Abstract
Oil from the Oligocene oil sands of the Lower Ganchaigou Formation in the Northern Qaidam Basin and the related asphaltenes was analyzed using bulk and organic geochemical methods to assess the organic matter source input, thermal maturity, paleo-environmental conditions, kerogen type, hydrocarbon quality, and the correlation between this oil and its potential source rock in the basin. The extracted oil samples are characterized by very high contents of saturated hydrocarbons (average 62.76%), low contents of aromatic hydrocarbons (average 16.11%), and moderate amounts of nitrogen–sulfur–oxygen or resin compounds (average 21.57%), suggesting that the fluid petroleum extracted from the Oligocene oil sands is of high quality. However, a variety of biomarker parameters obtained from the hydrocarbon fractions (saturated and aromatic) indicate that the extracted oil was generated from source rocks with a wide range of thermal maturity conditions, ranging from the early to peak oil window stages, which are generally consistent with the biomarker maturity parameters, vitrinite reflectance (approximately 0.6%), and Tmax values of the Middle Jurassic carbonaceous mudstones and organic-rich mudstone source rocks of the Dameigou Formation, as reported in the literature. These findings suggest that the studied oil is derived from Dameigou Formation source rocks. Furthermore, the source- and environment-related biomarker parameters of the studied oil are characterized by relatively high pristane/phytane ratios, the presence of tricyclic terpanes, low abundances of C27 regular steranes, low C27/C29 regular sterane ratios, and very low sterane/hopane ratios. These data suggest that the oil was generated from source rocks containing plankton/land plant matter that was mainly deposited in a lacustrine environment and preserved under sub-oxic to oxic conditions, and the data also indicate a potential relationship between the studied oil and the associated potential source rocks. The distribution of pristane, phytane, tricyclic terpanes, regular steranes and hopane shows an affinity with the studied Oligocene Lower Ganchaigou Formation oil to previously published Dameigou Formation source rocks. In support of this finding, the pyrolysis–gas chromatography results of the analyzed oil asphaltene indicate that the oil was primarily derived from type II organic matter, which is also consistent with the organic matter of the Middle Jurassic source rocks. Thus, the Middle Jurassic carbonaceous mudstones and organic rock mudstones of the Dameigou Formation could be significantly contributing source rocks to the Oligocene Lower Ganchaigou Formation oil sand and other oil reservoirs in the Northern Qaidam Basin.

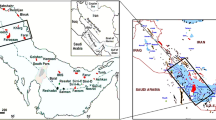
(modified after the Oil and Gas Resources Survey Center of the China Geological Survey 2009)


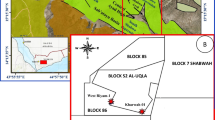
(modified after Qin et al. 2018)

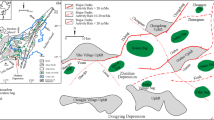
(modified from Tian et al. 2018)




(after Qin et al. 2018)




(modified after Peters and Moldowan 1993)

(adapted after Eglinton et al. 1990)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adegoke, H. I., AmooAdekola, F., Fatoki, O. S., & Ximba, B. J. (2014). Adsorption of Cr(VI) on synthetic hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles of different morphologies. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 31(1), 142–154.
Bao, J., Wang, Y., Song, C., Feng, Y., Hu, C., Zhong, S., et al. (2017). Cenozoic sediment flux in the Qaidam Basin, northern Tibetan Plateau, and implications with regional tectonics and climate. Global and Planetary Change, 155, 56–69.
Barwise, A. J. G. (1990). Role of nickel and vanadium in petroleum classification. Energy & Fuels, 4(6), 647–652.
Baumard, P., Budzinski, H., Garrigues, P., Dizer, H., & Hansen, P. D. (1999). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in recent sediments and mussels (Mytilus edulis) from the Western Baltic Sea: Occurrence, bioavailability and seasonal variations. Marine Environmental Research, 47(1), 17–47.
Cao, J., Bian, L., Hu, K., Liu, Y., Wang, L., Yang, S., et al. (2009). Benthic macro red alga: A new possible bio-precursor of Jurassic mudstone source rocks in the northern Qaidam Basin, northwestern China. Science in China, Series D: Earth Sciences, 52(5), 647–654.
CAPP (Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers). (2017). Crude oil forecast, markets and transportation. http://www.capp.ca/publications-and-statistics/publications/303440. Accessed 5 December 2017.
Chiavari, G., & Galletti, G. C. (1992). Pyrolysis—gas chromatography/mass spectrometry of amino acids. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 24(2), 123–137.
Clegg, H., Horsfield, B., Wilkes, H., Damsté, J., & Koopmans, M. (1998). Effect of artificial maturation on carbazole distributions, as revealed by the hydrous pyrolysis of an organic-sulphur-rich source rock (Ghareb Formation, Jordan). Organic Geochemistry, 29(8), 1953–1960.
Damsté, J. S. S., Kenig, F., Koopmans, M. P., Köster, J., Schouten, S., Hayes, J. M., et al. (1995). Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column stratification. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(9), 1895–1900.
De Grande, S. M. B., Neto, F. A., & Mello, M. R. (1993). Extended tricyclic terpanes in sediments and petroleum. Organic Geochemistry, 20(7), 1039–1047.
Du, D. D., Zhang, C. J., Mughal, M. S., Wang, X. Y., Blaise, D., Gao, J. P., et al. (2018). Detrital apatite fission track constraints on Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China: Evidence from Cenozoic strata in Lulehe section, Northern Qaidam Basin. Journal of Mountain Science, 15(3), 532–547.
Duan, Y., Zheng, C., Wang, Z., Wu, B., Wang, C., Zhang, H., et al. (2006). Biomarker geochemistry of crude oils from the Qaidam Basin, NW China. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 29(2), 175–188.
Dzou, L. I. P., Noble, R. A., & Senftle, J. T. (1995). Maturation effects on absolute biomarker concentration in a suite of coals and associated vitrinite concentrates. Organic Geochemistry, 23(7), 681–697.
Eggins, S. M., Kinsley, L. P. J., & Shelley, J. M. G. (1998). Deposition and element fractionation processes during atmospheric pressure laser sampling for analysis by ICP–MS. Applied Surface Science, 127, 278–286.
Eglinton, T. I., Damsté, J. S. S., Kohnen, M. E., & de Leeuw, J. W. (1990). Rapid estimation of the organic sulphur content of kerogens, coals and asphaltenes by pyrolysis–gas chromatography. Fuel, 69(11), 1394–1404.
EIA. (2012). Annual energy review 2011. United States. https://doi.org/10.2172/1212312.
Etxebarria, N., Zuloaga, O., Olivares, M., Bartolomé, L. J., & Navarro, P. (2009). Retention-time locked methods in gas chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216(10), 1624–1629.
Feng, J., Cao, J., Hu, K., Peng, X., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2013). Dissolution and its impacts on reservoir formation in moderately to deeply buried strata of mixed siliciclastic–carbonate sediments, northwestern Qaidam Basin, northwest China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 39(1), 124–137.
Fu, D., & Mazza, G. (2011). Optimization of processing conditions for the pretreatment of wheat straw using aqueous ionic liquid. Bioresource Technology, 102(17), 8003–8010.
Fu, J., Sheng, G., Xu, J., Eglinton, G., Gowar, A., Jia, R., et al. (1990). Application of biological markers in the assessment of paleoenvironments of Chinese non-marine sediments. Organic Geochemistry, 16(4–6), 769–779.
Galarraga, F., Reategui, K., Martïnez, A., Martínez, M., Llamas, J. F., & Márquez, G. (2008). V/Ni ratio as a parameter in palaeoenvironmental characterisation of nonmature medium-crude oils from several Latin American basins. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 61(1), 9–14.
Gao, Z., Zeng, L., & Niu, F. (2005). Unusually physical and chemical characteristics of oil sands from Qaidam basin, NW China. Geochemical Journal, 39(2), 121–130.
Grantham, P. J. (1986). Sterane isomerisation and moretane/hopane ratios in crude oils derived from Tertiary source rocks. Organic Geochemistry, 9(6), 293–304.
Gromet, L. P., Haskin, L. A., Korotev, R. L., & Dymek, R. F. (1984). The “North American shale composite”: Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48(12), 2469–2482.
Guo, T., Ren, S., Luo, X., Bao, S., Wang, S., Zhou, Z., et al. (2018). Accumulation conditions and prospective areas of shale gas in the Middle Jurassic Dameigou Formation, northern Qaidam Basin, Northwest China. Geological Journal, 53(6), 2944–2954.
Hakimi, M. H., & Abdullah, W. H. (2013). Organic geochemical characteristics and oil generating potential of the Upper Jurassic Safer shale sediments in the Marib-Shabowah Basin, western Yemen. Organic Geochemistry, 54, 115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2012.10.003.
Hakimi, M. H., Mohialdeen, I. M., Abdullah, W. H., Wimbledon, W., Makeen, Y. M., & Mustapha, K. A. (2015). Biomarkers and inorganic geochemical elements of Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous limestone sediments from Banik Village in the Kurdistan Region, Northern Iraq: Implications for origin of organic matter and depositional environment conditions. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(11), 9407–9421.
Hakimi, M., Selvanantham, T., Swinton, E., Padmore, R. F., Tong, Y., Kabbach, G., et al. (2011). Parkinson’s disease-linked LRRK2 is expressed in circulating and tissue immune cells and upregulated following recognition of microbial structures. Journal of Neural Transmission, 118(5), 795–808.
Holba, A. G., Dzou, L. I., Wood, G. D., Ellis, L., Adam, P., Schaeffer, P., et al. (2003). Application of tetracyclic polyprenoids as indicators of input from fresh-brackish water environments. Organic Geochemistry, 34(3), 441–469.
Horsfield, B. (1989). Practical criteria for classifying kerogens: Some observations from pyrolysis-gas chromatography. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53(4), 891–901.
Huang, R., Kerry, N., Yang, L., & Mohamed, G. (2016). Characterization and distribution of metal and nonmetal elements in the Alberta oil sands region of Canada. Chemosphere, 147, 218–229.
Huang, W. Y., & Meinschein, W. G. (1979). Sterols as ecological indicators. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 43(5), 739–745.
Huang, D., Zhang, D., & Li, J. (1994). The origin of 4-methyl steranes and pregnanes from Tertiary strata in the Qaidam Basin, China. Organic Geochemistry, 22(2), 343–348.
Hughes, T. J. (1995). Multiscale phenomena: Green’s functions, the Dirichlet-to-Neumann formulation, subgrid scale models, bubbles and the origins of stabilized methods. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 127(1–4), 387–401.
Ji, J., Zhang, K., Clift, P. D., Zhuang, G., Song, B., Ke, X., et al. (2017). High-resolution magnetostratigraphic study of the Paleogene–Neogene strata in the Northern Qaidam Basin: Implications for the growth of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Research, 46, 141–155.
Keym, M., Dieckmann, V., Horsfield, B., Erdmann, M., Galimberti, R., Kua, L. C., et al. (2006). Source rock heterogeneity of the Upper Jurassic Draupne Formation, North Viking Graben, and its relevance to petroleum generation studies. Organic Geochemistry, 37(2), 220–243.
Langmuir, D., & Melchior, D. (1985). The geochemistry of Ca, Sr, Ba and Ra sulfates in some deep brines from the Palo Duro Basin, Texas. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49(11), 2423–2432.
Larter, S. R., & Douglas, A. G. (1980). A pyrolysis-gas chromatographic method for kerogen typing. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 12, 579–583.
Lewan, M. D., & Maynard, J. B. (1982). Factors controlling enrichment of vanadium and nickel in the bitumen of organic sedimentary rocks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 46(12), 2547–2560.
Li, Y., Li, X., Wang, Y., Yu, Q., Yingjie, L., Xiaoyuan, L., et al. (2015). Effects of composition and pore structure on the reservoir gas capacity of Carboniferous shale from Qaidam Basin, China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 62, 44–57.
Li, L., Wu, C., Fan, C., Li, J., & Zhang, C. (2017). Carbon and oxygen isotopic constraints on paleoclimate and paleoelevation of the southwestern Qaidam basin, northern Tibetan Plateau. Geoscience Frontiers, 8(5), 1175–1186.
Lu, H., & Xiong, S. (2009). Magnetostratigraphy of the Dahonggou section, northern Qaidam Basin and its bearing on Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Qilian Shan and Altyn Tagh Fault. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 288(3–4), 539–550.
Lu, Z., Zhang, J., & Mattinson, C. (2018). Tectonic erosion related to continental subduction: An example from the eastern North Qaidam Mountains, NW China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 36(5), 653–666.
Makeen, Y. M., Abdullah, W. H., & Hakimi, M. H. (2015a). Biological markers and organic petrology study of organic matter in the Lower Cretaceous Abu Gabra sediments (Muglad Basin, Sudan): Origin, type and palaeoenvironmental conditions. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(1), 489–506.
Makeen, Y. M., Abdullah, W. H., & Hakimi, M. H. (2015b). The origin, type and preservation of organic matter of the Barremiane Aptian organic-rich shales in the Muglad Basin, Southern Sudan, and their relation to paleoenvironmental and paleoclimate conditions. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 65(187–197), 2015.
Makeen, Y. M., Abdullah, W. H., Hakimi, M. H., & Elhassan, O. M. (2015c). Organic geochemical characteristics of the Lower Cretaceous Abu Gabra Formation in the Great Moga oilfield, Muglad Basin, Sudan: Implications for depositional environment and oil-generation potential. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 103, 102–112.
Makeen, Y. M., Abdullah, W. H., Hakimi, M. H., Hadad, Y. T., Mustapha, K. A., & Elhassan, O. M. A. (2015d). Geochemical characteristics of crude oils, their asphaltene and related organic matter source inputs from Fula oilfields in the Muglad Basin, Sudan. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 67, 816–828.
Manzano, C., Muir, D., Kirk, J., Teixeira, C., Siu, M., Wang, X., et al. (2016). Temporal variation in the deposition of polycyclic aromatic compounds in snow in the Athabasca Oil Sands area of Alberta. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 542.
Mao, L., Xiao, A., Zhang, H., Wu, Z., Wang, L., Shen, Y., et al. (2016). Structural deformation pattern within the NW Qaidam Basin in the Cenozoic era and its tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 687, 78–93.
Marek, O., Mirjavad, G., Douglas, G., Liu, Q., & Thomas, H. (2013). Mineralogical and chemical composition of petrologic end members of Alberta oil sands. Fuel, 113, 148–157.
Mei, M., Bissada, K., Malloy, T., Darnell, L., & Liu, Z. (2018). Origin of condensates and natural gases in the Almond Formation reservoirs in southwestern Wyoming, USA. Organic Geochemistry, 116, 35–50.
Meng, Q. R., Hu, J. M., & Yang, F. Z. (2001). Timing and magnitude of displacement on the Altyn Tagh fault: Constraints from stratigraphic correlation of adjoining Tarim and Qaidam basins, NW China. Terra Nova, 13(2), 86–91.
Métivier, F., Gaudemer, Y., Tapponnier, P., & Meyer, B. (1998). Northeastward growth of the Tibet plateau deduced from balanced reconstruction of two depositional areas: The Qaidam and Hexi Corridor basins, China. Tectonics, 17(6), 823–842.
Mischke, S., Sun, Z., Herzschuh, U., Qiao, Z., & Sun, N. (2010). An ostracod-inferred large Middle Pleistocene freshwater lake in the presently hyper-arid Qaidam Basin (NW China). Quaternary International, 218(1–2), 74–85.
Mohialdeen, I. M. J., & Hakimi, M. H. (2016). Geochemical characterisation of Tithonian–Berriasian Chia Gara organic-rich rocks in northern Iraq with an emphasis on organic matter enrichment and the relationship to the bioproductivity and anoxia conditions. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 116, 181–197.
Mohialdeen, I. M. J., Hakimi, M. H., & Al-Beyati, F. M. (2015). Biomarker characteristics of some crude oils and oil–source rock correlation in the Kurdistan oilfields, Northern Iraq. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8, 507–523.
Moldowan, J. M., Sundararaman, P., & Schoell, M. (1986). Sensitivity of biomarker properties to depositional environment and/or source input in the Lower Toarcian of SW-Germany. Organic Geochemistry, 10(4–6), 915–926.
Niu, J., & Hu, J. (1999). Formation and distribution of heavy oil and tar sands in China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 16(1), 85–95.
Park, M., Kil, Y., Choi, J., Seol, J., & Kim, J. (2018). Biodegradation characteristics of bitumen from the Upper Devonian carbonates (Grosmont and Nisku formations) in Alberta, Canada. Geosciences Journal, 22(5), 751–763.
Pattan, J. N., & Pearce, N. J. G. (2009). Bottom water oxygenation history in southeastern Arabian Sea during the past 140 ka: Results from redox-sensitive elements. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 280(3–4), 396–405.
Peters, K. E., & Cassa, M. R. (1994). Applied source rock geochemistry. In: L. B. Magoon & W. G. Dow (Eds.), The petroleum system—from source to trap (Vol. 60, pp. 93–120). Tulsa: AAPG.
Peters, K. E., & Moldowan, J. M. (1993). The biomarker guide: Interpreting molecular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments. Choice Reviews Online, 30(5), 30–2690. https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.30-2690.
Peters, K. E., Walters, C. C., & Moldowan, J. M. (2004). The biomarker guide. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511524868.
Peters, K. E., Walters, C. C., & Moldowan, J. M. (2005). The biomarker guide. Biomarkers & isotopes in petroleum systems & earth history (2nd ed., p. 490). https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511524868.
Peters, K. E., Walters, C. C., & Moldowan, J. M. (2017). Biomarkers: assessment of petroleum source–rock age and depositional environment. In Encyclopedia of petroleum geoscience.
Pi, H. J., Hangya, B., Kvitsiani, D., Sanders, J. I., Huang, Z. J., & Kepecs, A. (2013). Cortical interneurons that specialize in disinhibitory control. Nature, 503(7477), 521.
Qin, J., Wang, S., Sanei, H., Jiang, C., Chen, Z., Ren, S., et al. (2018). Revelation of organic matter sources and sedimentary environment characteristics for shale gas formation by petrographic analysis of middle Jurassic Dameigou formation, northern Qaidam Basin, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 195(1), 373–385.
Rabbani, A. R., & Kamali, M. R. (2005). Source rock evaluation and petroleum geochemistry, offshore SW Iran. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 28(4), 413–428.
Radke, M., Welte, D. H., & Willsch, H. (1986). Maturity parameters based on aromatic hydrocarbons: Influence of the organic matter type. Organic Geochemistry, 10(1–3), 51–63.
Radke, M., Willsch, H., Leythaeuser, D., & Teichmüller, M. (1982). Aromatic components of coal: Relation of distribution pattern to rank. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 46(10), 1831–1848.
Reimann, C., de Caritat, P., Niskavaara, H., Finne, T. E., Kashulina, G., & Pavlov, V. A. (1998). Comparison of elemental contents in O-and C-horizon soils from the surroundings of Nikel, Kola Peninsula, using different grain size fractions and extractions. Geoderma, 84(1–3), 65–87.
Seifert, W. K., & Moldowan, J. M. (1978). Applications of steranes, terpanes and monoaromatics to the maturation, migration and source of crude oils. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 42(1), 77–95.
Shu, D., Xu, S., Wu, S., Li, S., Wang, D., Xiao, Y., et al. (2017). Jurassic sedimentary provenances of the Hongshan and Huobuxun sags in the eastern segment of the northern Qaidam Basin: Basin-Mountain coupling. Geological Journal, 52, 380–393.
Silva, R. S., Aguiar, H. G., Rangel, M. D., Azevedo, D. A., & Neto, F. R. A. (2011). Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with time of flight mass spectrometry applied to biomarker analysis of oils from Colombia. Fuel, 90(8), 2694–2699.
Sinninghe, D., & De, L. (1990). Analysis, structure and geochemical significance of organically-bound sulphur in the geosphere: State of the art and future research. Organic Geochemistry, 16(4–6), 1077–1101.
Sudiptya, B., & Berna, H. (2018). Flow control devices in SAGD completion design: Enhanced heavy oil/bitumen recovery through improved thermal efficiency. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 169, 297–308.
Ten, H., De, L., Rullkötter, J., & Damsté, J. S. (1987). Restricted utility of the pristane/phytane ratio as a palaeoenvironmental indicator. Nature, 330(6149), 641.
Tenenbaum, D. J. (2009). Oil sands development: A health risk worth taking? Environmental Health Perspectives, 117(4), A150.
Tian, J., Li, J., Pan, C., Tan, Z., Zeng, X., Guo, Z., et al. (2018). Geochemical characteristics and factors controlling natural gas accumulation in the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 160, 219–228.
Wang, J., Feng, L., Steve, M., Tang, X., Gail, T. E., & Mikael, H. (2015). China’s unconventional oil: A review of its resources and outlook for long-term production. Energy, 82, 31–42.
Wang, Y., Zheng, J., Zhang, W., Li, S., Liu, X., Yang, X., et al. (2012). Cenozoic uplift of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from the tectonic–sedimentary evolution of the western Qaidam Basin. Geoscience Frontiers, 3(2), 175–187.
Waseda, A., & Nishita, H. (1998). Geochemical characteristics of terrigenous-and marine-sourced oils in Hokkaido, Japan. Organic Geochemistry, 28(1–2), 27–41.
Wentzel, A., Ellingsen, T. E., Kotlar, H. K., Zotchev, S. B., & Throne-Holst, M. (2007). Bacterial metabolism of long-chain n-alkanes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 76(6), 1209–1221.
Wilhelms, A., & Larter, S. (2004). Shaken but not always stirred. Impact of petroleum charge mixing on reservoir geochemistry. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 237(1), 27–35.
William, K., Cristiana, L., Nigel, J., Geoff, J., Holly, F., Steve, J., et al. (2018). Petrography and trace element signatures of iron-oxides in deposits from the Middleback Ranges, South Australia: From banded iron formation to ore. Ore Geology Reviews, 93, 337–360.
Yang, Y., Zhang, B., Zhao, C., & Xu, T. (2004). Mesozoic source rocks and petroleum systems of the northeastern Qaidam basin, northwest China. AAPG Bulletin, 88(1), 115–125.
Yi, D., Wang, J., Shi, Y., Sun, X., Ma, X., Wang, P., et al. (2017). Evolution characteristic of gypsum-salt rocks of the upper member of Oligocene Lower Ganchaigou Fm in the Shizigou area, western Qaidam Basin. Natural Gas Industry B, 4(5), 390–398.
Yin, A., Dang, Y. Q., Wang, L. C., Jiang, W. M., Zhou, S. P., Chen, X. H., et al. (2008). Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Qaidam basin and its surrounding regions (Part 1): The southern Qilian Shan-Nan Shan thrust belt and northern Qaidam basin. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 120(7–8), 813–846.
Zhou, S., Huang, H., & Liu, Y. (2008). Biodegradation and origin of oil sands in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. Petroleum Science, 5(2), 87–94.
Zhou, J., Xu, F., Wang, T., Cao, A., & Yin, C. (2006). Cenozoic deformation history of the Qaidam Basin, NW China: Results from cross-section restoration and implications for Qinghai-Tibet Plateau tectonics. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 243(1–2), 195–210.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Basic geological survey of oil Shale and oil Sands in Songliao, Qaidam and Erlian Basins (Grant No. DD20160188), China Geological Survey and China Scholarship Council (Grant No. 201701760617), and two key laboratories including Key Laboratory for Evolution of Past Life and Environment in Northeast Asia (Jilin University) and the Organic Geochemistry Laboratories of the Department of Geology, University of Malaya, Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Shan, X., Makeen, Y.M. et al. Geochemical Characteristics of Oil from Oligocene Lower Ganchaigou Formation Oil Sand in Northern Qaidam Basin, China. Nat Resour Res 28, 1521–1546 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09466-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09466-9