Abstract
Introduction
NRG protocols for glioblastoma allow for clinical target volume (CTV) reductions at natural barriers; however, literature examining CTV contouring and the relevant white matter pathways is lacking. This study proposes consensus CTV guidelines, with a focus on areas of controversy while highlighting common errors in glioblastoma target delineation.
Methods
Ten academic radiation oncologists specializing in brain tumor treatment contoured CTVs on four glioblastoma cases. CTV expansions were based on NRG trial guidelines. Contour consensus was assessed and summarized by kappa statistics. A meeting was held to discuss the mathematically averaged contours and form consensus contours and recommendations.
Results
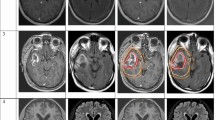
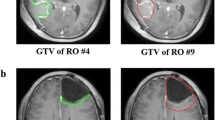
Contours of the cavity plus enhancement (mean kappa 0.69) and T2-FLAIR signal (mean kappa 0.74) showed moderate to substantial agreement. Experts were asked to trim off anatomic barriers while respecting pathways of spread to develop their CTVs. Submitted CTV_4600 (mean kappa 0.80) and CTV_6000 (mean kappa 0.81) contours showed substantial to near perfect agreement. Simultaneous truth and performance level estimation (STAPLE) contours were then reviewed and modified by group consensus. Anatomic trimming reduced the amount of total brain tissue planned for radiation targeting by a 13.6% (range 8.7–17.9%) mean proportional reduction. Areas for close scrutiny of target delineation were described, with accompanying recommendations.
Conclusions
Consensus contouring guidelines were established based on expert contours. Careful delineation of anatomic pathways and barriers to spread can spare radiation to uninvolved tissue without compromising target coverage. Further study is necessary to accurately define optimal target volumes beyond isometric expansion techniques for individual patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO, European Organisation for R, Treatment of Cancer Brain T, Radiotherapy G, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials G (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352 (10):987–996. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Niyazi M, Brada M, Chalmers AJ, Combs SE, Erridge SC, Fiorentino A, Grosu AL, Lagerwaard FJ, Minniti G, Mirimanoff RO, Ricardi U, Short SC, Weber DC, Belka C (2016) ESTRO-ACROP guideline “target delineation of glioblastomas”. Radiother Oncol 118(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2015.12.003
Burger PC, Dubois PJ, Schold SC Jr, Smith KR Jr, Odom GL, Crafts DC, Giangaspero F (1983) Computerized tomographic and pathologic studies of the untreated, quiescent, and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurosurg 58(2):159–169. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1983.58.2.0159
Earnest Ft, Kelly PJ, Scheithauer BW, Kall BA, Cascino TL, Ehman RL, Forbes GS, Axley PL (1988) Cerebral astrocytomas: histopathologic correlation of MR and CT contrast enhancement with stereotactic biopsy. Radiology 166(3):823–827. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.166.3.2829270
NRG-BN001 Randomized phase II tiral of hypofractionated dose-escalated photon IMRT or proton beam therapy versus conventional photon irradiation with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide in patient with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. https://www.nrgoncologyorg/Clinical-Trials/Protocol-Table
Wee CW, Sung W, Kang HC, Cho KH, Han TJ, Jeong BK, Jeong JU, Kim H, Kim IA, Kim JH, Kim SH, Kim S, Lee DS, Lee MY, Lim DH, Park HL, Suh CO, Yoon SM, Kim IH (2015) Evaluation of variability in target volume delineation for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a multi-institutional study from the Korean Radiation Oncology Group. Radiat Oncol 10:137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-015-0439-z
Allozi R, Li XA, White J, Apte A, Tai A, Michalski JM, Bosch WR, El Naqa I (2010) Tools for consensus analysis of experts’ contours for radiotherapy structure definitions. Radiother Oncol 97(3):572–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2010.06.009
Warfield SK, Zou KH, Wells WM (2004) Simultaneous truth and performance level estimation (STAPLE): an algorithm for the validation of image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23(7):903–921. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2004.828354
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33(1):159–174
Baisden JM, Sheehan J, Reish AG, McIntosh AF, Sheng K, Read PW, Benedict SH, Larner JM (2011) Helical tomotherapy simultaneous integrated boost provides a dosimetric advantage in the treatment of primary intracranial tumors. Neurol Res 33(8):820–824. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743132811Y.0000000035
Buglione M, Pedretti S, Poliani PL, Liserre R, Gipponi S, Spena G, Borghetti P, Pegurri L, Saiani F, Spiazzi L, Tesini G, Uccelli C, Triggiani L, Magrini SM (2016) Pattern of relapse of glioblastoma multiforme treated with radical radio-chemotherapy: could a margin reduction be proposed? J Neurooncol 128(2):303–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2112-2
McDonald MW, Shu HK, Curran WJ Jr, Crocker IR (2011) Pattern of failure after limited margin radiotherapy and temozolomide for glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79(1):130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.10.048
Minniti G, Amelio D, Amichetti M, Salvati M, Muni R, Bozzao A, Lanzetta G, Scarpino S, Arcella A, Enrici RM (2010) Patterns of failure and comparison of different target volume delineations in patients with glioblastoma treated with conformal radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide. Radiother Oncol 97(3):377–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2010.08.020
Paulsson AK, McMullen KP, Peiffer AM, Hinson WH, Kearns WT, Johnson AJ, Lesser GJ, Ellis TL, Tatter SB, Debinski W, Shaw EG, Chan MD (2014) Limited margins using modern radiotherapy techniques does not increase marginal failure rate of glioblastoma. Am J Clin Oncol 37(2):177–181. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e318271ae03
Wernicke AG, Smith AW, Taube S, Mehta MP (2016) Glioblastoma: radiation treatment margins, how small is large enough? Pract Radiat Oncol 6(5):298–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2015.12.002
Guram K, Smith M, Ginader T, Bodeker K, Pelland D, Pennington E, Buatti JM (2018) Using smaller-than-standard radiation treatment margins does not change survival outcomes in patients with high-grade gliomas. Pract Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2018.06.001
Scoccianti S, Detti B, Gadda D, Greto D, Furfaro I, Meacci F, Simontacchi G, Di Brina L, Bonomo P, Giacomelli I, Meattini I, Mangoni M, Cappelli S, Cassani S, Talamonti C, Bordi L, Livi L (2015) Organs at risk in the brain and their dose-constraints in adults and in children: a radiation oncologist’s guide for delineation in everyday practice. Radiother Oncol 114(2):230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2015.01.016
Mayo C, Yorke E, Merchant TE (2010) Radiation associated brainstem injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3 Suppl):S36–S41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.08.078
Mayo C, Martel MK, Marks LB, Flickinger J, Nam J, Kirkpatrick J (2010) Radiation dose-volume effects of optic nerves and chiasm. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3 Suppl):S28–S35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1753
Bhandare N, Jackson A, Eisbruch A, Pan CC, Flickinger JC, Antonelli P, Mendenhall WM (2010) Radiation therapy and hearing loss. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3 Suppl):S50–S57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.04.096
Gregoire V, Ang K, Budach W, Grau C, Hamoir M, Langendijk JA, Lee A, Le QT, Maingon P, Nutting C, O’Sullivan B, Porceddu SV, Lengele B (2014) Delineation of the neck node levels for head and neck tumors: a 2013 update. DAHANCA, EORTC, HKNPCSG, NCIC CTG, NCRI, RTOG, TROG consensus guidelines. Radiother Oncol 110(1):172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2013.10.010
Gilbert MR, Wang M, Aldape KD, Stupp R, Hegi ME, Jaeckle KA, Armstrong TS, Wefel JS, Won M, Blumenthal DT, Mahajan A, Schultz CJ, Erridge S, Baumert B, Hopkins KI, Tzuk-Shina T, Brown PD, Chakravarti A, Curran WJ Jr, Mehta MP (2013) Dose-dense temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 31(32):4085–4091. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.49.6968
Kumar N, Kumar R, Sharma SC, Mukherjee KK, Khandelwal N, Kumar R, Gupta PK, Bansal A, Kapoor R, Ghosal S (2012) To compare the treatment outcomes of two different target volume delineation guidelines (RTOG vs MD Anderson) in glioblastoma multiforme patients: a prospective randomized study. Neuro-Oncology 14:vi133–vi141 (Suppl 6)
Matsuo M, Miwa K, Tanaka O, Shinoda J, Nishibori H, Tsuge Y, Yano H, Iwama T, Hayashi S, Hoshi H, Yamada J, Kanematsu M, Aoyama H (2012) Impact of [11C]methionine positron emission tomography for target definition of glioblastoma multiforme in radiation therapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82(1):83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.09.020
Rieken S, Habermehl D, Giesel FL, Hoffmann C, Burger U, Rief H, Welzel T, Haberkorn U, Debus J, Combs SE (2013) Analysis of FET-PET imaging for target volume definition in patients with gliomas treated with conformal radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 109(3):487–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2013.06.043
Wakabayashi T, Iuchi T, Tsuyuguchi N, Nishikawa R, Arakawa Y, Sasayama T, Miyake K, Nariai T, Narita Y, Hashimoto N, Okuda O, Matsuda H, Kubota K, Ito K, Nakazato Y, Kubomura K (2017) Diagnostic performance and safety of positron emission tomography using (18)F-fluciclovine in patients with clinically suspected high- or low-grade gliomas: a multicenter phase IIb trial. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol 5(1):10–21. https://doi.org/10.22038/aojnmb.2016.7869
Funding
WRB’s work on this project was supported by a grant from National Institutes of Health Grant No. U24 CA180803,”Imaging and Radiation Oncology (IROC) Group”, David Followill, PI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
WRB’s reports travel expenses from AAPM, and honoraria from Augmenix Inc. These do not pertain to this work and WRB declares he has no conflict of interest with regard to this study. TJK is on a speaker’s bureau for AstraZeneca, has served as a consultant to Varian Medical Systems and was on an advisory board for Abbvie Inc. These do not pertain to this work and TJK declares he has no conflict of interest with regard to this study. CT is on a speaker’s bureau for Merck and Varian Medical Systems, advisory board for Novocure. These do not pertain to this work and CT declares she has no conflict of interest with regard to this study. TJCW reports travel expenses from Abbvie, AstraZeneca, and Elekta, serves as a consultant for Abbvie, Merck, Doximity, and Elekta, is on advisory boards for American Cancer Society of New Jersey and AstraZeneca, and Honoria from Elekta and Wolthers Kluwer, and stock options from Doximity. These do not pertain to this work and TJCW declares he has no conflict of interest with regard to this study. MPM has served as a consultant to Agenus, Insys, Remedy, IBA, Varian, Oncoceutics, Astra-Zeneca, Celgene, Tocagen, and is on the DSMB of Monteris, and the Board of Oncoceutics. These do not pertain to this work and MPM declares he has no conflict of interest with regard to this study. KPM has served as a consultant for Via Oncology Pathways; this does not pertain to this work and KPM declares he has no conflict of interest with regard to this study. MMK reports a research grant from EpicentRX, which does not pertain to this work and MMK declares she has no conflict of interest with regard to this study. AAS has participated in an advisory committee, received travel expenses, received honoraria, and received research funding from Blue Earth Diagnostics, as well as travel expenses and honoraria from DAVA Oncology; this does not pertain to this work and AAS declares he has no conflict of interest with regard to this study. SNB, JAB, AJG, SS do not have relevant financial relationships to disclose and declare they have no conflicts of interest with regard to this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kruser, T.J., Bosch, W.R., Badiyan, S.N. et al. NRG brain tumor specialists consensus guidelines for glioblastoma contouring. J Neurooncol 143, 157–166 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03152-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03152-9