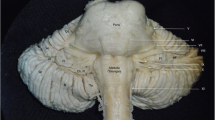
Technically advanced methods of the surgical treatment of nervous diseases require detailed knowledge of the microanatomy of the base of the brain. An original method of exposing the posterior cranial fossa and extracting the brain from the skull was used at the autopsies of 48 humans and yielded data on the microanatomical features in the zone at which the root of the trigeminal nerve enters the brainstem. Three variants of the arterial blood supply to the root of the trigeminal nerve and three variants of the venous drainage from the cerebellopontine angle were identified. This method of exposing the posterior cranial fossa at autopsy identified the topographical anatomical interactions between the root of the trigeminal nerve and the vessels of the base of the brain present while the patients were alive. Consideration of structural variants of the superior petrosal vein during surgical approaches to brainstem structures should allow the incidence of complications to be decreased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu. A. Grigoryan, “Microsurgical decompression in ‘hyperfunctional’ syndromes of the roots of the cranial nerves,” in: Proceedings of the IV Congress of Russian Neurosurgeons [in Russian], Moscow (2006), p. 449.
Yu. A. Grigoryan and K. Ya. Ogleznev, “Etiological factors in neuralgia syndrome,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr., No. 6, 8–22 (1994).
A. A. Zeimanov, Characteristics of the Topography and Blood Supply of the Intracranial Part of the Trigeminal Nerve [in Russian],Author’s Abstract of Master’s Thesis in Medical Sciences, Leningrad (1971).
V. A. Karlov, Facial Neuralgia [in Russian], Meditsina, Moscow (1991).
G. N. Kryzhanovskii, “The pathogenesis of central pain and itch syndromes: the theory of generator mechanisms,” Zh. Nevropatol. Psikhiatr., No. 7, 1090–1100 (1976).
K. Ya. Ogleznev,Yu. A. Grigoryan, and S. A. Shesterikov, Pathophysiological Mechanisms of the Appearance and Methods of Treatment of Facial Pain [in Russian], Nauka, Novosibirsk (1990).
A. V. Stepanchenko, Typical Trigeminal Neuralgia [in Russian], VKhM Publishing Group, Moscow (1994).
Yu. A. Shulev, K. S. Gordienko, and O. V. Posokhina, “Microvascular decompression in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia,” Neirokhirurgiya, No. 2, 7–14, (2004).
W. E. Dandy, “Concerning the cause of trigeminal neuralgia,” Am. J. Surg., 24, 1077–1083 (1934).
M. Duvernoy, Human Brain Stem Vessels, Thieme, New York (1978).
D. G. Hardy and A. L. Rhoton, “Microsurgical relationships of the superior cerebellar artery and the trigeminal nerve,” J. Neurosurg., 49, No. 5, 669–678 (1978).
R. Melzack and P. Wall, The Challenge of Pain, Basic Books, New York (1982).
P. J. Janetta, “Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by microoperative decompression,” in: Neurological Surgery, Spring, London (1990), 3rd edition, Vol. 6, pp. 3928–3942.
D. Ridder, A. Moller, J. Verlooy, et al., “Is the entry exit zone important in microvascular syndromes?” Neurosurgery, 51, No. 2, 427–434 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Morfologiya, Vol. 137, No. 1, pp. 17–21, January–February, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ustyuzhantsev, N.E., Chetvertnykh, V.A. & Balandina, I.A. The Vascular Network at the Site of Entry of the Trigeminal Nerve into the Brainstem. Neurosci Behav Physi 41, 13–17 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9370-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9370-9