Abstract
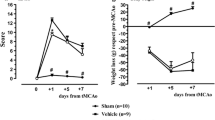
This study examined the neuroprotective ability of tetrapeptide l-Asp-Ala-His-Lys (DAHK) in permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. One DAHK dose (16 mg/kg) or saline solution were i.v. administered 30 min after occlusion and neurological deficit was evaluated at 2, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h using Longa scoring scale. The striatum infarction area was evaluated until 96 h after occlusion in both groups after staining with hematoxylin–eosin. DAHK-treated group showed a significant (P < 0.05) protection of 70% of neurological deficit at 96 h after occlusion, in comparison with the control-group that showed permanent neurological deficit. The DAHK-treated group showed a significant (P < 0.05) reduction of 52% infarction area in the striatum, as compared to control values. Results presented here support the possible therapeutic application of DAHK as a neuroprotective agent in human patients with stroke, as the peptide is part of human serum albumin, already being tested in clinical trials.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dodel RC, Haacke C, Zamzow K, Paweilik S, Spottke A, Rethfeldt M, Siebert U, Oertel WH, Schoffsky O, Back T (2004) Resource utilization and cost of stroke unit care in Germany. Value Health 7:144–152
American Heart Association (2005) Heart disease and stroke statistics. American Heart Association, Dallas
Spieler JF, Lanoe JL, Amarenco P (2004) Costs of stroke care according to handicap levels and stroke subtypes. Cerebrovasc Dis 17:134–142
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz M (1999) Pathobiology of ischemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22:391–397
Ginsberg MD (2003) Adventures in the pathophysiology of brain ischemic: penumbra, gene expression, neuroprotection: the 2002 Thomas Willis Lecture. Stroke 34:214–223
Hacke W, Ringleb P, Stingele R (1999) How did the results of ECASS II influence clinical practice of treatment of acute stroke. Rev Neurol 29:638–641
Alonso de Leciñana M, Diez-Tejedor E, Gutierrez M, Guerrero S, Carceller F, Roda JM (2005) New goals in ischemic stroke therapy: the experimental approach-harmonizing science with practice. Cerebrovasc Dis 20:59–168
Ginsberg MD (2008) Neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: past, present and future. Neuropharmacology 55:363–389
Belayev L, Liu Y, Zhao W, Busto R, Ginsberg MD (2001) Human albumin therapy of acute ischemic stroke: marked neuroprotective efficacy at moderate doses and with a broad therapeutic window. Stroke 32:553–560
Gum ET, Swanson RA, Alano C, Liu J, Hong S, Weinstein PR, Panter SS (2004) Human serum albumin and its N-terminal tetrapeptide (DAHK) block oxidant-induced neuronal death. Stroke 35:590–595
Merrifield B (1986) Solid phase synthesis. Science 232:341–347
Valdez-Cruz NA, Batista CV, Possani LD (1004) Phaiodactylipin, a glycosylated heterodimeric phospholipase A from the venom of the scorpion Anuroctonus phaiodactylus. Eur J Biochem 271:1453–1464
Batista CV, Del Pozo L, Zamudio FZ, Contreras S, Becerril B, Wanke E, Possani LD (2004) Proteomics of the venom from the Amazonian scorpion Tityus cambridgei and the role of prolines on mass spectrometry analysis of toxins. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 803:55–66
Possani LD, Martin BM, Svendsen I, Rode G, Erickson BW (1985) Scorpion toxins from Centruroides noxius and Tityus serrulatus: primary structures and sequence comparison by metric analysis. Biochem J 229:739–750
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Belayev L, Pinard E, Nallet H, Seylaz J, Liu Y, Riyamongkol P, Zhao W, Busto R, Ginsberg MD (2002) Albumin therapy of transient focal cerebral ischemia: in vivo analysis of dynamic microvascular responses. Stroke 33:1077–1084
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego, p 340
Niyaz M, Numakawa T, Matsuki Y, Kumamaru E, Adachi N, Kitazawa H, Kunugi H, Kudo M (2007) MCI-186 prevents brain tissue from neuronal damage in cerebral infarction through the activation of intracellular signaling. J Neurosci Res 85:2933–2942
Matsui T, Sinyama H, Asano T (1993) Beneficial effect of prolonged administration of albumin on ischemic cerebral edema and infarction after occlusion of middle cerebral artery in rats. Neurosurgery 33:293–300
Belayev L, Zhao W, Pattany PM, Weaver RG, Huh PW, Lin B, Busto R, Ginsberg MD (1998) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging confirms marked neuroprotective efficacy of albumin therapy in focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 29:2587–2599
Bar-Or D, Rael LT, Lau EP, Rao NKR, Thomas GW, Winkler JV, Yukl RL, Kingston RG, Curtis CG (2001) An analog of the human serum albumin N-terminus (Asp-Ala-His-Lys) prevents formation of copper-induced reactive oxygen species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:856–862
Bar-Or D, McDonald MC, Thiemermann C (2006) Reduction of infarct size in a rat model of regional myocardial ischemia and reperfusion by the synthetic peptide DAHK. Crit Care Med 34:1955–1959
Predki PF, Harford C, Brar P, Sarkar B (1992) Further characterization of the N-terminus copper(II)- and nickel(II)- binding motif of proteins. Studies of metal binding to chicken serum albumin and the native sequence peptide. Biochem J 287:211–215
Reinhart WH, Nagy C (1995) Albumin affects erythrocyte aggregation and sedimentation. Eur J Clin Invest 25:523–527
Acknowledgements
We want to thank the Fundación Miguel Alemán A.C. for the support of this study, and the support through a PROMEP/SEP fellowship granted to J. Carbajal-Sotelo. The authors acknowledged the support received from the laboratory of Dr. Lourival Possani from the Biotechnology Institute of UNAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz-Ruíz, A., Ríos, C., Carvajal-Sotelo, J. et al. Neuroprotective Effect of DAHK Peptide in an Occlusive Model of Permanent Focal Ischemia in Rats. Neurochem Res 35, 343–347 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-0060-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-0060-3