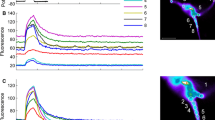
Changes in intracellular calcium ion concentrations are the main trigger for most physiological processes in neurons, including changes in gene expression and the processes of synaptic plasticity. Our experiments showed that high-amplitude EPSP in common snail command neurons, like action potentials, are accompanied by marked increases in intracellular calcium ion concentrations. The amplitude of calcium signals accompanying high-amplitude EPSP in command neurons was found to depend linearly on the strength of synaptic stimulation, while the dynamics of changes in the amplitude of EPSP themselves showed marked saturation as stimulus strength increased. This means that over a certain range of changes of membrane potential, calcium signals transmit stimulus strength more adequately than the level of depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron. We suggest that calcium signals evoked by high-amplitude EPSP can induce biochemical changes in neurons, thus mediating cellular responses in the range subthreshold for action potentials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. M. Balaban and I. A. Zakharov, Learning and Development. A Common Basis for Two Phenomena [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1992).
P. G. Kostyuk and O. A. Kryshtal’, Mechanisms of the Electrical Excitability of Nerve Cells. Biological and Technical Membranes Series [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1982).
A. G. Ter-Markaryan, T. A. Palikhova, and E. N. Sokolov, “Effects of atropine and d-tubocurarine on monosynaptic connections between identified neurons in the central nervous system of the common snail,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 40, No. 1, 183–184 (1990).
P. M. Balaban, “Cellular mechanisms of behavioral plasticity in terrestrial snail,” Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 26, No. 5, 597–630 (2002).
P. M. Balaban, N. I. Bravarenko, O. A. Maksimova, et al., “A single serotonergic modulatory cell can mediate reinforcement in the withdrawal network of the terrestrial snail,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 75, No. 1, 30–50 (2001).
T. A. Bravarenko, A. Y. Korshunova, and P. M. Malyshev, “Synaptic contact between mechanosensory neuron and withdrawal interneuron in terrestrial snail is mediated by L-glutamate-like transmitter,” Neurosci. Lett., 341, 237–240 (2003).
E. R. Kandel, J. H. Schwartz, and T. M. Jessell, Essentials of Neural Science and Behavior, Appleton Lange, Norwalk (1995).
A. Y. Malyshev and P. M. Balaban, “Identification of mechanoafferent neurons in terrestrial snail: Response properties and synaptic connections,” J. Neurophysiol., 87, No. 5, 2364–2371 (2002).
H. Markram and B. Sakmann, “Calcium transients in apical dendrites evoked by single subthreshold excitatory postsynaptic potentials via low-voltage activated calcium channels,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 5207–5211 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 98, No. 11, pp. 1298–1306, November, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malyshev, A.Y., Balaban, P.M. Changes in Intracellular Calcium Ion Concentrations during Generation of High-Amplitude EPSP in Neurons in the Common Snail. Neurosci Behav Physi 44, 681–686 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-014-9969-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-014-9969-3