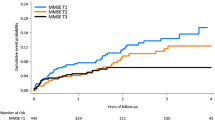
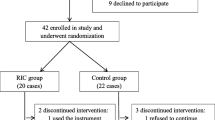
Objective. To investigate the efficacy of Cortexin in the treatment of cognitive and affective disorders in cerebral ischemia (AI) developing on the background of arterial hypertension or atherosclerosis. Materials and methods. We present an analysis of the all-Russian screening program for the efficacy of Cortexin, “Cognitive and Affective Disorders in the Treatment of Cerebral Ischemia with Cortexin” (KarKaDÉ), in 50,000 patients with AI developing on the background of arterial hypertension and/or atherosclerosis in 2013 in 70 Russian cities. Results. All patients received Cortexin at a dose of 10 mg/day for 10 days and were investigated before treatment and on days 11 and 30 after the first dose. More extensive analysis was applied to results from the treatment of 500 patients with stage II AI, mean age 63.7 ± 10.23 years. Treatment efficacy was evaluated using a five-point rating scale for subjective and objective neurological symptoms, the five-word memory test, the Schulte test, the MMSE, the Hamilton scales for evaluation of anxiety, and the short form of the Geriatric Depression Scale. Conclusions. Treatment decreased or completely eliminated focal neurological symptomatology and produced positive changes in measures of cognitive impairments, these changes being accompanied by normalization of patients’ emotional status and decreases in the level of depression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. A. Belova, V. V. Mashin, Yu. M. Nikitin, and V. G. Belov, Hypertensive Encephalopathy: Clinical-Pathogenetic Subtypes, Classification, and Diagnosis: Monograph, Ulyanovsk State Univ., Ulyanovsk (2010).
L. A. Belova, O. V. Gavrilyuk, N. V. Belova, et al., “Effects of antihypertensive treatment on the clinical-psychological characteristics of patients with hypertensive encephalopathy,” Saratov. Med. Zh., 7, No. 4, 866–870 (2011).
O. S. Levin and L. V. Golubeva, “Heterogeneity of moderate cognitive disorder: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects,” Consilium Medicum, 12, 106–110 (2006).
Z. A. Suslina, M. A. Piradov, Yu. Ya. Varakin, et al., Stroke: Diagnosis, Treatment, Prophylaxis, MEDpress-Inform, Moscow (2009).
Z. A. Suslina, A. V. Fonyakin (eds.), L. A. Geraskina, et al., Practical Cardioneurology, IMA-PRESS, Moscow (2010).
V. V. Mashin and A. S. Kadykov, Hypertensive Encephalopathy. Clinical Pathogenesis: Monograph, Nauchnoe Izdanie, Ulyanovsk (2002).
L. Belova, V. Mashin, and N. Belova, “Hypertensive encephalopathy: the role of arteriovenous interrelations in the formation of its clinical-pathogenetic subtypes,” Exp. Clin. Cardiol., 20, No. 7, 892–898 (2014).
R. Baroa, S. Martinez-Espinosa, E. Rodriguez-Garcia, et al., “Poststroke dementia. clinical features and risk factors,” Stroke, 31, 1494–1501 (2000).
O. V. Gavrilyuk, L. A. Belova, N. V. Belova, and V. V. Mashin, “Dyna mics of quality of life and compliance with antihypertensive treatment in patients with hypertensive encephalopathy,” Palliativ. Med. Reabil., No. 1, 28–30 (2011).
V. V. Mashin, E. A. Pinkova, L. N. Vinokurov, et al., “Risk factors for hypertensive encephalopathy and potential pathways to their pharmacological correction,” Med. Alman., 14, No. 1, 88–90 (2011).
V. V. Mashin, L. A. Belova, O. V. Gavrilyuk, and N. V. Belova, “Effects of antihypertensive treatment on the clinical-psychological characteristics of patients with hypertensive encephalopathy,” Saratov Nauchn. Zh., 7, No. 4, 866–870 (2011).
M. M. D’yakonov and P. D. Shabanov, “The question of the neuroprotective action of peptide properties,” Vestn. Voen.-Med. Akad., 33, No. 1, 255–258 (2011).
A. A. Skoromets and M. M. D’yakonov (eds.), Neuroprotection in Acute and Chronic Cerebral Circulatory Failure, Nauka, St. Petersburg (2007).
A. A. Skoromets and M. M. D’yakonov, Cortexin. Five Years of Experience in Russian Neurology, Nauka, St. Petersburg (2005).
P. D. Shabanov, A. A. Lebedev, and A. V. Droblenkov, Behavioral Effects of the Peptide Preparations Cortexin and Noopept in Modulation of the Stress-Antistress Systems in Early Ontogeny, Nauka, St. Petersburg (2009).
G. G. Neznamov and E. S. Teleshova, “Results of a comparative study of Noopept and piracetam in the treatment of patients with mild cognitive impairments in organic brain diseases of vascular and traumatic origin,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiat., 108, No. 3, 33–42 (2008).
R. Hebert, J. Lindsay, and R. Verrault, “Vascular Dementia. Incidence and risk factors in the Canadian Study of Health and Aging,” Stroke, No. 5, 1487–1493 (2000).
D. Neary, “Classification of the dementias,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiat., No. 1, 61–67 (2000).
N. N. Yakhno, “Cognitive disorders in neurological clinical practice,” Nevrol. Zh., 11, No. 1, 4–12 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii imeni S. S. Korsakova, Vol. 114, No. 9, Iss. 1, pp. 49–52, September, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mashin, V.V., Belova, L.A., Chaplanova, O.I. et al. An Open Clinical Trial of Cortexin in Cerebral Ischemia. Neurosci Behav Physi 46, 390–393 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-016-0247-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-016-0247-4