis through upregulation of p53 and p21 in malignant neuroblastoma cells having N-Myc amplification or non-amplification. Invest New Drugs 28:812–824
Karmakar S, Choudhury SR, Banik NL, Ray SK (2010) Activation of multiple molecular mechanisms for increasing apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G xenograft. J Cancer Sci Ther 2:107–113
Knizetova P, Ehrmann J, Hlobilkova A, Vancova I, Kalita O, Kolar Z, Bartek J (2008) Autocrine regulation of glioblastoma cell cycle progression, viability and radioresistance through the VEGF-VEGFR2 (KDR) interplay. Cell Cycle 7:2553–2561
Aldape KD, Ballman K, Furth A, Buckner JC, Giannini C, Burger PC et al (2004) Immunohistochemical detection of EGFRvIII in high malignancy grade astrocytomas and evaluation of prognostic significance. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:700–707
Sakahira H, Enari M, Nagata S (1998) Cleavage of CAD inhibitor in CAD activation and DNA degradation during apoptosis. Nature 391:96–99
Das CM, Aguilera D, Vasquez H, Prasad P, Zhang M, Wolff JE, Gopalakrishnan V (2007) Valproic acid induces p21 and topoisomerase-II (α/β) expression and synergistically enhances etoposide cytotoxicity in human glioblastoma cell lines. J Neurooncol 85:159–170
Selesniemi K, Reedy M, Gultice A, Guilbert LJ, Brown TLb (2005) Transforming growth factor-β induces differentiation of the labyrinthine trophoblast stem cell line SM10. Stem Cells Dev 14:697–711
Jones J, Bentas W, Blaheta RA, Makarevic J, Hudak L, Wedel S et al (2008) Modulation of adhesion and growth of colon and pancreatic cancer cells by the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid. Int J Mol Med 22:293–299
Zhang R, Banik NL, Ray SK (2008) Differential sensitivity of human glioblastoma LN18 (PTEN-positive) and A172 (PTEN-negative) cells to Taxol for apoptosis. Brain Res 1239:216–225
George J, Banik NL, Ray SK (2009) Bcl-2 siRNA augments taxol mediated apoptotic death in human glioblastoma U138MG and U251MG cells. Neurochem Res 34:66–78
Son MJ, Song HS, Kim MH, Kim JT, Kang CM, Jeon JW et al (2006) Synergistic effect and condition of pegylated interferon alpha with paclitaxel on glioblastoma. Int J Oncol 28:1385–1392
Pipas JM, Meyer LP, Rhodes CH, Cromwell LD, McDonnell CE, Kingman LS et al (2005) A Phase II trial of paclitaxel and topotecan with filgrastim in patients with recurrent or refractory glioblastoma multiforme or anaplastic astrocytoma. J Neurooncol 71:301–305
Pelloski CE, Lin E, Zhang L, Yung WK, Colman H, Liu JL et al (2006) Prognostic associations of activated mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt pathways in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 12:3935–3941
Beg AA, Baltimore D (1996) An essential role for NFκB in preventing TNF-α induced cell death. Science 274:782–784
Kemper EM, Boogerd W, Thuis I, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O (2004) Modulation of the blood-brain barrier in oncology: therapeutic opportunities for the treatment of brain tumours? Cancer Treat Rev 30:415–423
Roth W, Wagenknecht B, Grimmel C, Dichgans J, Weller M (1998) Taxol-mediated augmentation of CD95 ligand-induced apoptosis of human malignant glioma cells: association with bcl-2 phosphorylation but neither activation of p53 nor G2/M cell cycle arrest. Br J Cancer 77:404–411
Desai A, Vyas T, Amiji M (2008) Cytotoxicity and apoptosis enhancement in brain tumor cells upon coadministration of taxol and ceramide in nanoemulsion formulations. J Pharm Sci 97:2745–2756
Bokelmann I, Mahlknecht U (2008) Valproic acid sensitizes chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to apoptosis and restores the balance between pro- and antiapoptotic proteins. Mol Med 14:20–27
Häcker S, Dittrich A, Mohr A, Schweitzer T, Rutkowski S, Krauss J et al (2009) Histone deacetylase inhibitors cooperate with IFN-gamma to restore caspase-8 expression and overcome TRAIL resistance in cancers with silencing of caspase-8. Oncogene 28:3097–3110
Mielgo A, Torres VA, Clair K, Barbero S, Stupack DG (2009) Paclitaxel promotes a caspase 8-mediated apoptosis through death effector domain association with microtubules. Oncogene 28:3551–3562
Park SJ, Wu CH, Gordon JD, Zhong X, Emami A, Safa AR (2004) Taxol induces caspase-10-dependent apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:51057–51067
Haldar S, Jena N, Croce CM (1995) Inactivation of Bcl-2 by phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4507–4511
Kim R (2005) Recent advances in understanding the cell death pathways activated by anticancer therapy. Cancer 103:1551–1560
Cregan SP, Dawson VL, Slack RS (2004) Role of AIF in caspase dependent and caspase-independent cell death. Oncogene 23:2785–2796
Polster BM, Basañez G, Etxebarria A, Hardwick JM, Nicholls DG (2005) Calpain I induces cleavage and release of apoptosis-inducing factor from isolated mitochondria. J Biol Chem 280:6447–6454
Catalano MG, Poli R, Pugliese M, Fortunati N, Boccuzzi G (2007) Valproic acid enhances tubulin acetylation and apoptotic activity of taxol on anaplastic thyroid cancer cell lines. Endocr Relat Cancer 14:839–845
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported in part by the NS-57811 and NS-62327 grants from the National Institutes of Health and the SCIRF-11-002 grant from the State of South Carolina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy Choudhury, S., Karmakar, S., Banik, N.L. et al. Valproic Acid Induced Differentiation and Potentiated Efficacy of Taxol and Nanotaxol for Controlling Growth of Human Glioblastoma LN18 and T98G Cells. Neurochem Res 36, 2292–2305 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0554-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0554-7