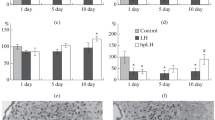
We report here our immunocytochemical studies establishing that the development of a depression-like state in rats following unavoidable stress in a “learned helplessness” model is accompanied by stable activation of the expression of transcription factor NGFI-A in the dorsal hippocampus (field CA1) and the magnocellular paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, along with an early wave of post-stress expression, which died down rapidly, in the ventral hippocampus (the dentate gyrus) and a long period of up to five days of high-level expression in the neocortex. In rats subjected to three sessions of preconditioning consisting of moderate hypobaric hypoxia (360 mmHg, 2 h, with intervals of 24 h), which did not form depression in these circumstances, there were significant changes in the dynamics of immunoreactive protein content in the hippocampus, with a stable increase in expression in the ventral hippocampus and only transient and delayed (by five days) expression in field CA1. In the neocortex (layer II), preconditioning eliminated the effects of stress, preventing prolongation of the first wave of NGFI-A expression to five days, while in the magnocellular hypothalamus, conversely, preconditioning stimulated a second (delayed) wave of the expression of this transcription factor. The pattern of NGFI-A expression in the hippocampus, neocortex, and hypothalamus seen in non-preconditioned rats appears to reflect the pathological reaction to aversive stress, which, rather than adaptation, produced depressive disorders. Post-stress modification of the expression of the product of the early gene NGFI-A in the brain induced by hypoxic preconditioning probably plays an important role in increased tolerance to severe psychoemotional stresses and is an important component of antidepressant mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. V. Beltikova and Ya. A. Kochetkov, “Characteristics of clinicalhormonal interactions in depressive disorders,” in: Current Problems in Psychiatric Endocrinology. Collection of Studies [in Russian], Moscow (2004), pp. 77–91.
E. A. Rybnikova, V. I. Mironova, E. I. Tyulkova, and M. O. Samoilov, “Anxiolytic effects of moderate hypobaric hypoxia in rats in a model of post-traumatic stress disorder,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 4, 475–482 (2008).
E. A. Rybnikova, L. I. Khozhai, E. I. Tyulkova, T. S. Glushchenko, N. A. Sitnik, M. Pelto-Huikko, V. A. Otellin, and M. V. Samoilov, “Expression of early gene proteins, structural changes in brain neurons in hypobaric hypoxia, and the correcting effect of preconditioning,” Morfologiya, 125, No. 2, 10–15 (2004).
M. O. Samoilov, E. A. Rybnikova, E. I. Tyulkova, L. A. Vataeva, V. A. Otellin, and L. I. Khozhai, “Effects of hypobaric hypoxia on behavioral responses and early gene expression in the rat brain: the correcting effect of preconditioning,” Dokl. Ros. Akad. Nauk., 381, 513–515 (2001).
E. Belaidi, P. C. Beguin, C. Ribuot, and D. Godin-Ribuot, “Hypoxic preconditioning: role of transcription factor HIF-1alpha,” Ann. Cardiol. Angiol., 55, No. 2, 70–73 (2006).
L. Bjartmar, I. M. Johansson, J. Marcusson, S. B. Ross, J. R. Seckl, and T. Olsson, “Selective effects on NGFI-A, MR, GR and NGFI-B hippocampal mRNA expression after chronic treatment with different subclasses of antidepressants in the rat,” Psychopharmacology (Berlin), 151, No. 1, 7–12 (2000).
B. Bozon, S. Davis, and S. Laroche, “Regulated transcription of the immediate-early gene Zif268: mechanisms and gene dosage-dependent function in synaptic plasticity and memory formation,” Hippocampus, 12, No. 5, 570–577 (2002).
X. Cao, R. A. Koski, A. Gashler, M. McKiernan, C. F. Morris, R. Gaffney, R. V. Hay, and V. P. Sikhatme, “Identification and characterization of the EGR-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals,” Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 1931–1939 (1990).
Y. Dai, M. Xu,Y. Wang, Z. Pasha, T. Li, and M. Ashraf, “HIF-1alpha induced-VEGF overexpression in bone marrow stem cells protects cardiomyocytes against ischemia,” J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 42, No. 6, 1036–1044, (2007).
S. Davis, B. Bozon, and S. Laroche, “How necessary is the activation of the immediate early gene zif 268 in synaptic plasticity and learning?” Brain Res., 142, No. 1, 17–30 (2003).
S. Fulda and K. M. Debatin, “HIF-1-regulated glucose metabolism: a key to apoptosis resistance?” Cell Cycle, 6, No. 7, 790–792 (2007).
M. T. Ghorbel, I. Seugnet, N. Hadj-Sahraoui, P. Topilko, G. Levi, and B. Demeneix, “Thyroid hormone effects on Krox-24 transcription in the post-natal mouse brain are developmentally regulated but are not correlated with mitosis,” Oncogene, 18, No. 4, 917–924 (1999).
T. Herdegen and J. D. Leah, “Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: control of gene expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF proteins,” Brain Res. Rev., 28, No. 3, 370–490 (1998).
D. M. Holtzman, R. A. Sheldon,W. Jaffe,Y. Cheng, and D. M. Ferriero, “Nerve growth factor protects the neonatal brain against hypoxic-ischemic injury,” Ann. Neurol., 39, No. 1, 114–122 (1996).
J. Honkaniemi and F. R. Sharp, “Global ischemia induces immediate-early genes encoding zinc finger transcription factors,” J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 16, No. 4, 557–565 (1996).
M. W. Jones, M. L. Errington, P. J. French, A. Fine, T. V. Bliss, S. Garel, P. Charnay, B. Bozon, S. Laroche, and S. Davis, “A requirement for the immediate early gene Zif268 in the expression of late LTP and longterm memories,” Nat. Neurosci., 4, No. 3, 289–296 (2001).
E. Knapska and L. Kaczmarek, “A gene for neuronal plasticity in the mammalian brain: Zif268/Egr-1/NGFI-A/Krox-24/TIS8/ZENK?” Prog. Neurobiol., 74, No. 4, 183–211 (2004).
T. W. Lovenberg, M. G. Erlander, B. M. Baron, and J. G. Sutcliffe, “Cloning of new 5-HT receptors,” Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol., 8, Supplement 2, 19–23 (1993).
S. Morinobu, H. Strausbaugh, R. Terwilliger, and R. S. Duman, “Regulation of c-Fos and NGFI-A by antidepressant treatments,” Synapse, 25, No. 4, 313–320 (1997).
T. Olsson, A. Hakansson, and J. R. Seckl, “Ketanserin selectively blocks acute stress-induced changes in NGFI-A and mineralocorticoid receptor gene expression in hippocampal neurons,” Neurosci., 76, No. 2, 441–448 (1997).
G. Paxinos and G. Watson, The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Academic Press, San Diego (1986).
C. Pipaon, A. Santos, and A. Perez-Castillo, “Thyroid hormone upregulates NGFI-A gene expression in rat brain during development,” J. Biol. Chem., 267, No. 1, 21–23 (1992).
J. L. Plassat, N. Amlaiky, and R. Hen, “Molecular cloning of a mammalian serotonin receptor that activates adenylate cyclase,” Mol. Pharmacol., 44, No. 2, 229–236 (1993).
J. B. Rosen, M. S. Fanselow, S. L. Young, M. Sitcoske, and S. Maren, “Immediate-early gene expression in the amygdala following footshock stress and contextual fear conditioning,” Brain Res., 796, No. 1–2, 132–142 (1998).
E. Rybnikova, V. Mironova, S. Pivina, R. Tulkova, N. Ordyan, L. Vataeva, E. Vershinina, E. Abritalin, A. Kolchev, N. Nalivaeva, A. J. Turner, and M. Samoilov, “Antidepressant-like effects of mild hypoxia preconditioning in the learned helplessness model in rats,” Neurosci. Lett., 417, No. 3, 234–239 (2007).
E. Rybnikova, E. Tulkova, M. Pelto-Huikko, and M. Samoilov, “Mild preconditioning hypoxia modifies nerve growth factorinduced gene A messenger RNA expression in the rat brain induced by severe hypoxia,” Neurosci. Lett., 329, No. 1, 49–52, (2002).
E. Rybnikova, L. Vataeva, E. Tyulkova, T. Gluschenko, V. Otellin, M. Pelto-Huikko, and M. O. Samoilov, “Mild hypoxia preconditioning prevents impairment of passive avoidance learning and suppression of brain NGFI-A expression induced by severe hypoxia,” Behav. Brain Res., 160, No. 1, 107–114 (2005).
E. A. Rybnikova,V. I. Mironova, S. G. Pivina, N. E. Ordyan, E. I. Tyulkova, and M. O. Samoilov, “Hypoxic preconditioning prevents development of post-stress depressions in rats,” Dokl. Biol. Sci., 411, 431–433 (2006).
R. M. Sapolsky, “Glucocorticoids and hippocampal atrophy in neuropsychiatric disorders,” Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 57, 925–935 (2000).
M. E. Seligman and G. Beagley, “Learned helplessness in the rat,” J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., 88, 534–541 (1975).
E. Senba and T. Ueyama, “Stress-induced expression of immediate early genes in the brain and peripheral organs of the rat,” Neurosci. Res., 29, No. 3, 183–207 (1997).
F. R. Sharp, R. Ran, A. Lu,Y. Tang, K. I. Strauss, T. Glass, T. Ardizzone, and M. Bernaudin, “Hypoxic preconditioning protects against ischemic brain injury,” NeuroRx, 1, No. 1, 26–35 (2004).
M. Sheng and M. E. Greenberg, “The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system,” Neuron, 44, No. 4, 477–485 (1990).
V. P. Sukhatme, X. Cao, L. C. Chang, C. Tsai-Morris, D. Stamenkovich, P. C. P. Ferreira, D. R. Cohen, S. A. Edwards, T. B. Shows, T. Curran, M. M. Le Beau, and E. D. Adamson, “A zinc fingerencoding gene coregulated with c-fos during growth and differentiation, and after cellular depolarization,” Cell, 53, 37–43 (1988).
A. P. Tsou, A, Kosaka, C. Bach, P. Zuppan, C. Yee, L. Tom, R. Alvarez, D. Ramsey, D. W. Bonnhaus, E. Stefanich, et al., “Cloning and expression of a 5-hydroxytryptamine7 receptor positively coupled to adenylyl cyclase,” J. Neurochem., 63, No. 2, 456–464 (1994).
R. Tupler, G. Perini, and M. R. Green, “Expressing the human genome,” Nature, 409, 832–833 (2001).
T. Ueyama, H. Ohya, R. Yoshimura, and E. Senba, “Effects of ethanol on the stress-induced expression of NGFI-A mRNA in the rat brain,” Alcohol, 18, No. 2–3, 171–176 (1999).
S. Umemoto,Y. Kawai, and E. Senba, “Differential regulation of IEGs in the rat PVH in single and repeated stress models,” Neuroreport, 6, No. 1, 201–204 (1994).
J. Q. Wang, “Regulation of immediate early gene c-fos and zif/268 mRNA expression in rat striatum by metabotropic glutamate receptor,” Mol. Brain Res., 57, No. 1, 46–53 (1998).
I. C. Weaver, A. C. D’Alessio, S. E. Brown, I. C. Hellstrom, S. Dymov, S. Sharma, M. Szyf, and M. J. Meaney, “The transcription factor nerve growth factor-inducible protein a mediates epigenetic programming: altering epigenetic marks by immediate-early genes,” J. Neurosci., 27, No. 7, 1756–1768 (2007).
V. L. Woodburn, N. J. Hayward, J. A. Poat, G. N. Woodruff, and J. Hughes, “The effect of dizocilpine and enadoline on immediate early gene expression in the gerbil global ischaemia model,” Neuropharmacology, 32, No. 10, 1047–1059 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 95, No. 4, pp., 405–416, April, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baranova, K.A., Rybnikova, E.A., Mironova, V.I. et al. Effects of Hypoxic Preconditioning on Expression of Transcription Factor NGFI-A in the Rat Brain after Unavoidable Stress in the “Learned Helplessness” Model. Neurosci Behav Physi 40, 693–700 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9313-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9313-5