Abstract
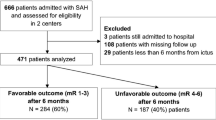
Advances in cancer treatment have dramatically increased long-term survivors. Prolonged survival increases comorbidity risk, but there is a paucity of studies on how cancer history alters clinical outcomes from subsequent diseases. This study aims to investigate whether positive cancer history influences clinical outcome following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). We retrospectively reviewed consecutive SAH patients admitted between January 2008 and March 2014. Medical histories, known SAH risk factors, and outcome were compared between SAH patients with and without cancer history. Out of the 498 SAH patients, 55 cases had cancer history, 438 cases had no cancer history and 5 cases had an unknown cancer history. Compared with SAH patients without cancer history, those with cancer history had poorer Hunt & Hess grade at SAH presentation (P = 0.021), and poorer modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score at discharge (P < 0.001). After adjustment for age, sex, modified Fisher, previous SAH, history of hypertension, current smoking status, and current alcohol consumption, positive cancer history remained an independent risk factor for poorer mRS0–6 [odds ratio (OR) = 2.25, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.28–3.94] and mRS6 (OR = 2.74, 95 % CI 1.40–5.37). Furthermore, stratified analysis by Hunt & Hess grade adjusted by age, sex, and modified Fisher scale, OR of poorer mRS0–6 was 2.12 (95 % CI 0.89–5.05) and OR of mRS6 was 3.68 (95 % CI 1.35–10.04). After adjustment of patients for demographic factors, classical risk factors for SAH and Hunt & Hess grade, previous cancer history is a risk factor for the poor functional outcome of SAH.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askoxylakis V, Thieke C, Pleger ST, Most P, Tanner J, Lindel K, Katus HA, Debus J, Bischof M (2010) Long-term survival of cancer patients compared to heart failure and stroke: a systematic review. BMC Cancer 10:105. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-105
Grisold W, Oberndorfer S, Struhal W (2009) Stroke and cancer: a review. Acta Neurol Scand 119:1–16. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2008.01059.x
Varki A (2007) Trousseau’s syndrome: multiple definitions and multiple mechanisms. Blood 110:1723–1729. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-10-053736
Cestari DM, Weine DM, Panageas KS, Segal AZ, DeAngelis LM (2004) Stroke in patients with cancer: incidence and etiology. Neurology 62:2025–2030
Zhang YY, Cordato D, Shen Q, Sheng AZ, Hung WT, Chan DK (2007) Risk factor, pattern, etiology and outcome in ischemic stroke patients with cancer: a nested case–control study. Cerebrovasc Dis 23:181–187. doi:10.1159/000097639
Zhang YY, Chan DK, Cordato D, Shen Q, Sheng AZ (2006) Stroke risk factor, pattern and outcome in patients with cancer. Acta Neurol Scand 114:378–383. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2006.00709.x
Rogers LR (2010) Cerebrovascular complications in patients with cancer. Semin Neurol 30:311–319. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1255224
Frontera JA, Claassen J, Schmidt JM, Wartenberg KE, Temes R, Connolly ES Jr, MacDonald RL, Mayer SA (2006) Prediction of symptomatic vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: the modified fisher scale. Neurosurgery 59:21–27; discussion 21–27. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000218821.34014.1B
Bath PM, Lees KR, Schellinger PD, Altman H, Bland M, Hogg C, Howard G, Saver JL, European Stroke Organisation Outcomes Working G (2012) Statistical analysis of the primary outcome in acute stroke trials. Stroke 43:1171–1178. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.641456
Hamdan A, Barnes J, Mitchell P (2014) Subarachnoid hemorrhage and the female sex: analysis of risk factors, aneurysm characteristics, and outcomes. J Neurosurg 121:1367–1373. doi:10.3171/2014.7.JNS132318
Rosengart AJ, Schultheiss KE, Tolentino J, Macdonald RL (2007) Prognostic factors for outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 38:2315–2321. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.484360
Andreasen TH, Bartek J Jr, Andresen M, Springborg JB, Romner B (2013) Modifiable risk factors for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 44:3607–3612. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001575
Yamada S, Koizumi A, Iso H, Wada Y, Watanabe Y, Date C, Yamamoto A, Kikuchi S, Inaba Y, Toyoshima H, Kondo T, Tamakoshi A, Japan Collaborative Cohort Study G (2003) Risk factors for fatal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the Japan Collaborative Cohort Study. Stroke 34:2781–2787. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000103857.13812.9A
Juvela S (2003) Prehemorrhage risk factors for fatal intracranial aneurysm rupture. Stroke 34:1852–1857. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000080380.56799.DD
Lantigua H, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Schmidt JM, Lee K, Badjatia N, Agarwal S, Claassen J, Connolly ES, Mayer SA (2015) Subarachnoid hemorrhage: who dies, and why? Crit Care 19:309. doi:10.1186/s13054-015-1036-0
Mocco J, Ransom ER, Komotar RJ, Schmidt JM, Sciacca RR, Mayer SA, Connolly ES Jr (2006) Preoperative prediction of long-term outcome in poor-grade aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 59:529–538; discussion 529–538. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000228680.22550.A2
Pegoli M, Mandrekar J, Rabinstein AA, Lanzino G (2015) Predictors of excellent functional outcome in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 122:414–418. doi:10.3171/2014.10.JNS14290
Pan YX, Chen KF, Lin YX, Wu W, Zhou XM, Zhang XS, Zhang X, Shi JX (2013) Intracisternal administration of SB203580, a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, attenuates cerebral vasospasm via inhibition of tumor-necrosis factor-alpha. J Clin Neurosci 20:726–730. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2012.09.012
Hooning MJ, Dorresteijn LD, Aleman BM, Kappelle AC, Klijn JG, Boogerd W, van Leeuwen FE (2006) Decreased risk of stroke among 10-year survivors of breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:5388–5394. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.5516
Budczies J, von Winterfeld M, Klauschen F, Kimmritz AC, Daniel JM, Warth A, Endris V, Denkert C, Pfeiffer H, Weichert W, Dietel M, Wittschieber D, Stenzinger A (2014) Comprehensive analysis of clinico-pathological data reveals heterogeneous relations between atherosclerosis and cancer. J Clin Pathol 67:482–490. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2013-202148
Navi BB, Reichman JS, Berlin D, Reiner AS, Panageas KS, Segal AZ, DeAngelis LM (2010) Intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage in patients with cancer. Neurology 74:494–501. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181cef837
Koppelmans V, Schagen SB, Poels MM, Boogerd W, Seynaeve C, van der Lugt A, Breteler MM (2011) Incidental findings on brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging in long-term survivors of breast cancer treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer 47:2531–2536. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.026
Li F, Downing BD, Smiley LC, Mund JA, Distasi MR, Bessler WK, Sarchet KN, Hinds DM, Kamendulis LM, Hingtgen CM, Case J, Clapp DW, Conway SJ, Stansfield BK, Ingram DA Jr (2014) Neurofibromin-deficient myeloid cells are critical mediators of aneurysm formation in vivo. Circulation 129:1213–1224. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.006320
Rea D, Brandsema JF, Armstrong D, Parkin PC, deVeber G, MacGregor D, Logan WJ, Askalan R (2009) Cerebral arteriopathy in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Pediatrics 124:e476–e483. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-0152
Jeong WK, Park SW, Lee SH, Kim CW (2008) Brachial artery aneurysm rupture in a patient with neurofibromatosis: a case report. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 16:247–250
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shibahara, I., Watanabe, T., Ezura, M. et al. Clinical features of subarachnoid hemorrhage in patients with positive cancer history. J Neurooncol 128, 129–136 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2085-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2085-1