Abstract
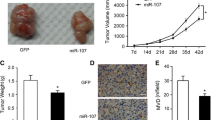
Angiogenesis is the hallmark of malignant gliomas positively correlated with the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression. We previously reported that expression levels of Nodal, a member of transforming growth factor-β super family, correlate with the malignant invasive behavior of human glioma cells. In this study, we show that knockdown of Nodal suppresses glioma angiogenesis by inhibition of VEGF. In human primary glioma specimens, expression of Nodal positively correlates with WHO glioma tumor grades and expression of VEGF in the corresponding glioma specimens. In human U87MG glioma cells, knockdown of endogenous Nodal by RNA interference (RNAi) significantly decreases colony formation and secretion of VEGF. In vivo, cellular depletion of Nodal in U87MG inhibited brain glioma growth and prolonged the survival of mice with U87MG/shNodal glioma compared with controls. Inhibition of Nodal suppressed tumor vessel growth in U87MG gliomas. Using Nodal inhibitor (SB431542), silencing Nodal, or overexpressing Nodal in the U87MG, GBM8401, and GBM glioma cells, our further experiments revealed that Nodal-induced VEGF expression might, at least in part, mediate through the ERK1/2-HIF-1α-mediated signaling pathway. Taken together, our data revealed that alteration of Nodal expression in glioma cells resulted in changes to VEGF secretion, and subsequent colony formation, in vivo tumor growth, and angiogenesis, all of which are consistent with the regulation of VEGF through the ERK1/2-HIF-1α-mediated signaling, suggesting that Nodal may serve as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of human gliomas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Fischer I, Gagner JP, Law M, Newcomb EW, Zagzag D (2005) Angiogenesis in gliomas: biology and molecular pathophysiology. Brain Pathol 15:297–310
Ma HI, Guo P, Li J, Lin SZ, Chiang YH, Xiao X, Cheng SY (2002) Suppression of intracranial human glioma growth after intramuscular administration of an adeno-associated viral vector expressing angiostatin. Cancer Res 62:756–763
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Folkman J (2006) Angiogenesis. Annu Rev Med 57:1–18
Jensen RL, Ragel BT, Whang K, Gillespie D (2006) Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) decreases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion and tumor growth in malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol 78:233–247
Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT (2007) Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:610–622
Ma HI, Lin SZ, Chiang YH, Li J, Chen SL, Tsao YP, Xiao X (2002) Intratumoral gene therapy of malignant brain tumor in a rat model with angiostatin delivered by adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector. Gene Ther 9:2–11
Kirsch M, Schackert G, Black PM (2000) Anti-angiogenic treatment strategies for malignant brain tumors. J Neurooncol 50:149–163
Norden AD, Drappatz J, Wen PY (2008) Novel anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant gliomas. Lancet Neurol 7:1152–1160
Cheng SY, Huang HJ, Nagane M, Ji XD, Wang D, Shih CC, Arap W, Huang CM, Cavenee WK (1996) Suppression of glioblastoma angiogenicity and tumorigenicity by inhibition of endogenous expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8502–8507
Chamberlain MC (2008) Antiangiogenic blockage: a new treatment for glioblastoma. Expert opinion on biological therapy 8:1449–1453
Millauer B, Shawver LK, Plate KH, Risau W, Ullrich A (1994) Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature 367:576–579
Kaminska B, Wesolowska A, Danilkiewicz M (2005) TGF beta signalling and its role in tumour pathogenesis. Acta Biochim Pol 52:329–337
Wick W, Naumann U, Weller M (2006) Transforming growth factor-beta: a molecular target for the future therapy of glioblastoma. Curr Pharm Des 12:341–349
Postovit LM, Margaryan NV, Seftor EA, Hendrix MJ (2008) Role of nodal signaling and the microenvironment underlying melanoma plasticity. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 21:348–357
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Kasemeier-Kulesa J, Kulesa PM, Postovit LM (2007) Reprogramming metastatic tumour cells with embryonic microenvironments. Nature Rev 7:246–255
Postovit LM, Costa FF, Bischof JM, Seftor EA, Wen B, Seftor RE, Feinberg AP, Soares MB, Hendrix MJ (2007) The commonality of plasticity underlying multipotent tumor cells and embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biochem 101:908–917
Topczewska JM, Postovit LM, Margaryan NV, Sam A, Hess AR, Wheaton WW, Nickoloff BJ, Topczewski J, Hendrix MJ (2006) Embryonic and tumorigenic pathways converge via Nodal signaling: role in melanoma aggressiveness. Nat Med 12:925–932
Lee CC, Jan HJ, Lai JH, Ma HI, Hueng DY, Gladys Lee YC, Cheng YY, Liu LW, Wei HW, Lee HM (2010) Nodal promotes growth and invasion in human gliomas. Oncogene 29:3110–3123
Postovit LM, Margaryan NV, Seftor EA, Kirschmann DA, Lipavsky A, Wheaton WW, Abbott DE, Seftor RE, Hendrix MJ (2008) Human embryonic stem cell microenvironment suppresses the tumorigenic phenotype of aggressive cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:4329–4334
Strizzi L, Postovit LM, Margaryan NV, Seftor EA, Abbott DE, Seftor RE, Salomon DS, Hendrix MJ (2008) Emerging roles of nodal and Cripto-1: from embryogenesis to breast cancer progression. Breast Dis 29:91–103
Hjelmeland MD, Hjelmeland AB, Sathornsumetee S, Reese ED, Herbstreith MH, Laping NJ, Friedman HS, Bigner DD, Wang XF, Rich JN (2004) SB-431542, a small molecule transforming growth factor-beta-receptor antagonist, inhibits human glioma cell line proliferation and motility. Mol Cancer Ther 3:737–745
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, Williams PM, Modrusan Z, Feuerstein BG, Aldape K (2006) Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 9:157–173
Lin YM, Jan HJ, Lee CC, Tao HY, Shih YL, Wei HW, Lee HM (2008) Dexamethasone reduced invasiveness of human malignant glioblastoma cells through a MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) dependent mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol 593:1–9
Jan HJ, Lee CC, Shih YL, Hueng DY, Ma HI, Lai JH, Wei HW, Lee HM (2010) Osteopontin regulates human glioma cell invasiveness and tumor growth in mice. Neuro Oncol 12:58–70
Dennie J, Mandeville JB, Boxerman JL, Packard SD, Rosen BR, Weisskoff RM (1998) NMR imaging of changes in vascular morphology due to tumor angiogenesis. Magn Reson Med 40:793–799
Jang T, Sathy B, Hsu YH, Merchant M, Recht B, Chang C, Recht L (2008) A distinct phenotypic change in gliomas at the time of magnetic resonance imaging detection. J Neurosurg 108:782–790
Tseng KY, Chung MH, Sytwu HK, Lee HM, Chen KY, Chang C, Lin CK, Yen CH, Chen JH, Lin GJ, Ma HI, Yeh YS, Ju DT, Liu MY, Hueng DY (2010) Osteopontin expression is a valuable marker for prediction of short-term recurrence in WHO grade I benign meningiomas. J Neurooncol 100:217–223
Wenger RH, Gassmann M (1997) Oxygen(es) and the hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Biol Chem 378:609–616
Wang XL, Xu R, Wu X, Gillespie D, Jensen R, Lu ZR (2009) Targeted systemic delivery of a therapeutic siRNA with a multifunctional carrier controls tumor proliferation in mice. Mol Pharm 6:738–746
Korkolopoulou P, Patsouris E, Konstantinidou AE, Pavlopoulos PM, Kavantzas N, Boviatsis E, Thymara I, Perdiki M, Thomas-Tsagli E, Angelidakis D, Rologis D, Sakkas D (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha/vascular endothelial growth factor axis in astrocytomas. Associations with microvessel morphometry, proliferation and prognosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 30:267–278
Gillespie DL, Flynn JR, Ragel BT, Arce-Larreta M, Kelly DA, Tripp SR, Jensen RL (2009) Silencing of HIF-1alpha by RNA interference in human glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Methods Mol Biol 487:283–301
Kaynar MY, Sanus GZ, Hnimoglu H, Kacira T, Kemerdere R, Atukeren P, Gumustas K, Canbaz B, Tanriverdi T (2008) Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha in tumors of patients with glioblastoma multiforme and transitional meningioma. J Clin Neurosci 15:1036–1042
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH, Kim KW (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) alpha: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med 36:1–12
Woods SA, McGlade CJ, Guha A (2002) Phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and MAPK/ERK kinase 1/2 differentially regulate expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human malignant astrocytoma cells. Neuro Oncol 4:242–252
Mandell JW, Hussaini IM, Zecevic M, Weber MJ, VandenBerg SR (1998) In situ visualization of intratumor growth factor signaling: immunohistochemical localization of activated ERK/MAP kinase in glial neoplasms. Am J Pathol 153:1411–1423
Sonoda Y, Kanamori M, Deen DF, Cheng SY, Berger MS, Pieper RO (2003) Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms drives oxygenation and growth but not progression to glioblastoma multiforme in a human model of gliomagenesis. Cancer Res 63:1962–1968
Acknowledgments
Shi-Yuan Cheng and Jia-Jean Yiin (University of Pittsburgh, Cancer Institute and Department of Pathology) provided us with invaluable suggestions in editing this manuscript. This study was supported by grants TSGH-C99-072, TSGH-C99-073, TSGH-C99-074, and TSGH-C99-149 (Dueng-Yuan Hueng) from the Tri-Service General Hospital; the grant B971113 from the Teh-Tzer Study Group for Human Medical Research Foundation, and in part by the Foundation for Advancement of Education, Sciences and Medicine, and grants DOH99-TD-B-111-003 and DOH99-TD-C-111-008 from Taiwan Department of Health for Taipei Medical University-the Center of Excellence for Clinical Trial and Research in Neuroscience, and the Center of Excellence for Cancer Research. We thank the technical support from the Functional and Micro-Magnetic Resonance Imaging Center supported by the National Research Program for Genomic Medicine, National Science Council, NSC95-3112-B-001-009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hueng, DY., Lin, GJ., Huang, SH. et al. Inhibition of Nodal suppresses angiogenesis and growth of human gliomas. J Neurooncol 104, 21–31 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0467-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0467-3