Abstract
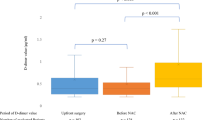
The efficacy of combined serum d-dimer level measurement and Doppler ultrasonography of the lower extremity was investigated for screening of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with neuroepithelial tumor. Eighty-one patients with neuroepithelial tumor were prospectively studied. All patients underwent measurement of serum d-dimer levels and Doppler ultrasonography of the lower extremity. The serum d-dimer level was measured every week, and Doppler ultrasonography was performed two and two weeks after surgery, then every two weeks until discharge, or every two weeks for patients who did not undergo surgery. If the serum d-dimer level increased over 10.0 μg/ml, Doppler ultrasonography or computed tomography was performed to detect VTE. VTE occurred in 12 (14.8%) patients (seven males and five females; age 34–75, mean 59.0 years). Only one patient was symptomatic, whereas 11 patients identified by the screening were without symptoms. Five patients were treated with anticoagulant therapy, one with prophylactic inferior vena cava filter placement with anticoagulant therapy, and the other six were closely followed up without medication. No patient died of pulmonary embolism. Serial Doppler ultrasonography showed thrombus regression or organization and no thrombus extension. The maximum serum d-dimer value was significantly higher in patients with VTE than in those without VTE (mean 14.5 vs. 3.46 μg/ml, P < 0.001). The d-dimer cutoff value of 5.4 μg/ml could be used to identify VTE with 83% sensitivity and 84% specificity. The combination of sequential serum d-dimer measurement and Doppler ultrasonography of the lower extremity is an efficient and non-invasive procedure for identifying asymptomatic VTE in patients with neuroepithelial tumor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heit JA, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN, Petterson TM, O’Fallon WM, Melton LJ III (2000) Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population-based case–control study. Arch Intern Med 160:809–815
Khorana AA (2003) Malignancy, thrombosis and Trousseau: the case for an eponym. J Thromb Haemost 1:2463–2465
Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM, Lyman GH (2007) Frequency, risk factors, and trends for venous thromboembolism among hospitalized cancer patients. Cancer 110:2339–2346
Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM, Lyman GH (2007) Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J Thromb Haemost 5:632–634
Chew HK, Wun T, Harvey D, Zhou H, White RH (2006) Incidence of venous thromboembolism and its effect on survival among patients with common cancers. Arch Intern Med 166:458–464
Sorensen HT, Mellemkjaer L, Olsen JH, Baron JA (1000) Prognosis of cancers associated with venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 343:1846–1850
Agnelli G, Piovella F, Buoncristiani P, Severi P, Pini M, D’Angelo A, Beltrametti C, Damiani M, Andrioli GC, Pugliese R, Iorio A, Brambilla G (1998) Enoxaparin plus compression stockings compared with compression stockings alone in the prevention of venous thromboembolism after elective neurosurgery. N Engl J Med 339:80–85
Semrad TJ, O’Donnell R, Wun T, Chew H, Harvey D, Zhou H, White RH (2007) Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in 9489 patients with malignant glioma. J Neurosurg 106:601–608
Stein PD, Beemath A, Meyers FA, Skaf E, Sanchez J, Olson RE (2006) Incidence of venous thromboembolism in patients hospitalized with cancer. Am J Med 119:60–68
Mack WJ, Ducruet AF, Hickman ZL, Kalyvas JT, Cleveland JR, Mocco J, Schmidt M, Mayer SA, Connolly ES Jr (2008) Doppler ultrasonography screening of poor-grade subarachnoid hemorrhage patients increases the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Neurol Res 9:889–892
Becker DM, Philbrick JT, Abbitt PL (1989) Real-time ultrasonography for the diagnosis of lower extremity deep venous thrombosis. The wave of the future? Arch Intern Med 8:1731–1734
Cogo A, Lensing AW, Wells P, Prandoni P, Buller HR (1995) Noninvasive objective tests for the diagnosis of clinically suspected deep-vein thrombosis. Haemostasis 1–2:27–39
Gottlieb RH, Widjaja J, Tian L, Rubens DJ, Voci SL (1999) Calf sonography for detecting deep venous thrombosis in symptomatic patients: experience and review of the literature. J Clin Ultrasound 8:415–420
Kassaï B, Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Sonie S, Shah NR, Leizorovicz A (2004) A systematic review of the accuracy of ultrasound in the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis in asymptomatic patients. Thromb Haemost 4:655–666
Kearon C, Julian JA, Newman TE, Ginsberg JS (1998) Noninvasive diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. McMaster Diagnostic Imaging Practice Guidelines Initiative. Ann Intern Med 8:663–677
Mustafa BO, Rathbun SW, Whitsett TL, Raskob GE (2002) Sensitivity and specificity of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of upper extremity deep vein thrombosis: a systematic review. Arch Intern Med 4:401–404
Segal JB, Eng J, Tamariz LJ, Bass EB (2007) Review of the evidence on diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Ann Fam Med 5:63–73
Wells PS, Lensing AW, Davidson BL, Prins MH, Hirsh J (1995) Accuracy of ultrasound for the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis in asymptomatic patients after orthopedic surgery. A meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 1:47–53
White RH, McGahan JP, Daschbach MM, Hartling RP (1989) Diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis using duplex ultrasound. Ann Intern Med 111:297–304
Prisco D, Grifoni E (2009) The role of d-dimer testing in patients with suspected venous thromboembolism. Semin Thromb Hemost 35:50–59
Brown MD, Rowe BH, Reeves MJ, Bermingham JM, Goldhaber SZ (2002) The accuracy of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay d-dimer test in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a meta-analysis. Ann Emerg Med 2:133–144
Brown MD, Lau J, Nelson RD, Kline JA (2003) Turbidimetric d-dimer test in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a metaanalysis. Clin Chem 11:1846–1853
Heim SW, Schectman JM, Siadaty MS, Philbrick JT (2004) d-dimer testing for deep venous thrombosis: a metaanalysis. Clin Chem 7:1136–1147
Kobayashi T (2004) [Pulmonary thromboembolism. Deep vein thrombosis (venous thromboembolism)]. Acta Obstet Gynaecol Jpn 56:382–391
Stein PD, Hull RD, Patel KC, Olson RE, Ghali WA, Brant R, Biel RK, Bharadia V, Kalra NK (2004) d-dimer for the exclusion of acute venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 8:589–602
Louis ND (ed) (2007) WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. IARC, Lyon
Laporte S, Mismetti P, Décousus H, Uresandi F, Otero R, Lobo JL, Monreal M et al (2008) Clinical predictors for fatal pulmonary embolism in 15,520 patients with venous thromboembolism: findings from the Registro Informatizado de la Enfermedad TromboEmbolica venosa (RIETE) Registry. Circulation 117:1711–1716
Levitan N, Dowlati A, Remick SC, Tahsildar HI, Sivinski LD, Beyth R, Rimm AA (1999) Rates of initial and recurrent thromboembolic disease among patients with malignancy versus those without malignancy. Risk analysis using Medicare claims data. Medicine 78:285–291
Kawaguchi T, Kumabe T, Kanamori M, Yamashita Y, Sonoda Y, Watanabe M, Tominaga T (2009) [Venous thromboembolism in patients with malignant glioma]. Jpn J Neurosurg 18:294–299
Brandes AA, Scelzi E, Salmistraro G, Ermani M, Carollo C, Berti F, Zampieri P, Baiocchi C, Fiorentino MV (1997) Incidence of risk of thromboembolism during treatment high-grade gliomas: a prospective study. Eur J Cancer 33:1592–1596
Simanek R, Vormittag R, Hassler M, Roessler K, Schwarz M, Zielinski C, Pabinger I, Marosi C (2007) Venous thromboembolism and survival in patients with high-grade glioma. Neurooncology 9:89–95
Ay C, Vormittag R, Dunkler D, Simanek R, Chiriac AL, Drach J, Quehenberger P, Wagner O, Zielinski C, Pabinger I (2009) d-dimer and prothrombin fragment 1 + 2 predict venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer: results from the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study. J Clin Oncol 27:4124–4129
Eichinger S, Minar E, Bialonczyk C, Hirschl M, Quehenberger P, Schneider B, Weltermann A, Wagner O, Kyrle PA (2003) d-dimer levels and risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism. JAMA 290:1071–1074
Palareti G, Legnani C, Cosmi B, Guazzaloca G, Pancani C, Coccheri S (2002) Risk of venous thromboembolism recurrence: high negative predictive value of d-dimer performed after oral anticoagulation is stopped. Thromb Haemost 87:7–12
Palareti G, Legnani C, Cosmi B, Valdré L, Lunghi B, Bernardi F, Coccheri S (2003) Predictive value of d-dimer test for recurrent venous thromboembolism after anticoagulation withdrawal in subjects with a previous idiopathic event and in carriers of congenital thrombophilia. Circulation 108:313–318
Kirwan CC, McDowell G, McCollum CN, Kumar S, Byrne GJ (2008) Early changes in the haemostatic and procoagulant systems after chemotherapy for breast cancer. Br J Cancer 99:1000–1006
Satoh T, Matsumoto K, Uno K, Sakurai M, Okada S, Onuki M, Minaguchi T, Tanaka YO, Homma S, Oki A, Yoshikawa H (2008) Silent venous thromboembolism before treatment in endometrial cancer and the risk factors. Br J Cancer 99:1034–1039
Ray WZ, Strom RG, Blackburn SL, Ashley WW, Sicard GA, Rich KM (2009) Incidence of deep venous thrombosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 110:1010–1014
Seidel AC, Cavalheri G Jr, Miranda F Jr (2008) The role of duplex ultrasonography in the diagnosis of lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis in non-hospitalized patients. Int Angiol 5:377–384
McQueen AS, Elliott ST, Keir MJ (2009) Ultrasonography for suspected deep vein thrombosis: how useful is single-point augmentation? Clin Radiol 2:148–155
Agnelli G, Radicchia S, Nenci GG (1995) Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis in asymptomatic high-risk patients. Haemostasis 25:40–48
Nurmohamed MT, van Riel AM, Henkens CM, Koopman MM, Que GT, d’Azemar P, Büller HR, ten Cate JW, Hoek JA, van der Meer J, van der Heul C, Turpie AG, Haley S, Sicurella A, Gent M (1996) Low molecular weight heparin and compression stockings in the prevention of venous thromboembolism in neurosurgery. Thromb Haemost 75:233–238
Collen JF, Jackson JL, Shorr AF, Moores LK (2008) Prevention of venous thromboembolism in neurosurgery: a metaanalysis. Chest 134:237–249
Danish SF, Burnett MG, Ong JG, Sonnad SS, Maloney-Wilensky E, Stein SC (2005) Prophylaxis for deep venous thrombosis in craniotomy patients: a decision analysis. Neurosurgery 56:1286–1292
Seinturier C, Bosson JL, Colonna M, Imbert B, Carpentier PH (2005) Site and clinical outcome of deep vein thrombosis of the lower limbs: an epidemiological study. J Thromb Haemost 3:1362–1367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawaguchi, T., Kumabe, T., Kanamori, M. et al. Early detection of venous thromboembolism in patients with neuroepithelial tumor: efficacy of screening with serum d-dimer measurements and Doppler ultrasonography. J Neurooncol 101, 495–504 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0276-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0276-8