Abstract
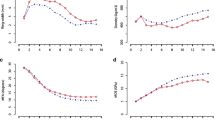
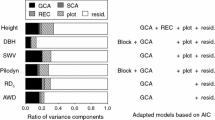
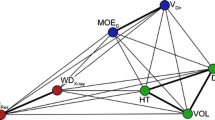
Genetic parameters for wood mechanical properties and their correlations with growth traits are not well established in the important tree genus Eucalyptus L’Hér. Based on a progeny trial of 115 open-pollinated families of Eucalyptus cloeziana F. Muell., this study estimated the heritability and trait–trait correlations for growth, including height (H), diameter at breast height (D) and volume (V), and wood mechanical traits, including basic density (BD), green density (GD), modulus of elasticity (MOE), modulus of rupture (MOR) and parallel-to-grain compressive strength (σc). Narrow-sense heritability (h 2 i ) ranged from 0.04 to 0.35 for growth across ages 0.5–9.5 years and from 0.06 to 0.24 for wood mechanical properties at age 9.5, indicating low to moderate magnitude of additive genetic control of these traits. Phenotypic (r p ) and additive genetic (r g ) correlations at the final age of 9.5 years were consistently significantly positive between growth traits and mostly significantly positive between wood mechanical traits, while r p and r g were small and adversely significant, respectively, between the two types of traits, posing a challenge for concomitant improvement of growth and wood traits. In addition, r p and r g coefficients between age 9.5 and earlier years for each of the growth traits H, D and V were all positively significant (except for H 2.5) and had a generally increasing trend with age, suggesting the possibility of early selection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcorn PJ, Bauhus J, Smith RGB, Thomas D, James R, Nicotra A (2008) Growth response following green crown pruning in plantation-grown Eucalyptus pilularis and E. cloeziana. Can J For Res 38:770–781. doi:10.1139/X07-185
Alcorn PJ, Forrester DI, Smith RGB, Thomas DS, James RN, Nicotra AB, Bauhus J (2013) Crown structure and vertical foliage distribution in 4-year-old plantation-grown Eucalyptus pilularis and Eucalyptus cloeziana. Trees 27:555–566. doi:10.1007/s00468-012-0809-1
Andrew RL, Wallis IR, Harwood CE, Foley WJ (2010) Genetic and environmental contributions to variation and population divergence in a broad-spectrum foliar defence of Eucalyptus tricarpa. Ann Bot 105:707–717. doi:10.1093/aob/mcq034
Apiolaza LA, Raymond CA, Yeo BJ (2005) Genetic variation of physical and chemical wood properties of Eucalyptus globulus. Silvae Genet 54:160–166
Baltunis BS, Wu HX, Powell MB (2007) Inheritance of density, microfibril angle, and modulus of elasticity in juvenile wood of Pinus radiata at two locations in Australia. Can J For Res 37:2164–2174. doi:10.1139/X07-061
Blackburn D, Hamilton M, Harwood C, Innes T, Potts B, Williams D (2010) Stiffness and checking of Eucalyptus nitens sawn boards: genetic variation and potential for genetic improvement. Tree Genet Genomes 6:757–765. doi:10.1007/s11295-010-0289-7
Blake T, Bevilacqua E, de Barbosa MM (1990) Early selection of fast-growing Eucalyptus clones and species. IPEF Int 1:26–34
Boland DJ, Brooker MIH, Chippendale GM, Hall N, Hyland BPM, Johnson RD, Kleinig DA, Turner JD (1984) Forest trees of Australia. Thomas Nelson Australia and CSIRO, Melbourne
Bootle KR (2005) Wood in Australia: types, properties and uses, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Sydney
Borralho NMG, Kanowski PJ, Cotterill PP (1992) Genetic control of growth of Eucalyptus globulus in Portugal. I. Genetic and phenotypic parameters. Silvae Genet 41:39–45
Brooker MIH (2000) A new classification of the genus Eucalyptus L’Hér. (Myrtaceae). Aust Syst Bot 13:79–148. doi:10.1071/SB98008
Burdon RD, Britton RAJ, Walford GB (2001) Wood stiffness and bending strength in relation to density in four native provenances of Pinus radiata. NZ J For Sci 31:130–146
Bush D, McCarthy K, Meder R (2011) Genetic variation of natural durability traits in Eucalyptus cladocalyx (sugar gum). Ann For Sci 68:1057–1066. doi:10.1007/s13595-011-0121-z
Ceng JY (2007) Study on two-way tree volume dynamic model of Eucalyptus plantations in Guangxi. J South China Agric Univ 28:91–95
Chen J-B, Xiang D-Y, Zhang Z-Y, Xu J-M, Kan R-F (2009) Studies on longitudinal compressive strength variance of Eucalyptus cloeziana. China For Sci Technol 23:63–66
Clarke B, McLeod I, Vercoe T (2009) Trees for farm forestry: 22 promising species. Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation, Canberra
Cornelius J (1994) Heritabilities and additive genetic coefficients of variation in forest trees. Can J For Res 24:372–379. doi:10.1139/x94-050
Costa e Silva J, Borralho NMG, Araújo JA, Vaillancourt RE, Potts BM (2009) Genetic parameters for growth, wood density and pulp yield in Eucalyptus globulus. Tree Genet Genomes 5:291–305. doi:10.1007/s11295-008-0174-9
Deng Z (2012) Genetic structure of Eucalyptus cloeziana by SSR markers. Dissertation, Guangxi University
Dickinson GR, Leggate W, Bristow M, Nester M, Lewty MJ (2000) Thinning and pruning to maximise yields of high value timber products from tropical and sub-tropical hardwood plantations. In: Snell A, Vize S (eds) Opportunities for the new millennium proceedings of the Australian Forest Growers Biennial conference. Australian Forest Growers Association, Cairns, pp 32–42
Dickson RL, Raymond CA, Joe W, Wilkinson CA (2003) Segregation of Eucalyptus dunnii logs using acoustics. For Ecol Manag 179:243–251. doi:10.1016/S0378-1127(02)00519-4
Dieters MJ, White TL, Hodge GR (1995) Genetic parameter estimates for volume from full-sib tests of slash pine (Pinus elliottii). Can J For Res 25:1397–1408. doi:10.1139/x95-152
Drinnan AN, Ladiges PY (1989) Operculum development in Eucalyptus cloeziana and Eucalyptus informal subg. Monocalyptus (Myrtaceae). Plant Syst Evol 166:183–196. doi:10.1007/BF00935948
FAO (1979) Eucalypts for planting. FAO, Rome
Gan S, Li M, Li F, Wu K, Wu J, Bai J (2004) Genetic analysis of growth and susceptibility to bacterial wilt (Ralstonia solanacearum) in Eucalyptus by interspecific factorial crossing. Silvae Genet 53:254–258
Gilmour AR, Gogel BJ, Cullis BR, Thompson R (2009) ASReml user guide release 3.0. VSN International Ltd, Hemel Hempstead
Greaves BL, Borralho NMG, Raymond CA, Evans R, Whiteman PH (1997) Age-age correlations in, and relationships between basic density and growth in Eucalyptus nitens. Silvae Genet 46:264–270
Griffin AR, Cotterill PP (1988) Genetic variation in growth of out-crossed, selfed and open-pollinated progenies of Eucalyptus regnans and some implications for breeding strategy. Silvae Genet 37:124–131
Hamilton MG, Raymond CA, Harwood CE, Potts BM (2009) Genetic variation in Eucalyptus nitens pulpwood and wood shrinkage traits. Tree Genet Genomes 5:307–316. doi:10.1007/s11295-008-0179-4
Hamilton MG, Potts BM, Greaves BL, Dutkowski GW (2010) Genetic correlations between pulpwood and solid-wood selection and objective traits in Eucalyptus globulus. Ann For Sci 67:511. doi:10.1051/forest/2010013
Hamilton MG, Acuna M, Wiedemann JC, Mitchell R, Pilbeam DJ, Brown MW, Potts BM (2015) Genetic control of Eucalyptus globulus harvest traits. Can J For Res 45:615–624. doi:10.1139/cjfr-2014-0428
He X, Li F, Li M, Weng Q, Shi J, Mo X, Gan S (2012) Quantitative genetics of cold hardiness and growth in Eucalyptus as estimated from E. urophylla × E. tereticornis hybrids. New For 43:383–394. doi:10.1007/s11056-011-9287-3
Hein PRG, Bouvet J-M, Mandrou E, Vigneron P, Clair B, Chaix G (2012) Age trends of microfibril angle inheritance and their genetic and environmental correlations with growth, density and chemical properties in Eucalyptus urophylla S.T. Blake wood. Ann For Sci 69:681–691. doi:10.1007/s13595-012-0186-3
Hirakawa Y, Yamashita K, Fujisawa Y, Nakada R, Kijidani Y (1997) The effects of S2 microfibril angles and density on MOE in sugi tree logs. In: Butterfield BG (ed) Proceedings of IAWA/IUFRO international workshop on the significance of microfibril angle to wood quality, Westport, pp 312–322
Hodge GR, Dvorak WS (2001) Genetic parameters and provenance variation of Pinus caribaea var. hondurensis in 48 international trials. Can J For Res 31:496–511. doi:10.1139/x00-189
Hung TD, Brawner JT, Meder R, Lee DJ, Southerton S, Thinh HH, Dieters MJ (2015) Estimates of genetic parameters for growth and wood properties in Eucalyptus pellita F. Muell. to support tree breeding in Vietnam. Ann For Sci 72:205–217. doi:10.1007/s13595-014-0426-9
Keenan RJ, Ivory M, Lawson S, Lee D, Leggate W, Lewty MJ, Nikles DG, Ryan P, Walker S (1998) Hardwood plantation research and development: a strategy to support a hardwood plantation industry in Queensland. Queensland Forestry Research Institute, Brisbane
Kien ND, Jansson G, Harwood C, Thinh HH (2009) Genetic control of growth and form in Eucalyptus urophylla in northern Vietnam. J Trop For Sci 21:50–65
Kien ND, Jansson G, Harwood CE, Almqvist C, Thinh HH (2010) Genetic variation in wood basic density and Pilodyn penetration and their relationships with growth, stem straightness, and branch size for Eucalyptus urophylla in Northern Vietnam. NZ J For Sci 38:160–174
Kumar S (2004) Genetic parameter estimates for wood stiffness, strength, internal checking, and resin bleeding for radiata pine. Can J For Res 34:2601–2610. doi:10.1139/X04-128
Lee D, Ryan P, Nikles G (1997) Provenance variation of Eucalyptus cloeziana exhibited at Pomona in south-eastern Queensland. In: Kikkawa J, Dart P, Doley D, Ishii K, Lamb D, Suzuki K (eds) Overcoming impediments to reforestation: tropical forest rehabilitation in the Asia-Pacific region. BIO-REFOR, Japan, pp 187–189
Li C-R, Xiang D-Y, Chen J-B, Zhai X-C, Kan R-F, Lan J (2012) Study on wood basic density variation of Eucalyptus cloziana. J Cent South Univ For Technol 32(6):158–163
Luo J, Arnold R, Lu W, Lin Y (2014) Genetic variation in Eucalyptus camaldulensis and E. tereticornis for early growth and susceptibility to the gall wasp Leptocybe invasa in China. Euphytica 196:397–411. doi:10.1007/s10681-013-1042-8
Lynch M, Walsh B (1998) Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
MacDonald AC, Borralho NMG, Potts BM (1997) Genetic variation for growth and wood density in Eucalyptus globulus ssp. globulus in Tasmania (Australia). Silvae Genet 46:236–241
Magnussen S (1989) Effects and adjustments of competition bias in progeny trials with single-tree plots. For Sci 35:532–547
Manaturagimath BB, Bulgannawar GN, Parameswarappa S, Burley J (1991) Provenance trial on Eucalyptus cloeziana in western Ghats of Karnataka, India. Indian For 117:1013–1020
Marques OG Jr, Andrade HB, Ramalho MAP (1996) Assessment of the early selection efficiency in Eucalyptus cloeziana F. Muell. Silvae Genet 45:359–361
Muneri A, Raymond CA (2000) Genetic parameters and genotype-by-environment interactions for basic density, pilodyn penetration and stem diameter in Eucalyptus globulus. For Genet 7:317–328
Ngugi MR, Doley D, Hunt MA, Dart P, Ryan P (2003) Leaf water relations of Eucalyptus cloeziana and Eucalyptus argophloia in response to water deficit. Tree Physiol 23:335–343. doi:10.1093/treephys/23.5.335
Ngugi MR, Doley D, Hunt MA, Ryan P, Dart P (2004) Physiological responses to water stress in Eucalyptus cloeziana and E. argophloia seedlings. Trees 18:381–389. doi:10.1007/s00468-003-0316-5
Osorio LF, White TL, Huber DA (2001) Age trends of heritabilities and genotype-by-environment interactions for growth traits and wood density from clonal trials of Eucalyptus grandis Hill ex Maiden. Silvae Genet 50:30–37
Osorio LF, White TL, Huber DA (2003) Age-age and trait-trait correlations for Eucalyptus grandis Hill ex Maiden and their implications for optimal selection age and design of clonal trials. Theor Appl Genet 106:735–743. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1124-9
Pryor LD, Johnson LAS, Whitecross MI, McGillivray DJ (1967) The perianth and taxonomic affinities of Eucalyptus cloeziana F. Muell. Aust J Bot 15:145–149. doi:10.1071/BT9670145
Qi S (2002) Eucalyptus in China, 2nd edn. Chinese Forestry Press, Beijing
Silva PHM, Miranda AC, Moraes MLT, Furtado EL, Stape JL, Alvares CA, Sentelhas PC, Mori ES, Sebbenn AM (2013) Selecting for rust (Puccinia psidii) resistance in Eucalyptus grandis in São Paulo State, Brazil. For Ecol Manag 303:91–97. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2013.04.002
Stackpole DJ, Vaillancourt RE, de Aguigar M, Potts B (2010) Age trends in genetic parameters for growth and wood density in Eucalyptus globulus. Tree Genet Genomes 6:179–193. doi:10.1007/s11295-009-0239-4
Stackpole DJ, Vaillancourt RE, Rodrigues J, Potts BM (2011) Genetic variation in the chemical components of Eucalyptus globulus wood. G3 1:151–159. doi:10.1534/g3.111.000372
Tang Q (2006) Studies on tissue culture of Eucalyptus cloeziana. Dissertation, Guangxi University
Turnbull JW (1979) Geographic variations in Eucalyptus cloeziana. Dissertation, Australia National University
Warren E, Smith RGB, Apiolaza LA, Walker JCF (2009) Effect of stocking on juvenile wood stiffness for three Eucalyptus species. New For 37:241–250. doi:10.1007/s11056-008-9120-9
Wei X, Borralho NMG (1997) Genetic control of wood basic density and bark thickness and their relationships with growth traits of Eucalyptus urophylla in south east China. Silvae Genet 46:245–250
Wei X, Borralho NMG (1998) Genetic control of growth traits of Eucalyptus urophylla S. T. Blake in South East China. Silvae Genet 47:158–165
Weng Q, He X, Li F, Li M, Yu X, Shi J, Gan S (2014) Hybridizing ability and heterosis between Eucalyptus urophylla and E. tereticornis for growth and wood density over two environments. Silvae Genet 63:15–24
Williams ER, Matheson AC, Harwood CE (2002) Experimental design and analysis for use in tree improvement, 2nd edn. CSIRO, Melbourne
Xiang D-Y, Wang M-X, Huang M-R, Chen J-B, Kan R-F, Zhang Z-Y, Chen D-L (2012) Variations of modulus of elasticity in Eucalyptus cloeziana. J South China Agric Univ 33:73–76
Yang JL, Evans R (2003) Prediction of MOE of eucalypt wood from microfibril angle and density. Holz Roh Werkst 61:449–452. doi:10.1007/s00107-003-0424-3
Zhang F, Li L, Zhang L, Xu Z (2012) Study of the determination of the elastic constants and mechanical property parameters of five kinds of wood commonly used in furniture. For Mach Woodwork Equip 40:16–19
Zhou W, Li C, Chen J, Wu R, Guo D, Xiang D (2014) Study on the variation and adaptability in provenance of Eucalyptus cloeziana. J Southwest For Univ 34:36–41. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1914.2014.04.007
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by grants from Guangxi Department of Forestry (2014-4, 2014-35 & 2015-6) and Key Laboratory of State Forestry Administration on Central South Fast-growing Timber Cultivation (14-A-01-01). The authors thank Guicheng Yu, Jun Wu, Jianfan Li, Yaomei Bin, Shidong Chen, Lu Li, Guanglan Huang and Xi Sun from Yulin Forestry Research Institute for kind assistance in field trial establishment, maintenance and investigation as well as wood sample collection. Thanks are also due to Jiachun Lin and Zhaoyuan Zhang from Guangxi Forestry Research Institute for valuable cooperation in field trial investigation, wood sample collection and standard measurement. We are grateful to John Turnbull for regional grouping of the provenances, Kevin Harding for critical reading of an earlier version of the manuscript and the two anonymous reviewers for helpful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Weng, Q., Chen, JB. et al. Genetic parameters for growth and wood mechanical properties in Eucalyptus cloeziana F. Muell.. New Forests 48, 33–49 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-016-9554-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-016-9554-4