Abstract
Purpose
This study evaluated the long-term tumor control rate (TCR) and symptomatic outcomes of patients treated with gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS) for trigeminal schwannomas (TSs).
Methods
Thirty-two patients with TS who underwent GKRS between January 1994 and January 2013 with at least 2 years of follow-up were enrolled in the study. Clinical charts and surgical records were retrospectively reviewed to evaluate factors affecting TCR and symptomatic outcomes. The median patient age was 57.5 years (max = 81, interquartile range [IQR] = 51–67), and the median tumor volume was 3.55 cm3 (max = 25.2 cm3, IQR = 2.0–6.2 cm3). The median marginal and maximum doses were 13.0 Gy (max = 18.0 Gy, IQR = 12.5–15 Gy) and 23.8 Gy (max = 35 Gy, IQR = 21.7–25.0 Gy), respectively.
Results
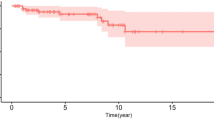
At a median follow-up of 90.5 months (max = 281 months, IQR = 49–139.75 months), the actuarial 3-, 5-, and 10-year TCR were 93.8, 86.2, and 80.8%, respectively. Our data and multivariate analysis indicated that the target volume was the only significant factor determining TCR and that larger tumors (> 5 cm3) were more likely to progress (p = 0.011). Cystic tumors had a higher incidence of transient enlargement and temporary symptom change compared to those in solid tumors. An unfavorable outcome of symptoms was observed in five patients (15.6%). Complications were observed in two patients (6.25%), including hydrocephalus and radio-induced trigeminal neuropathy, respectively.
Conclusions
GKRS can be a safe and effective treatment modality for TS with long-term follow-up, especially for small tumors. An extended period of follow-up observation is required to conclude the clinical response to GKRS.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GKRS:
-
Gamma knife radiosurgery
- IQR:
-
Inter-quartile range
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- TCR:
-
Tumor control rate
- TS:
-
Trigeminal schwannoma
References
Goel A, Muzumdar D, Raman C (2003) Trigeminal neuroma: analysis of surgical experience with 73 cases. Neurosurgery 52(4):783–790 (discussion 790)
Yasui T, Hakuba A, Kim SH, Nishimura S (1989) Trigeminal neurinomas: operative approach in eight cases. J Neurosurg 71(4):506–511. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1989.71.4.0506
Taha JM, Tew JM Jr, van Loveren HR, Keller JT, el-Kalliny M (1995) Comparison of conventional and skull base surgical approaches for the excision of trigeminal neurinomas. J Neurosurg 82(5):719–725. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1995.82.5.0719
McCormick PC, Bello JA, Post KD (1988) Trigeminal schwannoma. Surgical series of 14 cases with review of the literature. J Neurosurg 69(6):850–860. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1988.69.6.0850
Sun J, Zhang J, Yu X, Qi S, Du Y, Ni W, Hu Y, Tian Z (2013) Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal schwannoma: a clinical retrospective study in 52 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 91(4):236–242. https://doi.org/10.1159/000345258
Yianni J, Dinca EB, Rowe J, Radatz M, Kemeny AA (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal schwannomas. Acta Neurochir 154(2):277–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1146-7
Peker S, Bayrakli F, Kilic T, Pamir MN (2007) Gamma-knife radiosurgery in the treatment of trigeminal schwannomas. Acta Neurochir 149(11):1133–1137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1285-9 (discussion 1137)
Kano H, Niranjan A, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Dade Lunsford L (2009) Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal schwannoma: tumor control and functional preservation Clinical article. J Neurosurg 110(3):553–558
Hasegawa T, Kato T, Iizuka H, Kida Y (2013) Long-term results for trigeminal schwannomas treated with gamma knife surgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87(5):1115–1121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.09.010
Kim KM, Park CK, Chung HT, Paek SH, Jung HW, Kim DG (2007) Long-term outcomes of gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery of vestibular schwannomas. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 42(4):286–292. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2007.42.4.286
Chopra R, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC (2007) Long-term follow-up of acoustic schwannoma radiosurgery with marginal tumor doses of 12 to 13 Gy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68(3):845–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.01.001
Hasegawa T, Kida Y, Yoshimoto M, Koike J (2007) Trigeminal schwannomas: results of gamma knife surgery in 37 cases. J Neurosurg 106(1):18–23. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2007.106.1.18
Nakamura H, Jokura H, Takahashi K, Boku N, Akabane A, Yoshimoto T (2000) Serial follow-up MR imaging after gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21(8):1540–1546
Nagano O, Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Ono J, Matsuda S, Yamakami I, Saeki N (2008) Transient expansion of vestibular schwannoma following stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 109(5):811–816. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns/2008/109/11/0811
Phi JH, Paek SH, Chung HT, Jeong SS, Park CK, Jung HW, Kim DG (2007) Gamma Knife surgery and trigeminal schwannoma: is it possible to preserve cranial nerve function? J Neurosurg 107(4):727–732. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns-07/10/0727
Rahmathulla G, Barnett GH (2011) Vestibular schwannoma of oscillating size: a case report and review of literature. Surg Neurol Int 2:187. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.91142
de Ipolyi AR, Yang I, Buckley A, Barbaro NM, Cheung SW, Parsa AT (2008) Fluctuating response of a cystic vestibular schwannoma to radiosurgery: case report. Neurosurgery 62(5):E1164–E1165. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000325880.13494.f2 (discussion E1165)
Pollock BE (2006) Management of vestibular schwannomas that enlarge after stereotactic radiosurgery: treatment recommendations based on a 15 year experience. Neurosurgery 58(2):241–248. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000194833.66593.8b (discussion 241–248)
Pan L, Wang EM, Zhang N, Zhou LF, Wang BJ, Dong YF, Dai JZ, Cai PW (2005) Long-term results of Leksell gamma knife surgery for trigeminal schwannomas. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):220–224
Pollock BE, Foote RL, Stafford SL (2002) Stereotactic radiosurgery: the preferred management for patients with nonvestibular schwannomas? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 52(4):1002–1007
Nettel B, Niranjan A, Martin JJ, Koebbe CJ, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2004) Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal schwannomas. Surg Neurol 62(5):435–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2004.02.035 (discussion 444–436).
Brisman R, Mooij R (2000) Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: dose-volume histograms of the brainstem and trigeminal nerve. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):155–158. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.supplement
Tuleasca C, Carron R, Resseguier N, Donnet A, Roussel P, Gaudart J, Levivier M, Regis J (2012) Patterns of pain-free response in 497 cases of classic trigeminal neuralgia treated with Gamma Knife surgery and followed up for least 1 year. J Neurosurg 117(Suppl):181–188. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.8.gks121015
Funding
There is no personal financial or institutional interest in any of the drugs, materials, or devices described in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, J., Lee, S.H., Choi, S.K. et al. Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal schwannoma: a 20-year experience with long-term treatment outcome. J Neurooncol 140, 89–97 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2934-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2934-1