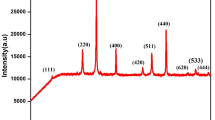
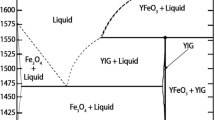
Abstract
Glasses in the system 51.7 B2O3/9.3 K2O/1 P2O5/10.4 Fe2O3/(27.6 − y) MgO/y ZnO (with y = 0, 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 13.8, and 20) were prepared by the conventional melt quenching method. The glass samples were thermally treated at 560 °C for 3 h in ambient conditions. Using 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy, the effect of the substitution of MgO by ZnO in the glass network and the effect on the precipitated crystallized phase was studied. The results showed that the ratio of Zn2+:Mg2+ in the precipitated crystals increases with the ZnO concentration in the glass. The isomer shift values indicated that iron occurs as Fe3+, which is distributed at the tetrahedral (A) and the octahedral [B] sites. Introducing ZnO leads to a relative increase of the Fe3+ concentration at the B sites at the expense of that occupying the A sites. This indicates the precipitation of ZnxMg1-x Fe2O4 nanoparticles, where Zn2+ ions favorably occupy the A sites. The average hyperfine field of the samples showed a strong dependence on the Zn concentration. At the highest Zn concentration of 13.8 and 20 mol%, the samples are paramagnetic, while for the smaller ones, the samples are superparamagnetic.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharoni A (1973) Relaxation time of superparamagnetic particles with cubic anisotropy. Phys Rev B 7:1103–1107
Blasse G (1964) Crystal chemistry and some magnetic properties of mixed metal oxides with spinel structure. Philips reseach reports, supplement 3. Philips Research Laboratories, Eindhoven, p 139
Bretcanu O, Spriano S, Vitale CB, Verné E (2006a) Synthesis and characterization of coprecipitation-derived ferrimagnetic glass-ceramic. J Mater Sci 41:1029–1037
Bretcanu O, Verné E, Cöisson M, Tiberto P, Allia P (2006b) Temperature effect on the magnetic properties of the coprecipitation derived ferrimagnetic glass-ceramics. J Magn Magn Mater 300:412–417
Chen Q, Rondinone AJ, Chakoumakos CB, Zhang JZ (1999) Synthesis of superparamagnetic MgFe2O4 nanoparticles by coprecipitation. J Magn Magn Mater 194:1–7
Durrani SK, Naz S, Mehmood M et al (2016) Structural, impedance and Mössbauer studies of magnesium ferrite synthesized via sol–gel auto-combustion process. J Saudi Chem Soc 21(8):899–910
Dyar MD (1985) A review of Mössbauer data on inorganic glasses: the effects of composition on iron valency and coordination. Am Mineral 70:304–316
El Shabrawy S, Bocker C, Rüssel C (2016) Crystallization of MgFe2O4 from a glass in the system K2O/B2O3/MgO/P2O5/Fe2O3. Solid State Sci 60:85–91
El Shabrawy S, Bocker C, Tzankov D et al (2017) The effect of zinc substitution on the magnetism of magnesium ferrite nanostructures crystallized from borate glasses. Ceram Int 43:3804–3810
Fayeka MK, Ata-AHaha SS, Refaia HS, Mostafa MF (2000) On the hyperfine parameters of copper nickel-aluminum ferrite. 2nd Conference on Nuclear and Particle Physics, Cairo, Egypt, 13–17 Nov 1999
Gerlach S, Claußen O, Rüssel C (1998) Thermodynamics of iron in alkali–magnesia–silica glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 238:75–82
Gonser U, Schaaf P, Aubertin F (1991) Simultaneous triple radiation Mössbauer spectroscopy (STRMS). Hyperfine Interact 66:95–100
Harizanova R, Völksch G, Rüssel C (2009) Microstructures formed during devitrification of Na2O·Al2O3·B2O3·SiO2·Fe2O3 glasses. J Mater Sci 45:1350–1353
Harizanova R, Gugov I, Rüssel C, Tatchev D, Raghuwanshi VS, Hoell A (2011) Crystallization of (Fe, Mn)-based nanoparticles in sodium-silicate glasses. J Mater Sci 46:7169–7176
He Y, Yang X, Lin J et al (2015) Mössbauer spectroscopy, structural and magnetic studies of Zn2+ substituted magnesium ferrite nanomaterials prepared by sol-gel method. J Nanomater 2015:e854840
Issa B, Obaidat IM, Albiss BA, Haik Y (2013) Magnetic nanoparticles: surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int J Mol Sci 14:21266–21305
Jayasuriya KD, OʼNeill HSC, Berry AJ, Campbell SJ (2015) A Mössbauer study of the oxidation state of Fe in silicate melts. Am Mineral 89:1597–1609
Khot SS, Shinde NS, Ladgaonkar BP et al (2011) Magnetic and structural properties of magnesium zinc ferrites synthesized at different temperature. Adv Appl Sci Res 4:460–471
Kliava J, Edelman I, Ivanova O, Ivantsov R, Bayukov O, Petrakovskaja E, Zaikovskiy V, Bruckental I, Yeshurun Y, Stepanov S (2008) Formation and evolution of magnetic nanoparticles in borate glass simultaneously doped with Fe and Mn oxides. J Appl Phys 104:103917
Kulkarni RG, Joshi HH (1985) The magnetic properties of the mg-Zn ferrite system by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Solid State Commun 53:1005–1008
Kulkarni RG, Joshi HH (1986) Comparison of magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 prepared by wet-chemical and ceramic methods. J Solid State Chem 64:141–147
Kurmude DV, Kale CM, Aghav PS, Shengule DR, Jadhav KM (2014) Superparamagnetic behavior of zinc-substituted nickel ferrite nanoparticles and its effect on Mossbauer and magnetic parameters. J Supercond Nov Magn 27:1889–1897
Liu C, Zou B, Rondinone AJ, Zhang ZJ (2000) Chemical control of superparamagnetic properties of magnesium and cobalt spinel ferrite nanoparticles through atomic level magnetic couplings. J Am Chem Soc 122:6263–6267
McBain SC, Yiu HH, Dobson J (2008) Magnetic nanoparticles for gene and drug delivery. Int J Nanomedicine 3:169–180
Nath BK, Chakrabarti PK, Das S, Kumar U, Mukhopadhyay PK, Das D (2004) Mössbauer, X-ray diffraction and AC susceptibility studies on nanoparticles of zinc substituted magnesium ferrite. Eur Phys J B 39:417–425
Nath BK, Chakrabarti PK, Das S et al (2005) Mossbauer studies on nanoparticles of zinc substituted magnesium ferrite. J Surf Sci Technol 21:169–182
Néel L (1949) Théorie du traînage magnétique des ferromagnétiques en grains fins avec applications aux terres cuites. Ann Géophys 5:99–136
Niyaifar M (2014) Effect of preparation on structure e and magnetic properties of ZnFe2O4. J Magn 19:101–105
Okita A, Saito F, Sasaki S, Toyoda T, Koinuma H (1998) Determination of cation distribution in Mn–Zn–Fe ferrite by X-ray anomalous scattering. Jpn J Appl Phys 37:3441–3445
Ounnunkad S, Winotai P, Phanichphant S (2006) Cation distribution and magnetic behavior of Mg1 − xZnxFe2O4 ceramics monitored by Mössbauer spectroscopy. J Electroceram 16:363–368
Pascuta P, Vladescu A, Borodi G, Culea E, Tetean R (2011) Structural and magnetic properties of zinc ferrite incorporated in amorphous matrix. Ceram Int 37:3343–3349
Rixecker G, Schaaf P, Gonser U (1993) Depth selective analysis of phases and spin textures in amorphous, nanocrystalline and crystalline ribbons treated with an excimer laser. J Phys Appl Phys 26:870–879
Rüssel C, Sprachmann G (1991) Electrochemical methods for investigations in molten glass, illustrated at iron- and arsenic-doped soda-lime-silica glass melts. J Non-Cryst Solids 127:197–206
Sandu V, Nicolescu MS, Kuncser V, Damian R, Sandu E (2012) Magnetic glass-ceramics. J Adv Ceram 1:138–143
Schaaf P, Krämer A, Blaes L, Wagner G, Aubertin F, Gonser U (1991) Simultaneous conversion electron, conversion X-ray and transmission Mössbauer spectroscopy. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 53:184–186
Shabrawy SE, Bocker C, Miglierini M, Schaaf P, Tzankov D, Georgieva M, Harizanova R, Rüssel C (2017) Mössbauer study and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 crystallized from the glass system B2O3/K2O/P2O5/MgO/Fe2O3. J Magn Magn Mater 421:306–315
Sharifi I, Shokrollahi H, Amiri S (2012) Ferrite-based magnetic nanofluids used in hyperthermia applications. J Magn Magn Mater 324:903–915
Siddique M, Butt NM (2010) Effect of particle size on degree of inversion in ferrites investigated by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Phys B Condens Matter 405:4211–4215
Sun C, Lee JSH, Zhang M (2008) Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1252–1265
Tricker MJ, Thomas JM, Omar MH, Osman A, Bishay A (1974) Mössbauer and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies of heat-treated calcium borate glasses containing iron. J Mater Sci 9:1115–1122
Woltz S, Rüssel C (2004) Self organized nano crystallinity of magnetite precipitated from a 4.9Na2O · 33.3CaO · 17.1Fe2O3 · 44.7B2O3 glass. J Non-Cryst Solids 337:226–231
Woltz S, Hiergeist R, Görnert P, Rüssel C (2006) Magnetite nanoparticles prepared by the glass crystallization method and their physical properties. J Magn Magn Mater 298:7–13
Worsch C, Büttner M, Schaaf P et al (2012) Magnetic properties of multicore magnetite nanoparticles prepared by glass crystallisation. J Mater Sci 48:2299–2307
Yahya N, Mohamad Nor Aripin AS, Aziz A et al (2008) Synthesis and charaterization of magnesium zinc ferrites as electromagnetic source. Am J Eng Appl Sci 1:54–57
Zhang Y, Wen D (2012) Infrared emission properties of RE (RE = La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, and Dy) and Mn co-doped Co0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 ferrites. Mater Chem Phys 131:575–580
Zhang Y, Lin J, Wen D (2010) Structure, infrared radiation properties and Mössbauer spectroscopic investigations of Co0.6Zn0.4NixFe2-xO4 ceramics. J Mater Sci Technol 26:687–692
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We declare that we agree with the ethical standards of the journal.
Part of this study was funded by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) and Bundesministerium für Forschung und Technologie via DESY PT under grant 05K16Sl1.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Shabrawy, S., Miglierini, M., Schaaf, P. et al. Mössbauer spectroscopy of ZnxMg1-x Fe2O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.74) nanostructures crystallized from borate glasses. J Nanopart Res 20, 81 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4180-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4180-z