Abstract
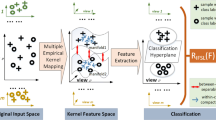
Different views of one object usually represent different aspects of the object, and a single view is unlikely to comprehensively describe the object. In multi-view learning, comprehensive utilization of multi-view information is helpful. In this paper, we propose a novel supervised latent subspace learning method called multi-view intact discriminant space learning (MIDSL) by efficiently integrating complementary multi-view information of different views. MIDSL learns a latent intact discriminant space by employing Fisher discrimination criterion to fully use class label information, which can well guide exploiting useful discriminant information, of labeled training samples. MIDSL can simultaneously minimize the within-class scatter and maximize the between-class scatter of the feature representations of different objects in the learned latent intact discriminant space. Aiming to utilize unlabeled samples to help mining more useful information for better learning latent intact discriminant space, we extend MIDSL method in semi-supervised scenario and propose semi-supervised multi-view intact discriminant space learning (SMIDSL) method. We further extend MIDSL and SMIDSL methods by kernel technique and propose kernelized multi-view intact discriminant space learning (KMIDSL) and kernelized semi-supervised multi-view intact discriminant space learning (KSMIDSL) methods. Experimental results on Caltech 101, LFW, MNIST and RGB-D datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma A, Kumar A, Daume H, Jacobs DW (2012) Generalized multiview analysis: a discriminative latent space. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2160–2167
Sun S (2013) A survey of multi-view machine learning. Neural Comput Appl 23(7):2031–2038
Kan M, Shan S, Zhang H, Lao S, Chen X (2016) Multi-view discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(1):188–194
Jiang Y, Liu J, Li Z, Lu H (2014) Semi-supervised unified latent factor learning with multi-view data. Mach Vis Appl 25(7):1635–1645
Korn F, Pagel BU, Faloutsos C (2001) On the dimensionality curse and the self-similarity blessing. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 13(1):96–111
Wang W, Zhou ZH (2013) Co-training with insufficient views. In: Proceedings of the Asian conference on machine learning, pp 467–482
Li SY, Jiang Y, Zhou ZH (2014) Partial multi-view clustering. In: Proceedings of the conference on the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1968–1974
Li Y, Nie F, Huang H, Huang J (2015) Large-scale multi-view spectral clustering via bipartite graph. In: Proceedings of the conference on the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 2750–2756
Gönen M, Alpaydın E (2011) Multiple kernel learning algorithms. J Mach Learn Res 12(7):2211–2268
Xu Z, Jin R, Yang H, King I, Lyu MR (2010) Simple and efficient multiple kernel learning by group lasso. In: Proceedings of the international conference on machine learning, pp 1175–1182
Zhang D, He J, Liu Y, Si L Lawrence R (2011) Multi-view transfer learning with a large margin approach. In: Proceedings of the international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 1208–1216
White M, Zhang X, Schuurmans D, Yu YL (2012) Convex multi-view subspace learning. In: Proceedings of the conference on neural information processing systems, pp 1673–1681
Hardoon D, Szedmak S, Shawe-Taylor J (2004) Canonical correlation analysis: an overview with application to learning methods. Neural Comput 16(12):2639–2664
Dhillon P, Foster D, Ungar L (2011) Multi-view learning of word embeddings via CCA. In: Proceedings of the conference on neural information processing systems, pp 199–207
Xing X, Wang K, Yan T, Lv Z (2016) Complete canonical correlation analysis with application to multi-view gait recognition. Pattern Recognit 50:107–117
Viinikanoja J, Klami A, Kaski S (2010) Variational Bayesian mixture of robust CCA. In: Proceedings of the conference on the European conference on machine learning, pp 370–385
Jia Y, Salzmann M, Darrell T (2010) Factorized latent spaces with structured sparsity. In: Proceedings of the conference on neural information processing systems, pp 982–990
Xia T, Tao D, Mei T, Zhang Y (2010) Multiview spectral embedding. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 40(6):1438–1446
Chen N, Zhu J, Xing EP (2010) Predictive subspace learning for multi-view data: a large margin approach. In: Proceedings of the conference on neural information processing systems, pp 361–369
Xu C, Tao D, Li Y, Xu C (2013) Large-margin multi-view Gaussian process for image classification. In: Proceedings of the international conference on internet multimedia computing and service, pp 7–12
Guo Y, Tao D, Liu W, Cheng J (2016) Multiview Cauchy estimator feature embedding for depth and inertial sensor-based human action recognition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 47(4):617–627
Xu C, Tao D, Xu C (2015) Multi-view intact space learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(12):2531–2544
Belhumeur PN, Hespanha JP, Kriegman DJ (1997) Eigenfaces vs. fisherfaces: recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(7):711–720
Jensen CA, El-Sharkawi MA, Marks RJ (2001) Power system security assessment using neural networks: feature selection using Fisher discrimination. IEEE Trans Power Syst 16(4):757–763
Yang M, Zhang L, Feng X, Zhang D (2014) Sparse representation based fisher discrimination dictionary learning for image classification. Int J Comput Vis 109(3):209–232
Jing XY, Wu F, Dong X, Shan S, Chen S (2017) Semi-supervised multi-view correlation feature learning with application to webpage classification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, pp 1374–1381
Shen X, Sun Q (2014) A novel semi-supervised canonical correlation analysis and extensions for multi-view dimensionality reduction. J Vis Commun Image Represent 25(8):1894–1904
Chen X, Chen S, Xue H, Zhou X (2012) A unified dimensionality reduction framework for semi-paired and semi-supervised multi-view data. Pattern Recognit 45(5):2005–2018
Guan Z, Zhang L, Peng J, Fan J (2015) Multi-view concept learning for data representation. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(11):3016–3028
Luo Y, Tao D, Ramamohanarao K, Xu C, Wen Y (2015) Tensor canonical correlation analysis for multi-view dimension reduction. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(11):3111–3124
Salzmann M, Ek CH, Urtasun R, Darrell T (2010) Factorized orthogonal latent spaces. In: Proceedings of the international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics, pp 701–708
Li J, Xu C, Yang W, Sun C, Tao D (2017) Discriminative multi-view interactive image re-ranking. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(7):3113–3127
Yuan Y, Lin J, Wang Q (2016) Hyperspectral image classification via multitask joint sparse representation and stepwise MRF optimization. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(12):2966–2977
Yi S, Lai Z, He Z, Cheung YM, Liu Y (2017) Joint sparse principal component analysis. Pattern Recognit 61:524–536
Zhang P, You X, Ou W, Chen CP, Cheung YM (2016) Sparse discriminative multi-manifold embedding for one-sample face identification. Pattern Recognit 52:249–259
He Z, Yi S, Cheung YM, You X, Tang YY (2017) Robust object tracking via key patch sparse representation. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(2):354–364
Gangeh MJ, Fewzee P, Ghodsi A, Kamel MS, Karray F (2014) Multiview supervised dictionary learning in speech emotion recognition. IEEE ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 22(6):1056–1068
Bennett KP, Momma M, Embrechts MJ (2002) MARK: a boosting algorithm for heterogeneous kernel models. In: Proceedings of the ACM international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 24–31
Xu X, Tsang IW, Xu D (2013) Soft margin multiple kernel learning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(5):749–761
Sonnenburg S, Rätsch G, Schäfer C, Schölkopf B (2006) Large scale multiple kernel learning. J Mach Learn Res 7(7):1531–1565
Rakotomamonjy A, Bach F, Canu S, Grandvalet Y (2007) More efficiency in multiple kernel learning. In: Proceedings of the international conference on machine learning, pp 775–782
Kloft M, Brefeld U, Sonnenburg S, Zien A (2011) Lp-norm multiple kernel learning. J Mach Learn Res 12(3):953–997
Zhang G, Sun H, Xia G, Sun Q (2016) Multiple kernel sparse representation-based orthogonal discriminative projection and its cost-sensitive extension. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(9):4271–4285
Wang Q, Gu Y, Tuia D (2016) Discriminative multiple kernel learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(7):3912–3927
Feng J, Jiao L, Sun T, Liu H, Zhang X (2016) Multiple kernel learning based on discriminative kernel clustering for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54(11):6516–6530
Shrivastava A, Patel VM, Chellappa R (2014) Multiple kernel learning for sparse representation-based classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(7):3013–3024
Blum A, Mitchell T (1998) Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In: Proceedings of the international conference on computational learning theory, pp 92–100
You X, Peng Q, Yuan Y, Cheung YM, Lei J (2011) Segmentation of retinal blood vessels using the radial projection and semi-supervised approach. Pattern Recognit 44(10–11):2314–2324
Wang W, Zhou ZH (2007) Analyzing co-training style algorithms. In: Proceedings of the European conference on machine learning, pp 454–465
Zhou ZH, Li M (2005) Tri-training: exploiting unlabeled data using three classifiers. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 17(11):1529–1541
Li G, Chang K, Hoi SC (2012) Multiview semi-supervised learning with consensus. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(11):2040–2051
Wang Q, Lin J, Yuan Y (2016) Salient band selection for hyperspectral image classification via manifold ranking. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(6):1279–1289
Appice A, Guccione P, Malerba D (2017) A novel spectral-spatial co-training algorithm for the transductive classification of hyperspectral imagery data. Pattern Recognit 63:229–245
Wang J, Wang X, Tian F, Liu CH, Yu H, Liu Y (2016) Adaptive multi-view semi-supervised nonnegative matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of the international conference on neural information processing, pp 435–444
Zhang Z (1997) Parameter estimation techniques: a tutorial with application to conic fitting. Image Vis Comput 15(1):59–76
Lu H, Plataniotis KN, Venetsanopoulos AN (2008) MPCA: multilinear principal component analysis of tensor objects. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 19(1):18–39
Aronszajn N (1950) Theory of reproducing kernels. Trans Am Math Soc 68(3):337–404
Roth V, Steinhage V (1999) Nonlinear discriminant analysis using kernel functions. In: Proceedings of the conference on neural information processing systems, pp 568–574
Li F, Rob F, Pietro P (2007) Learning generative visual models from few training examples: an incremental Bayesian approach tested on 101 object categories. Comput Vis Image Underst 106(1):59–70
Huang G, Mattar M, Lee H Learned-Miller EG (2012) Learning to align from scratch. In: Proceedings of the conference on neural information processing systems, pp 764–772
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
Lai K, Bo L, Ren X, Fox D (2011) A large-scale hierarchical multi-view RGB-D object dataset. In: Proceedings of the international conference on robotics and automation, pp 1817–1824
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Zeiler MD, Fergus R (2014) Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, pp 818–833
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 248–255
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, Berg AC, Fei-Fei L (2015) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60(2):91–110
Acknowledgements
This work is partially funded by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant Numbers of 61272273 and 61702280. It is also supported by NSFC-Key Project of General Technology Fundamental Research United Fund (No. U1736211), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20170900), Natural Science Fund for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (No. 17KJB520025), the Scientific Research Staring Foundation for Introduced Talents in NJUPT (NUPTSF, No. NY217009), Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (No. XJKY14016). In addition, it is also funded by Education Department of Jiangxi Province under Grant No. GJJ151076.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, X., Wu, F., Jing, XY. et al. Multi-view Intact Discriminant Space Learning for Image Classification. Neural Process Lett 50, 1661–1685 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-9951-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-9951-0