Abstract
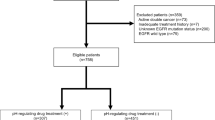
Introduction Erlotinib and Gefitinib (EGFRi) are small molecules specifically inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). We present here data of an exploratory study evaluating EGFRi monotherapy in patients with recurrent or progressive malignant glioma. Patients 21 patients with recurrent or progressive malignant glioma were included in this study. EGFRi treatment was started at a median of 1.8 years (range 0.54 to 10.95) after initial surgery. 20/21 patients had undergone radiotherapy and all patients had received at least one (range 1 to 5, median 2) line of systemic antineoplastic therapy. Patients received 100 or 150 mg Erlotinib or 250 mg Gefitinib orally per day. Results Median age at primary diagnosis was 47.9 years (range 31.9 to 76 years). 18 patients received a total of 92.8 months (median 3.03) of Erlotinib treatment and 3 patients received a total of 16.1 months (median 6.06) of Gefitinib treatment. The best responses were partial remission in one patient receiving Erlotinib and in two patients receiving Gefitinib, respectively. Median time to progression was 3.05 months. Six months after start of EGFRi treatment, 4/21 (19%) patients were progression-free and 6/21(29%) patients were alive. Expression of EGFRwt, EGFRvIII, PTEN, phospho-Akt or EGFRvIII/PTEN co-expression in tumor cells did not significantly associate with time to progression or survival time. In one patient EGFRi administration had to be discontinued due to toxicity (grade 3 rash). Conclusion EGFRi monotherapy is associated with therapeutic efficacy in only a small fraction of patients with malignant gliomas. Biomarkers reliably predicting tumor response to EGFRi need to be identified.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Hegi ME, van den Bent MJ et al (2006) Changing paradigms–an update on the multidisciplinary management of malignant glioma. Oncologist 11:165–180
Louis N, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavanee WK (eds) (2007) World Health Organization classification of tumours of the central nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2007) Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol 170:1445–1453
Aldape KD, Ballman K, Furth A et al (2004) Immunohistochemical detection of EGFRvIII in high malignancy grade astrocytomas and evaluation of prognostic significance. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:700–707
Shinojima N, Tada K, Shiraishi S et al (2003) Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 63:6962–6970
Learn CA, Hartzell TL, Wikstrand CJ et al (2004) Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition by mutant epidermal growth factor receptor variant III contributes to the neoplastic phenotype of glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res 10:3216–3224
Haas-Kogan DA, Prados MD, Tihan T et al (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor, protein kinase B/Akt, and glioma response to erlotinib. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:880–887
Kuan CT, Wikstrand CJ, Bigner DD (2001) EGF mutant receptor vIII as a molecular target in cancer therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer 8:83–96
Normanno N, De Luca A, Bianco C et al (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene 366:2–16
Bareschino MA, Schettino C, Troiani T et al (2007) Erlotinib in cancer treatment. Ann Oncol 18(Suppl 6):vi35–41
Rocha-Lima CM, Soares HP, Raez LE et al (2007) EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control 14:295–304
Prados MD, Lamborn KR, Chang S et al (2006) Phase 1 study of erlotinib HCl alone and combined with temozolomide in patients with stable or recurrent malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol 8:67–78
Franceschi E, Cavallo G, Lonardi S et al (2007) Gefitinib in patients with progressive high-grade gliomas: a multicentre phase II study by Gruppo Italiano Cooperativo di Neuro-Oncologia (GICNO). Br J Cancer 96:1047–1051
Halatsch ME, Schmidt U, Behnke-Mursch J et al (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme and other malignant brain tumours. Cancer Treat Rev 32:74–89
Raizer JJ (2005) HER1/EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 74:77–86
Rich JN, Reardon DA, Peery T et al (2004) Phase II trial of gefitinib in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 22:133–142
Lassman AB, Rossi MR, Raizer JJ et al (2005) Molecular study of malignant gliomas treated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: tissue analysis from North American Brain Tumor Consortium Trials 01–03 and 00–01. Clin Cancer Res 11:7841–7850
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I et al (2005) Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med 353:2012–2024
Friedman HS, Bigner DD (2005) Glioblastoma multiforme and the epidermal growth factor receptor. N Engl J Med 353:1997–1999
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr. et al (1990) Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8:1277–1280
Choe G, Horvath S, Cloughesy TF et al (2003) Analysis of the phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase signaling pathway in glioblastoma patients in vivo. Cancer Res 63:2742–2746
Perren A, Weng LP, Boag AH et al (1999) Immunohistochemical evidence of loss of PTEN expression in primary ductal adenocarcinomas of the breast. Am J Pathol 155:1253–1260
Van Den Bent MJ, Brandes AA, Rampling R et al: Randomized phase II trial of erlotinib versus temozolomide or BCNU in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: EORTC 26034. American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, Chicago, USA
Krishnan S, Brown PD, Ballman KV et al (2006) Phase I trial of erlotinib with radiation therapy in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: results of North Central Cancer Treatment Group protocol N0177. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:1192–1199
Agero AL, Dusza SW, Benvenuto-Andrade C et al (2006) Dermatologic side effects associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. J Am Acad Dermatol 55:657–670
Wacker B, Nagrani T, Weinberg J et al (2007) Correlation between development of rash and efficacy in patients treated with the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in two large phase III studies. Clin Cancer Res 13:3913–3921
Li B, Chang CM, Yuan M et al (2003) Resistance to small molecule inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor in malignant gliomas. Cancer Res 63:7443–7450
Marie Y, Carpentier AF, Omuro AM et al (2005) EGFR tyrosine kinase domain mutations in human gliomas. Neurology 64:1444–1445
Cappuzzo F (2005) Erlotinib in gliomas: should selection be based on EGFR and Akt analyses? J Natl Cancer Inst 97:868–869
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Darell D. Bigner (Duke University, NC, USA) for providing L8A4 antibody and Gerda Ricken and Irene Leisser (both Institute of Neurology, Medical University of Vienna, Austria) for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Preusser, M., Gelpi, E., Rottenfusser, A. et al. Epithelial Growth Factor Receptor inhibitors for treatment of recurrent or progressive high grade glioma: an exploratory study. J Neurooncol 89, 211–218 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9608-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9608-3