Abstract
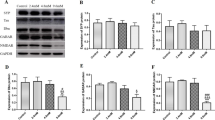
To investigate the mechanism of carbon disulfide-induced neuropathy, male wistar rats were administrated by gavage at dosage of 300 or 500 mg/kg carbon disulfide, five times per week for 12 weeks. By the end of the exposure, the animals produced a slight or moderate level of neurological deficits, respectively. Cerebrums of carbon disulfide-intoxicated rats and their age-matched controls were Triton-extracted and centrifuged at a high speed (100,000 × g) to yield a pellet fraction of NF polymer and a corresponding supernatant fraction, which presumably contained mobile monomer. Then, the contents of six cytoskeletal protein (NF-L, NF-M, NF-H, α-tubulin, β-tubulin, and β-actin) in both fractions were determined by immunoblotting. Results showed that the contents of the three neurofilament subunits in the pellet and the supernatant fraction decreased significantly regardless of dose levels (P < 0.01). As for microtubule proteins, in the pellet fraction of cerebrum, the levels of α-tubulin and β-tubulin demonstrated some inconsistent changes. However, in the supernatant fractions, the content of α-tubulin and β-tubulin increased significantly in both two dose groups (P < 0.01). In comparison to neurofilament and tubulin proteins, the content of β-actin changed less markedly, only the supernatant fraction of the high dose group displayed significant increase (P < 0.01), but the others remained unaffected. These findings suggested that the changes of cytoskeleton protein contents in rat cerebrum were associated with the intoxication of carbon disulfide, which might be involved in the development of carbon disulfide neurotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. O. Beauchamp J. S. Bus J. A. Popp C. J. Boreiko L. Goldberg (1983) ArticleTitleCritical review of the literature on carbon disulfide toxicity Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 11 IssueID3 169–278 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXltVSgtro%3D Occurrence Handle6349939
J. Stetkiewicz T. Wronska-Nofer (1998) ArticleTitleUpdating of hygiene standards for carbon disulfide based on health risk assessment Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Hlth. 11 IssueID2 129–143 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvis1Gjsg%3D%3D
E. C. Vigliani (1954) ArticleTitleCarbon disulfide poisoning in viscose rayon factories Br. J. Ind. Med. 11 235–244 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG2MXjslOntQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle13208941
H. A. Peters R. L. Levine C. G. Matthews L. J. Chapman (1988) ArticleTitleExtrapyramidal and other neurological manifestations associated with carbon disulfide fumigant exposure Arch. Neurol. 45 537–540 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieC1M3ksVU%3D Occurrence Handle2833878
C. C. Chu C. C. Huang R. S. Chen T. S. Shih (1995) ArticleTitleCarbon disulfide induced polyneuropathy in viscose rayon workers Occup. Environ. Med. 52 404–407 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsFKrtbY%3D Occurrence Handle7627318
C. C. Huang (2004) ArticleTitleCarbon disulfide neurotoxicity: Taiwan experience Acta Neurol. Taiwan 13 IssueID1 3–9 Occurrence Handle15315294
M. R. Gottfried D. G. Graham M. Morgan H. W. Cases J. S. Bus (1985) ArticleTitleThe morphology of carbon disulfide neurotoxicity Neurotoxicology 6 IssueID4 89–96 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimC3Mbjt1A%3D Occurrence Handle3003629
P. S. Spencer H. H. Schaumburg (1977) ArticleTitleUltrastructural studies of the dying back process III. The evolution of experimental giant axonal degeneration J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 36 276–299 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSiC38%2Fkt1A%3D Occurrence Handle190357
D. G. Graham V. Amarnath W. M. Valentine S. J. Pyle D. C. Anthony (1995) ArticleTitlePathogenetic studies of hexane and carbon disulfide neurotoxicity Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 25 IssueID2 91–112 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXlsVCksro%3D Occurrence Handle7612176
E. J. Lehning A. Persaud K. R. Dyer B. S. Jortner R. M. LoPachin (1998) ArticleTitleBiochemical and morphologic characterization of acrylamide peripheral neuropathy Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 151 IssueID2 211–221 Occurrence Handle10.1006/taap.1998.8464 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXls1Snsbk%3D Occurrence Handle9707497
R. Gilioli C. Bulgheroni P. A. Bertazzi A. M. Cirla M. Tomasini M. G. Cassitto M. T. Jacovone (1978) ArticleTitleStudy of neurological and neurophysiological impairment in carbon disulphide workers Med. Lav. 69 IssueID2 130–143 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSeC1MbivVU%3D Occurrence Handle661738
C. Vasilescu A. Florescu (1980) ArticleTitleClinical and electrophysiological studies of carbon disulfide polyneuropathy J. Neurol. 224 59–70 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00313208 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6D3cfmvFU%3D Occurrence Handle6157800
D. W. Herr K. T. Vo D. L. Morgan R. C. Sills (1998) ArticleTitleCarbon disulfide neurotoxicity in rats: VI. Electrophysiological examination of caudal tail nerve compound action potentials and nerve conduction velocity Neurotoxicology 19 IssueID1 129–146 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhtlajt7c%3D Occurrence Handle9498229
P. S. Spencer M. I. Sabri H. H. Schaumburg C. L. Moore (1979) ArticleTitleDoes a defect of energy metabolism in the nerve fiber underlie axonal degeneration in polyneuropathies? Ann. Neurol. 6 501–507
M. J. McKenna V. DiStefano (1977) ArticleTitleCarbon disulfide. II. A proposed mechanism for the action of carbon disulfide on dopamine beta-hydroxylase J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 202 IssueID2 253–266 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXksl2htLo%3D Occurrence Handle886465
J. Teisinger (1974) ArticleTitleNew advances in the toxicology of carbon disulfide Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 35 IssueID2 55–61 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2cXktleqtLo%3D Occurrence Handle4817119
W. M. Valentine V. Amarnath D. G. Graham D. L. Morgan R. C. Sills (1997) ArticleTitleCS2-mediated cross-linking of erythrocyte spectrin and neurofilament protein: Dose response and temporal relationship to the formation of axonal swellings Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 142 IssueID1 95–105 Occurrence Handle10.1006/taap.1996.8028 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXltFKqsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9007038
Y. H. Gao Y. X. Liang W. Z. Fu (1998) ArticleTitleEffect of carbon disulfide on neurofilament and erythrocytic membrane structure in rats Chinese J. Ind. Med. 11 267–270
R. M. LoPachin D. He M. L. Reid (2005) ArticleTitle2,5-Hexanedione-induced changes in the neurofilament subunit pools of rat peripheral nerve Neurotoxicology 26 IssueID2 229–240 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.neuro.2004.09.007 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtlegu7k%3D Occurrence Handle15713344
R. M. LoPachin D. He M. L. Reid L. A. Opanashuk (2004) ArticleTitle2,5-Hexanedione-induced changes in the monomeric neurofilament protein content of rat spinal cord fractions Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 198 IssueID1 61–73 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.taap.2004.03.002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXltVCisbg%3D Occurrence Handle15207649
T. L. Zhang X. L. Zhao Z. P. Zhu L. H. Yu X. Y. Han C. L. Zhang K. Q. Xie (2005) ArticleTitle2,5-Hexanedione induced decrease in cytoskeletal proteins of rat sciatic-tibial nerve Neurochem. Res. 30 IssueID2 177–183 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s11064-004-2439-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXivFeltL4%3D Occurrence Handle15895820
V. C. Moser P. M. Phillips D. L. Morgan R. C. Sills (1998) ArticleTitleCarbon disulfide neurotoxicity in rats: VII. Behavioral evaluations using a functional observational battery Neurotoxicology 19 IssueID1 147–157 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhtlajtL0%3D Occurrence Handle9498230
M. Tsuda T. Tashiro Y. Komiya (1997) ArticleTitleIncreased solubility of high molecular mass neurofilament subunit by suppression of dephosphorylation: Its relation to axonal transport J. Neurochem. 68 2558–2565 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjsVylu7g%3D Occurrence Handle9166753
F. C. Chiu W. T. Norton (1982) ArticleTitleBulk preparation of CNS cytoskeleton and the separation of individual neurofilament proteins by gel filtration: Dye-binding characteristics and amino acid compositions J. Neurochem. 39 1252–1260 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXhvVOj Occurrence Handle6889631
T. B. Shea R. K. Sihag R. A. Nixon (1990) ArticleTitleDynamics of phosphorylation and assembly of the high molecular weight neurofilament subunit in NB2a/d1 neuroblastoma J. Neurochem. 55 1784–1792 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXmt1ymt7s%3D Occurrence Handle2213024
T. B. Shea D. C. Dahl R. A. Nixon I. Fischer (1997) ArticleTitleTriton-soluble phosphovariants of the heavy neurofilament subunit in developing and mature mouse central nervous system J. Neurosci. Res. 48 515–523 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXkt1eksLc%3D Occurrence Handle9210521
J. A. Cohlberg H. Hajarian T. Tran P. Alipourjeddi A. Noveen (1995) ArticleTitleNeurofilament protein heterotetramers as assembly intermediates J. Biol. Chem. 270 9334–9339 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXlt1ajt7c%3D Occurrence Handle7721855
M. K. Lee Z. Xu P. C. Wong D. W. Cleveland (1993) ArticleTitleNeurofilaments are obligate heteropolymers in vivo J. Cell. Biol. 122 1337–1350 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.122.6.1337 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXlslygtrk%3D Occurrence Handle8376466
R. A. Nixon S. E. Lewis (1986) ArticleTitleDifferential turnover of phosphate groups on neurofilament subunits in mammalian neurons in vivo J. Biol. Chem. 261 IssueID35 16298–16301 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XmtVKksbY%3D Occurrence Handle3782120
R. A. Nixon S. E. Lewis C. A. Marotta (1987) ArticleTitlePost-translational modification of neurofilament proteins by phosphate during axoplasmic transport in retinal ganglion cell neurons J. Neurosci. 7 IssueID4 1145–1158 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXhvFensr4%3D Occurrence Handle2437257
M. K. Lee D. W. Cleveland (1994) ArticleTitleNeurofilament function and dysfunction: Involvement in axonal growth and neuronal disease Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 6 IssueID1 34–40 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0955-0674(94)90113-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXis1Krtbw%3D Occurrence Handle7513179
R. C. Sills G. J. Harry D. L. Morgan W. M. Valentine D. G. Graham (1998) ArticleTitleCarbon disulfide neurotoxicity in rats: V. Morphology of axonal swelling in the muscular branch of the posterior tibial nerve and spinal cord Neurotoxicology 19 IssueID1 117–127 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhtlajt7g%3D Occurrence Handle9498228
N. Hirokawa S. Terada T. Funakoshi S. Takeda (1997) ArticleTitleSlow axonal transport: The subunit transport model Cell Biol. 7 384–388
J. T. Yabe W. K.-H. Chan T. Chylinski S. Lee A. Pimenta T. B. Shea (2001) ArticleTitleThe predominant form in which neurofilament subunits undergo axonal transport varies during axonal initiation, elongation and maturation Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 48 61–83 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1097-0169(200101)48:1<61::AID-CM6>3.0.CO;2-S Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkvF2mug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11124711
N. Hirokawa S. Takeda (1998) ArticleTitleGene targeting studies begin to reveal the function of neurofilament proteins J. Cell. Biol. 143 IssueID1 1–4 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.143.1.1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmsFalsbs%3D Occurrence Handle9763415
G. A. Elder V. L. Friedrich P. Bosco C. Kang A. Gourov P. H. Tu V. M. Lee R. A. Lazzarini (1998) ArticleTitleAbsence of the mid-sized neurofilament subunit decreases axonal calibers, levels of light neurofilament (NF-L), and neurofilament content J. Cell. Biol. 141 IssueID3 727–739 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.141.3.727 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXivVGjsbk%3D Occurrence Handle9566972
Q. Zhu M. Lindenbaum F. Levavasseur H. Jacomy J. P. Julien (1998) ArticleTitleDisruption of the NF-H gene increases axonal microtubule content and velocity of neurofilament transport: Relief of axonopathy resulting from the toxin beta,beta′-iminodipropionitrile J. Cell. Biol. 143 IssueID1 183–193 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.143.1.183 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmsFalt74%3D Occurrence Handle9763430
D. F. Watson K. P. Fittro P. N. Hoffman J. W. Griffin (1991) ArticleTitlePhosphorylation-related immunoreactivity and the rate of transport of neurofilaments in chronic 2,5-hexanedione intoxication Brain Res. 539 103–109 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-8993(91)90691-N Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhtFKmsbo%3D Occurrence Handle1707736
T. Sakaguchi M. Okada T. Kitamura K. Kawasaki (1993) ArticleTitleReduced diameter and conduction velocity of myelinated fibers in the sciatic nerve of a neurofilament-dificient mutant quail Neurosci. Lett. 153 65–68 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3940(93)90078-Y Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB1cfislA%3D Occurrence Handle8510825
L. A. Opanashuk D. K. He E. J. Lehning R. M. Lopachin (2001) ArticleTitleDiketone peripheral neuropathy III. Neurofilament gene expression Neurotoxicology 22 215–220 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0161-813X(00)00011-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkslClsrY%3D Occurrence Handle11405253
R. P. Gupta M. B. Abou-Donia (1996) ArticleTitleAlterations in the neutral proteinase activities of central and peripheral nervous systems of acrylamide-, carbon disulfide-, or 2,5-hexanedione-treated rats Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 29 IssueID1 53–66 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmsFSqtbw%3D Occurrence Handle8887940
H. C. Pant (1988) ArticleTitleDephosphorylation of neurofilament proteins enhances their susceptibility to degradation by calpain Biochem. J. 256 IssueID2 665–668 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXitVSquw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle2851997
C. Perrone Capano R. Pernas-Alonso U. Porzio Particledi (2001) ArticleTitleNeurofilament homeostasis and motoneurone degeneration Bioessays 23 24–33 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7lsVyitg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11135306
M. V. Rao J. Campbell A. Yuan A. Kumar T. Gotow Y. Uchiyama R. A. Nixon (2003) ArticleTitleThe neurofilament middle molecular mass subunit carboxyl-terminal tail domains is essential for the radial growth and cytoskeletal architecture of axons but not for regulating neurofilament transport rate J. Cell. Biol. 163 IssueID5 1021–1031 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.200308076 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpvVaks70%3D Occurrence Handle14662746
P. N. Hoffman D. W. Cleveland (1988) ArticleTitleNeurofilament and tubulin expression recapitulates the developmental program during axonal regeneration: Induction of a specific b-tubulin isotype Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85 4530–4533 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXkvFSlur4%3D Occurrence Handle3132717
P. F. Moskowitz R. Smith J. Pickett A. Frankfurter M. M. Oblinger (1993) ArticleTitleExpression of the class III b-tubulin gene during axonal regeneration of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons J. Neurosci. Res. 34 129–134 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jnr.490340113 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXlslWhuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8423633
F. D. Miller W. Tetzlaff M. A. Bisby J. W. Fawcett R. J. Milner (1989) ArticleTitleRapid induction of the major embryonic a-tubulin mRNA, T alpha1, during nerve regeneration in adult rats J. Neurosci. 9 1452–1463 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXit12msb8%3D Occurrence Handle2703888
F. J. Liuzzi S. M. Bufton A. I. Vinik (1998) ArticleTitleStreptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus causes changes in primary sensory neuronal cytoskeletal mRNA levels that mimic those caused by axotomy Exp. Neurol. 154 IssueID2 381–388 Occurrence Handle10.1006/exnr.1998.6938 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXms1KjtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9878176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, F., Yu, S., Zhao, X. et al. Carbon Disulfide-Induced Changes in Cytoskeleton Protein Content of Rat Cerebral Cortex. Neurochem Res 31, 71–79 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-9140-1
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-9140-1