Abstract
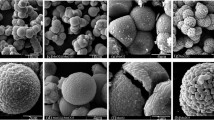
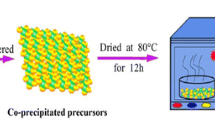
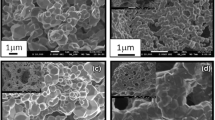
The high-voltage spinel is a promising cathode material in next generation of lithium-ion batteries. Samples LiNi0.5 − xMn1.5 + xO4 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1) are synthesized by a simple co-precipitation method, in which pH value and temperature conditions do not need control. In the simple co-precipitation method, NaHCO3 solution is poured into transition metal solution to produce precursor. Ni and Mn are distributed uniformly in the products. The as-prepared samples are composed of ~ 200 nm primary particles. Samples LiNi0.5 − xMn1.5 + xO4 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1) are also tested to study the effects of different Ni/Mn ratios. Sample LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 delivers discharge capacities of 130 mAh g−1 at 0.2 C. The decreasing of Ni/Mn ratio in samples reduces specific capacity. With the decreasing of Ni/Mn ratios in spinel, amount of Mn3+ are increased. Attributed to its high Mn3+ contents, sample LiNi0.4Mn1.6O4 delivers the highest discharge capacity of 106 mAh g−1 at a large current density of 15 C, keeping 84.5% of that at 0.2 C rate. With the increasing of Ni/Mn ratios in spinel, cycling performance is improved. Sample LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 shows the best cycling stability, keeping 94.4% and 90.4% of the highest discharge capacities after 500 cycles at 1 C and 1000 cycles at 5 C.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axmann P, Gabrielli G, Wohlfahrt-Mehrens M (2016) Tailoring high-voltage and high-performance LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for high energy lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 301:151–159
Bauer S, Biasi L, Glatthaar S, Toukam L, Geßwein H, Baumbach T (2015) In operando study of the high voltage spinel cathode material LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 using two dimensional full-field spectroscopic imaging of Ni and Mn. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:16388–16397
Cai Y, Huang Y, Wang X, Jia D, Tang X (2014) Long cycle life, high rate capability of truncated octahedral LiMn2O4 cathode materials synthesized by a solid-state combustion reaction for lithium ion batteries. Ceram Int 40:14039–14043
Cai Y, Huang Y, Wang X, Cai D, Jia W, Tang X (2015) Facile synthesis of LiMn2O4 octahedral nanoparticles as cathode materials for high capacity lithium ion batteries with long cycle life. J Power Sources 278:574–581
Cai Y, Huang Y, Jia W, Wang X, Guo Y, Jia D, Guo Z (2016) Super high-rate, long cycle life of europium-modified, carbon-coated, hierarchical mesoporous lithium-titanate anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 4:9949–9957
Chemelewski KR, Shin DW, Li W, Manthiram A (2013) Octahedral and truncated high-voltage spinel cathodes: the role of morphology and surface planes in electrochemical properties. J Mater Chem A 1:3347
Croguennec L, Palacin MR (2015) Recent achievements on inorganic electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Am Chem Soc 137:3140–3156
Fang Y, Huang Y, Zhang S, Jia W, Wang X, Guo Y, Wang L (2017) Synthesis of unique hierarchical mesoporous layered-cube Mn2O3 by dual-solvent for high-capacity anode material of lithium-ion batteries. Chem Eng J 315:583–590
Fang Y, Huang Y, Tong W, Cai Y, Wang X, Guo Y, Zong J (2018) Synthesis of hollow peanut-like hierarchical mesoporous LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode materials with exceptional cycle performance for lithium-ion batteries by a simple self-template solid-state method. J Alloys Compd 743:707–715
Goodenough JB (2014) Electrochemical energy storage in a sustainable modern society. Energy Environ Sci 7:14–18
Gu YJ, Zang QF, Liu HQ, Ding JX, Wang YM, Wang HF, Wei WG (2014) Characterization and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 prepared by a carbonate co-precipitation method. Int J Electrochem Sci 9:1
Gu YJ, Li Y, Fu Y, Zang QF, Liu HQ, Ding JX, Ni J (2015) LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 synthesized through ammonia-mediated carbonate precipitation. Electrochim Acta 176:1029–1035
Kim JH, Myung ST, Yoon CS, Kang SG, Sun YK (2004) Comparative study of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4-δ and LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes having two crystallographic structures: Fd3m and P4332. Chem Mater 16:906
Kunduraci M, Amatucci GG (2006) Synthesis and characterization of nanostructured 4.7 V LixMn1.5Ni0.5O4 spinels for high-power lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc 153:A1345
Kunduraci M, Amatucci GG (2007) Effect of oxygen non-stoichiometry and temperature on cation ordering in LiMn2−xNixO4 (0.50≥ x≥ 0.36) spinels. J Power Sources 165:359–367
Kunduraci M, Al-sharab JF, Amatucci GG (2006) High-power nanostructured LiMn2-xNixO4 high-voltage lithium-ion battery electrode materials: electrochemical impact of electronic conductivity and morphology. Chem Mater 18:3585–3592
Lee ES, Nam KW, Hun E, Manthiram A (2012) Influence of cation ordering and lattice distortion on the charge–discharge behavior of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel between 5.0 and 2.0 V. Chem Mater 24:3610
Li XP, Li WS (2014) Crystallographic facet-and size-controllable synthesis of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with excellent cyclic stability as cathode of high voltage lithium ion battery. J Mater Chem A 2:11987
Li SR, Chen CH, Camardese J, Dahn JR (2013) High precision coulometry study of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4/Li coin cells. J Electrochem Soc 160:A1517–A1523
Liu G, Park KS, Song J, Goodenough JB (2013a) Influence of thermal history on the electrochemical properties of Li[Ni0.5Mn1.5]O4. J Power Sources 243:260
Liu J, Sun Z, Xie J, Chen H, Wu N, Wu B (2013b) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5−xCuxMn1.5−yAlyO4 (x= 0, 0.05, y= 0, 0.05) as 5 V spinel materials. J Power Sources 240:95–100
Liu H, Zhu G, Zhang L, Qu Q, Shen M, Zheng H (2015) Controllable synthesis of spinel lithium nickel manganese oxide cathode material with enhanced electrochemical performances through a modified oxalate co-precipitation method. J Power Sources 274:1180–1187
Luo W (2015) Effect of morphology on the physical and electrochemical properties of the high-voltage spinel cathode LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. J Alloy Compd 636:24
Lv YZ, Jin YZ, Xue Y, Wu J, Zhang XG, Wang ZB (2014) Electrochemical properties of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 synthesized by a solid-state method. RSC Adv 4:26022–26029
Manthiram, Chemelewski K, Lee ES (2014) A perspective on the high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ Sci 7:1339
Moorhead-Rosenberg Z, Shin DW, Chemelewski KR, Goodenough JB, Manthiram A (2012) Quantitative determination of Mn3+ content in LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 spinel cathodes by magnetic measurements. Appl Phys Lett 100:213909
Mou J, Deng Y, He L, Zheng Q, Jiang N, Lin D (2018) Critical roles of semi-conductive LaFeO3 coating in enhancing cycling stability and rate capability of 5 V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials. Electrochim Acta 260:101–111
Park OK, Cho Y, Lee S, Yoo HC, Song HK, Cho J (2011) Who will drive electric vehicles, olivine or spinel? Energy Environ Sci 4:1621–1633
Pieczonka NPW, Liu Z, Lu P, Olson KL, Moote J, Powell BR (2013) Understanding transition-metal dissolution behavior in LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 high-voltage spinel for lithium ion batteries. J Phys Chem C 117:15947–15957
Ren W, Luo R, Liu ZS, Tan XY, Fu ZY, Liao SJ (2014) Effect of Ni/Mn ratio on the performance of LiNixMn2−xO4 cathode material for lithium-ion battery. Ionics 20:1361–1366
Santhanam R, Rambabu B (2010) Research progress in high voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 material. J Power Sources 195:5442–5451
Song J, Shin DW, Lu Y, Amos CD, Manthiram A, Goodenough JB (2012) Role of oxygen vacancies on the performance of Li[Ni0.5-xMn1.5+x]O4 (x=0, 0.05, and 0.08) spinel cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. Chem Mater 24:3101–3109
Tong W, Huang Y, Cai Y, Guo Y, Wang X, Jia D, Zong J (2018) Synthesis of hierarchical mesoporous lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide spheres with high rate capability for lithium-ion batteries. Appl Surf Sci 428:1036–1045
Wan L, Deng Y, Yang C, Xu H, Qin X, Chen G (2015) Ni/Mn ratio and morphology-dependent crystallographic facet structure and electrochemical properties of the high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material. RSC Adv 5:25988–25997
Xiao J, Chen X, Sushko PV, Sushko ML, Kovarik L, Feng J, Choi D (2012) High performance LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel controlled by Mn3+ concentration and site disorder. Adv Mater 24:2109
Xiao J, Yu X, Zheng J, Zhou Y, Gao F, Chen X, Bai J, Yang X-Q, Zhang J-G (2013) Interplay between two-phase and solid solution reactions in high-voltage spinel cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 242:736–741
Xue Y, Wang ZB, Yu FD, Zhang Y, Yin GP (2014) Ethanol-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with excellent long-term cyclability at high rate for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 2:4185–4191
Xue Y, Wang ZB, Zheng LL, Yu FD, Liu BS, Zhou YX (2017) Investigation on spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 synthesized by MnCO3 prepared under different conditions for lithium-ion batteries. ChemistrySelect 2:4324
Yao Y, Liu H, Li G, Peng H, Chen K (2014) Multi-shelled porous LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 microspheres as a 5 V cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Mater Chem Phys 143:867–872
Yi TF, Hu XG (2007) Preparation and characterization of sub-micro LiNi0.5−xMn1.5+xO4 for 5 V cathode materials synthesized by an ultrasonic-assisted co-precipitation method. J Power Sources 167:185–191
Yi TF, Mei J, Zhu YR (2016) Key strategies for enhancing the cycling stability and rate capacity of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as high-voltage cathode materials for high power lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 316:85–105
Yin C, Zhou H, Yang Z, Li J (2018) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for Li-ion batteries by the metal-organic framework method. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:13625–13634
Zhang M, Wang J, Xia Y, Liu Z (2012) Microwave synthesis of spherical spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 518:68–73
Zhang Y, Jia D, Tang Y, Huang Y, Pang W, Guo Z, Zhou Z (2018) In situ chelating synthesis of hierarchical LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 polyhedron assemblies with ultralong cycle life for Li-ion batteries. Small 14:1704354
Zhu Z, Yan H, Zhang D, Li W, Lu Q (2013) Preparation of 4.7 V cathode material LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by an oxalic acid-pretreated solid-state method for lithium-ion secondary battery. J Power Sources 224:13–19
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21273058 and 21673064), China postdoctoral science foundation (Grant Nos. 2017M621285 and 2018T110292), and Harbin technological achievements transformation projects (2016DB4AG023) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y., Zheng, LL., Wang, ZB. et al. Simple co-precipitation synthesis of high-voltage spinel cathodes with different Ni/Mn ratios for lithium-ion batteries. J Nanopart Res 20, 257 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4363-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4363-7