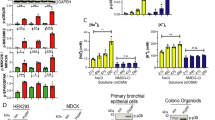
Abstract
Changes in external osmolarity, including both hyper- or hyposmotic conditions, elicit the tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of tyrosine kinase receptors (TKR). We show here that the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is activated by both cell swelling (hyposmolarity, isosmotic urea, hyperosmotic sorbitol) or shrinkage (hyperosmotic NaCl or raffinose) and discuss the mechanisms by which these apparently opposed conditions come to the same effect, i.e., EGFR activation. Evidence suggests that this results from early activation of integrins, p38 and tyrosine kinases of the Src family, which are all activated in the two anisosmotic conditions. TKR transactivation by integrins and p38 is likely occurring via an effect on the metalloproteinases. Information discussed in this review, points to TKR as elements in osmotransduction as a useful mechanism to amplify and diversify the initial response to anisosmolarity and cell volume changes, due to their privileged situation as convergence point for numerous intracellular signaling pathways. The variety of effector pathways connected to TKR is advantageous for the cell to cope with the changes in cell volume including adaptation to stress, cytoskeleton remodeling, adhesion reactions, cell survival and the adaptive mechanisms to ultimately restore the original cell volume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Pasantes-Morales R. Franco B. Ordaz L. D. Ochoa (2002) ArticleTitleMechanisms counteracting swelling in brain cells during hyponatremia Arch. Med. Res. 33 237–244 Occurrence Handle12031627 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0188-4409(02)00353-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XktVKntbY%3D
J. A. Leis L. K. Bekar W. Walz (2005) ArticleTitlePotassium homeostasis in the ischemic brain Glia 50 407–416 Occurrence Handle15846795 Occurrence Handle10.1002/glia.20145
H. K. Kimelberg (1995) ArticleTitleCurrent concepts of brain edema. Review of laboratory investigations J. Neurosurg. 83 1051–1059 Occurrence Handle7490620 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28%2Fos1yksQ%3D%3D
W. Walz (2000) ArticleTitleRole of astrocytes in the clearance of excess extracellular potassium Neurochem. Int. 36 291–230 Occurrence Handle10732996 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0197-0186(99)00137-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXitVantr4%3D
P. M. Palevsky (1998) ArticleTitleHypernatremia Semin. Nephrol. 18 20–30 Occurrence Handle9459286 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7hvFektg%3D%3D
F. Wehner H. Olsen H. Tinel E. Kinne-Saffran R. K. Kinne (2003) ArticleTitleCell volume regulation: Osmolytes, osmolyte transport, and signal transduction Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 148 1–80 Occurrence Handle12687402 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXitlKr
H. Pasantes-Morales R. Franco M. E. Torres-Márquez K. Hernández-Fonseca A. Ortega (2000) ArticleTitleAmino acid osmolytes in regulatory volumen decrease and isovolumetric regulation in brain cells: Contribution and mechanisms Cell Physiol. Biochem. 10 362–370 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000016369
A. Sardini J. S. Amey K. H. Weylandt M. Nobles M. A. Valverde C. F. Higgins (2003) ArticleTitleCell volume regulation and swelling-activated chloride channels Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1618 153–162 Occurrence Handle14729152 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjsV2qtg%3D%3D
S. K. Woo S. D. Lee H M. Kwon (2002) ArticleTitleTonEBP transcriptional activator in the cellular response to increased osmolality Pflugers Arch. 444 579–585 Occurrence Handle12194010 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmtlGisbo%3D
B. C. Tilly N. Berghe Particlevan den L. G. Tertoolen M. J. Edixhoven H. R. Jonge Particlede (1993) ArticleTitleProtein tyrosine phosphorylation is involved in osmoregulation of ionic conductances J.␣Biol. Chem. 268 19919–19922 Occurrence Handle7690749 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXltlKgtrs%3D
S. Morales-Mulia V. Cardin M. E. Torres-Márquez A. Crevenna H. Pasantes-Morales (2001) ArticleTitleInfluence of protein kinases on the osmosensitive release of taurine from cerebellar neurons Neurochem. Int. 38 153–161 Occurrence Handle11137884 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXotVaruw%3D%3D
B. C. Tilly M. Gaestel K. Engel M. J Edixhoven H. R. Jonge Particlede (1996) ArticleTitleHypo-osmotic cell swelling activates the p38 MAP kinase signalling cascade FEBS Lett. 395 133–136 Occurrence Handle8898080 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-5793(96)01028-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmslGnt7Y%3D
R. Lezama A. Ortega B. Ordaz H. Pasantes- Morales (2005) ArticleTitleHyposmolarity-induced ErbB4 phosphorylation and its influence on the non-receptor tyrosine kinase network response in cultured cerebellar granule neurons J. Neurochem. 93 1189–1198 Occurrence Handle15934939 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03110.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXltVans7c%3D
H. Pasantes-Morales R. Franco (2002) ArticleTitleInfluence of protein tyrosine kinases on cell volume change-induce taurine release Cerebellum 1 103–109 Occurrence Handle12882359 Occurrence Handle10.1080/147342202753671231 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xkslahsr0%3D
D. M. Cohen (2005) ArticleTitleSRC family kinases in cell volume regulation Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 288 C483–C493 Occurrence Handle15692147 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXisVKrtbs%3D
V. Cardin R. Lezama M. E. Torres-Marquez H. Pasantes-Morales (2003) ArticleTitlePotentiation of the osmosensitive taurine release and cell volume regulation by cytosolic Ca2+ rise in cultured cerebellar astrocytes Glia 44 119–128 Occurrence Handle14515328 Occurrence Handle10.1002/glia.10271
M. Bustamante F. Roger M. Bochaton G. Gabbiani P. Yves E. Féraille (2003) ArticleTitleRegulatory volume increase is associated with p38 kinase-dependent actin cytoskeleton remodeling in rat kidney MTAL Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 285 F336–F347 Occurrence Handle12724128 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmsVagu7o%3D
E. K. Hoffmann (2000) ArticleTitleIntracellular signaling involved in volume regulatory decrease Cell Physiol. Biochem. 10 273–288 Occurrence Handle11125206 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjt1alu7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1159/000016356
J. A. Lunn E. Rozengurt (2004) ArticleTitleHyperosmotic stress induces rapid focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation at tyrosines 397 and 577. Role of Src family kinases and Rho family GTPases J. Biol. Chem. 279 45266–45278 Occurrence Handle15302877 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M314132200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXosFylsLo%3D
O. Nahm S. Kyoon J. Handler H. Kwon (2002) ArticleTitleInvolvement of multiple kinase pathways in stimulation of gene transcription by hypertonicity Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 282 C49–C58 Occurrence Handle11742797 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlsVKgug%3D%3D
M. T. Uhlik A. N. Abell N. L. Johnson W. Sun B. D. Cuevas K. E. Lobel-Rice E. A. Horne M. L. Dell’ Acqua G. L. Johnson (2003) ArticleTitleRac-MEKK3–MKK3 scaffolding for p38 MAPK activation during hyperosmotic shock Nat. Cell Biol. 5 1104–1110 Occurrence Handle14634666 Occurrence Handle10.1038/ncb1071 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXptlGns7c%3D
D. Sheikh-Hamad M. C. Gustin (2004) ArticleTitleMAP kinases and the adaptive response to hypertonicity: Functional preservation from yeast to mammals Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 287 F1102–F1110 Occurrence Handle15522988 Occurrence Handle10.1152/ajprenal.00225.2004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtVOmu7rK
J. Schlessinger (2000) ArticleTitleCell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases Cell 103 211–225 Occurrence Handle11057895 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00114-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXns1Cltrs%3D
P. Dent A. Yacoub J. Contessa R. Caron G. Amorino K. Valerie M. P. Hagan S. Grant R. Schmidt-Ullrich (2003) ArticleTitleStress and radiation-induced activation of multiple␣intracellular signaling pathways Radiat. Res. 159 283–300 Occurrence Handle12600231 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXitFyqsLg%3D
C. Li Q. Xu (2000) ArticleTitleMechanical stress-initiated signal transductions in vascular smooth muscle cells Cell Signal. 12 435–445 Occurrence Handle10989277 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmtlKjsrc%3D
R. Franco R. Lezama B. Ordaz H. Pasantes-Morales. (2004) ArticleTitleEpidermal growth factor receptor is activated by hyposmolarity and is an early signal modulating osmolyte efflux pathways in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts J. Cell Mol. Physiol. 447 830–839 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhvFCntbs%3D
C. Rosette M. Karin (1996) ArticleTitleUltraviolet light and osmotic stress: Activation of the JNK cascade through multiple growth factor and cytokine receptors Science 274 1194–1197 Occurrence Handle8895468 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.274.5290.1194 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmvVyitr0%3D
H. Cheng J. Kartenbeck K. Kabsch X. Mao M. Marques A. Alonso (2002) ArticleTitleStress kinase p38 mediates EGFR transactivation by hyperosmolar concentrations of sorbitol J. Cell Physiol. 192 234–243 Occurrence Handle12115730 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jcp.10134 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xlt1Kqu7Y%3D
H. Xu W. Tian J. Lindsley T. Oyama J. Capasso C. Rivard H. Cohen S. Bagnasco S. Anderson D. Cohen (2005) ArticleTitleEphA2: Expression in the renal medulla and regulation by hypertonicity and urea stress in vitro and in vivo Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 288 F855–F866 Occurrence Handle15561974 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXjtlOqtb0%3D
D. Ouwens D. Gomes J. Dekker A. Maassen (2001) ArticleTitleHyperosmotic stress activates the insulin receptor in CHO cells Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1540 97–106 Occurrence Handle11513972 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmtFWjtbc%3D
M. Horio A. Ito Y. Matsuoka T. Moriyama Y. Orita M. Takenaka E. Imai (2001) ArticleTitleApoptosis induced by hypertonicity in Madin Darley Canine Kidney cells: Protective effect of betaine Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 16 483–490 Occurrence Handle11239020 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXis1eqsLo%3D
B. Stahl H. Wiesinger B. Hamprecht (1989) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of sorbitol uptake in rat glial primary cultures J. Neurochem. 53 665–671 Occurrence Handle2760614 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXltlWgu7k%3D
G.R. Kracke G.G. Preston T.H. Stanley (1994) ArticleTitleIdentification of a sorbitol permease in human erythrocytes Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 266 C343–C350 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXitFemu70%3D
T. Berl G. Siriwardana L. Ao L. Butterfield L. Heasley (1997) ArticleTitleMultiple mitogen-activated protein kinase are regulated by hyperosmolality in mouse IMCD cells Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 41 F305–F311
A. Galvez J. Ulloa M. Chiong A. Criollo. V. Eisner L. Barros S. Lavandero (2003) ArticleTitleAldose reductase induce by hyperosmotic stress mediates cardiomyocyte apoptosis J. Biol. Chem. 278 38484–38494 Occurrence Handle12881532 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M211824200 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnslSqu74%3D
N. J. Boudreau P. L. Jones (1999) ArticleTitleExtracellular matrix and integrin signalling: The shape of things to come Biochem. J. 339 481–488 Occurrence Handle10215583 Occurrence Handle10.1042/0264-6021:3390481 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXksFKrsrc%3D
L. Moro M. Venturino C. Bozzo L. Silengo F. Altruda L. Beguinot G. Tarone P. Defilippi (1998) ArticleTitleIntegrins induce activation of EGF receptor: Role in MAP kinase induction and adhesion-dependent cell survival EMBO J. 17 6622–6632 Occurrence Handle9822606 Occurrence Handle10.1093/emboj/17.22.6622 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnvF2jt78%3D
S. vom Dahl F. Schliess R. Reissmann B. Gorg O. Weiergraber M. Kocalkova F. Dombrowski D. Haussinger (2003) ArticleTitleInvolvement of integrins in osmosensing and signaling toward autophagic proteolysis in rat liver J. Biol. Chem. 278 27088–27095 Occurrence Handle12721289 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXltlKquro%3D
I. H. Lambert (2003) ArticleTitleReactive oxygen species regulate swelling-induced taurine efflux in NIH3T3 mouse fibroblasts J. Membr. Biol. 192 19–32 Occurrence Handle12647031 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00232-002-1061-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXit1Shtb0%3D
T. Yang A. Zhan M. Honeggar D. E. Kohan D. Mizel K. Sanders J. R. Hoidal J. P. Briggs J. B. Schnermann (2005) ArticleTitleHypertonic induction of COX-2 in collecting duct cells by reactive oxygen species of mitochondrial origin J. Biol. Chem. 280 34966–34973 Occurrence Handle16024921 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtVyks73F
D. Xu L. Wang J. Olson L. Lu (2001) ArticleTitleAsymetrical response of p38 kinase activation to volume changes in primary rat astrocytes Exp. Biol. Med. 226 927–933 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXotFKiurw%3D
B. Shah K. Catt (2004) ArticleTitleMatrix metalloproteinase-dependent EGF receptor activation in hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy Trends Endocrinol. Metabol. 15 241–243 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXmsVGju7o%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue dedicated to Dr. Simo S. Oja
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lezama, R., Díaz-Téllez, A., Ramos-Mandujano, G. et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor is a Common Element in the Signaling Pathways Activated by Cell Volume Changes in Isosmotic, Hyposmotic or Hyperosmotic Conditions. Neurochem Res 30, 1589–1597 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-8837-5
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-8837-5