Abstract
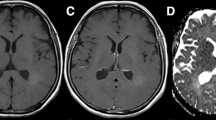
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) MRI sequences have become an indispensible tool for defining the malignant boundary in patients with brain tumors by nulling the signal contribution from cerebrospinal fluid allowing both regions of edema and regions of non-enhancing, infiltrating tumor to become hyperintense on resulting images. In the current study we examined the utility of a three-dimensional double inversion recovery (DIR) sequence that additionally nulls the MR signal associated with white matter, implemented either pre-contrast or post-contrast, in order to determine whether this sequence allows for better differentiation between tumor and normal brain tissue. T1- and T2-weighted, FLAIR, dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC)-MRI estimates of cerebral blood volume (rCBV), contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images (T1+C), and DIR data (pre- or post-contrast) were acquired in 22 patients with glioblastoma. Contrast-to-noise (CNR) and tumor volumes were compared between DIR and FLAIR sequences. Line profiles across regions of tumor were generated to evaluate similarities between image contrasts. Additionally, voxel-wise associations between DIR and other sequences were examined. Results suggested post-contrast DIR images were hyperintense (bright) in regions spatially similar those having FLAIR hyperintensity and hypointense (dark) in regions with contrast-enhancement or elevated rCBV due to the high sensitivity of 3D turbo spin echo sequences to susceptibility differences between different tissues. DIR tumor volumes were statistically smaller than tumor volumes as defined by FLAIR (Paired t test, P = 0.0084), averaging a difference of approximately 14 mL or 24 %. DIR images had approximately 1.5× higher lesion CNR compared with FLAIR images (Paired t test, P = 0.0048). Line profiles across tumor regions and scatter plots of voxel-wise coherence between different contrasts confirmed a positive correlation between DIR and FLAIR signal intensity and a negative correlation between DIR and both post-contrast T1-weighted image signal intensity and rCBV. Additional discrepancies between FLAIR and DIR abnormal regions were also observed, together suggesting DIR may provide additional information beyond that of FLAIR.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lima FR, Kahn SA, Soletti RC, Biasoli D, Alves T, da Fonseca AC, Garcia C, Romao L, Brito J, Holanda-Afonso R, Faria J, Borges H, Moura-Neto V (1826) Glioblastoma: therapeutic challenges, what lies ahead. Biochim Biophys Acta 338–349:2012
Mouthuy N, Cosnard G, Abarca-Quinones J, Michoux N (2011) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging to differentiate high-grade gliomas and brain metastases. J Neuroradiol 39(5):301–307
Iliadis G, Kotoula V, Chatzisotiriou A, Televantou D, Eleftheraki AG, Lambaki S, Misailidou D, Selviaridis P, Fountzilas G (2012) Volumetric and MGMT parameters in glioblastoma patients: survival analysis. BMC Cancer 12:3
Farace P, Giri MG, Meliado G, Amelio D, Widesott L, Ricciardi GK, Dall’Oglio S, Rizzotti A, Sbarbati A, Beltramello A, Maluta S, Amichetti M (2011) Clinical target volume delineation in glioblastomas: pre-operative versus post-operative/pre-radiotherapy MRI. Br J Radiol 84:271–278
Tsuchiya K, Mizutani Y, Hachiya J (1996) Preliminary evaluation of fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery MR in the diagnosis of intracranial tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:1081–1086
Husstedt HW, Sickert M, Kostler H, Haubitz B, Becker H (2000) Diagnostic value of the fast-FLAIR sequence in MR imaging of intracranial tumors. Eur Radiol 10:745–752
Essig M, Hawighorst H, Schoenberg SO, Engenhart-Cabillic R, Fuss M, Debus J, Zuna I, Knopp MV, van Kaick G (1998) Fast fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery (FLAIR) MRI in the assessment of intraaxial brain tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:789–798
Geurts JJ, Pouwels PJ, Uitdehaag BM, Polman CH, Barkhof F, Castelijns JA (2005) Intracortical lesions in multiple sclerosis: improved detection with 3D double inversion-recovery MR imaging. Radiology 236:254–260
Bedekar D, Jensen T, Schmainda KM (2010) Standardization of relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) image maps for ease of both inter- and intrapatient comparisons. Magn Reson Med 64:907–913
Ellingson BM, Cloughesy TF, Lai A, Nghiemphu PL, Mischel PS, Pope WB (2011) Quantitative volumetric analysis of conventional MRI response in recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab. Neuro Oncol 13:401–409
Pope WB, Sayre J, Perlina A, Villablanca JP, Mischel PS, Cloughesy TF (2005) MR imaging correlates of survival in patients with high-grade gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2466–2474
Pope WB, Chen JH, Dong J, Carlson MR, Perlina A, Cloughesy TF, Liau LM, Mischel PS, Nghiemphu P, Lai A, Nelson SF (2008) Relationship between gene expression and enhancement in glioblastoma multiforme: exploratory DNA microarray analysis. Radiology 249:268–277
Felsberg GJ, Silver SA, Brown MT, Tien RD (1994) Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Gliomatosis cerebri. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1745–1753
Seewann A, Kooi EJ, Roosendaal SD, Pouwels PJ, Wattjes MP, van der Valk P, Barkhof F, Polman CH, Geurts JJ (2012) Postmortem verification of MS cortical lesion detection with 3D DIR. Neurology 78:302–308
Coebergh JA, Roosendaal SD, Polman CH, Geurts JJ, van Woerkom TC (2010) Acute severe memory impairment as a presenting symptom of multiple sclerosis: a clinical case study with 3D double inversion recovery MR imaging. Mult Scler 16:1521–1524
Simon B, Schmidt S, Lukas C, Gieseke J, Traber F, Knol DL, Willinek WA, Geurts JJ, Schild HH, Barkhof F, Wattjes MP (2010) Improved in vivo detection of cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis using double inversion recovery MR imaging at 3 Tesla. Eur Radiol 20(7):1675–1683
Moraal B, Roosendaal SD, Pouwels PJ, Vrenken H, van Schijndel RA, Meier DS, Guttmann CR, Geurts JJ, Barkhof F (2008) Multi-contrast, isotropic, single-slab 3D MR imaging in multiple sclerosis. Eur Radiol 18:2311–2320
Roosendaal SD, Moraal B, Vrenken H, Castelijns JA, Pouwels PJ, Barkhof F, Geurts JJ (2008) In vivo MR imaging of hippocampal lesions in multiple sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(4):726–731
Wattjes MP, Lutterbey GG, Gieseke J, Traber F, Klotz L, Schmidt S, Schild HH (2007) Double inversion recovery brain imaging at 3T: diagnostic value in the detection of multiple sclerosis lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:54–59
Geurts JJ, Roosendaal SD, Calabrese M, Ciccarelli O, Agosta F, Chard DT, Gass A, Huerga E, Moraal B, Pareto D, Rocca MA, Wattjes MP, Yousry TA, Uitdehaag BM, Barkhof F (2011) Consensus recommendations for MS cortical lesion scoring using double inversion recovery MRI. Neurology 76:418–424
Morimoto E, Kanagaki M, Okada T, Yamamoto A, Mori N, Matsumoto R, Ikeda A, Mikuni N, Kunieda T, Paul D, Miyamoto S, Takahashi R, Togashi K (2012) Anterior temporal lobe white matter abnormal signal (ATLAS) as an indicator of seizure focus laterality in temporal lobe epilepsy: comparison of double inversion recovery, FLAIR and T2W MR imaging. Eur Radiol 23(1):3–11
Rugg-Gunn FJ, Boulby PA, Symms MR, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2006) Imaging the neocortex in epilepsy with double inversion recovery imaging. Neuroimage 31(1):39–50
Li Q, Zhang Q, Sun H, Zhang Y, Bai R (2011) Double inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging at 3 T: diagnostic value in hippocampal sclerosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 35:290–293
Zhang Q, Li Q, Zhang J, Zhang Y (2011) Double inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the preoperative evaluation of hippocampal sclerosis: correlation with volumetric measurement and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS). J Comput Assist Tomogr 35:406–410
Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Li Q (2011) Double inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging of subcortical band heterotopia: a report of 2 cases. J Comput Assist Tomogr 35:31–32
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Turetschek K, Wunderbaldinger P, Bankier AA, Zontsich T, Graf O, Mallek R, Hittmair K (1998) Double inversion recovery imaging of the brain: initial experience and comparison with fluid attenuated inversion recovery imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 16:127–135
Sethi V, Yousry TA, Muhlert N, Ron M, Golay X, Wheeler-Kingshott C, Miller DH, Chard DT (2012) Improved detection of cortical MS lesions with phase-sensitive inversion recovery MRI. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:877–882
Nelson F, Poonawalla AH, Hou P, Huang F, Wolinsky JS, Narayana PA (2007) Improved identification of intracortical lesions in multiple sclerosis with phase-sensitive inversion recovery in combination with fast double inversion recovery MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1645–1649
Funding
UCLA Institute for Molecular Medicine Seed Grant (BME); UCLA Radiology Exploratory Research Grant (BME); University of California Cancer Research Coordinating Committee Grant (BME); ACRIN Young Investigator Initiative Grant (BME); Art of the Brain (TFC); Ziering Family Foundation in memory of Sigi Ziering (TFC); Singleton Family Foundation (TFC); Clarence Klein Fund for Neuro-Oncology (TFC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harris, R.J., Cloughesy, T.F., Pope, W.B. et al. Pre- and post-contrast three-dimensional double inversion-recovery MRI in human glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 112, 257–266 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1057-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1057-y