Abstract
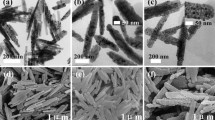
ZnO@γ-Fe2O3 core–shell nanocomposites were synthesized by a facile thermal decomposition approach. ZnO nanorods were first synthesized by calcination of zinc acetate at 300 °C, in air. γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles were then deposited on the surface of ZnO nanorods by the thermal decomposition of iron acetylacetonate at 200 °C in diphenyl ether. The structure, composition, optical and magnetic properties of the nanocomposites were studied using an array of techniques. XRD results suggest the presence of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and ZnO, and FE-SEM images indicate formation of shell of iron oxide on the ZnO nanorods. Transmission electron microscopy studies clearly show that ZnO possesses rod morphology (length = 1.1 ± 0.1 μm, diameter = 40.1 ± 7 nm) and TEM images of the ZnO@γ-Fe2O3 nanocomposites show uniform shell of γ-Fe2O3 coated on the ZnO nanorods and thickness of the γ-Fe2O3 shell varies from 10 to 20 nm. Diffuse reflectance spectra of ZnO@γ-Fe2O3 nanocomposites reveal extended optical absorption in the visible range (400–600 nm) and photoluminescence spectra indicate that the ZnO@γ-Fe2O3 nanocomposites exhibit enhanced defect emission. The ZnO@γ-Fe2O3 core–shell nanocomposites show superparamagnetic behaviour at room temperature. The core–shell nanocomposites exhibit enhanced visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of congo red in an aqueous solution as compared to pure ZnO nanorods and γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. The enhanced photocatalytic activity is attributed to good visible-light absorption and effective charge separation at the interface of ZnO@γ-Fe2O3 core–shell nanocomposites.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah Mirzaie R, Kamrani F, Anaraki Firooz A, Khodadadi AA (2012) Effect of α-Fe2O3 addition on the morphological, optical and decolorization properties of ZnO nanostructures. Mater Chem Phys 133:311–316. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.01.029
Amin N, Arajs S (1987) Morin temperature of annealed submicronic α-Fe2O3 particles. Phys Rev B 35(10):4810–4811. doi:10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Apte SK, Naik SD, Sonawane RS, Kale BB, Baeg JO (2007) Synthesis of nanosize-necked structure α- and γ-Fe2O3 and its photocatalytic activity. J Am Ceram Soc 90(2):412–414. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2006.01424.x
Ayyappan S, Gnanaprakash G, Panneerselvam G, Antony MP, Philip J (2008) Effect of surfactant monolayer on reduction of Fe3O4 nanoparticles under vacuum. J Phys Chem C 112(47):18376–18383. doi:10.1021/jp8052899
Azizi K, Heydari A (2014) Vitamin B1 supported on silica-encapsulated γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: design, characterization and application as a greener biocatalyst for highly efficient acylation. RSC Adv 4(17):8812–8816. doi:10.1039/c3ra46437g
Balti I, Smiri LS, Rabu P, Gautron E, Viana B, Jouini N (2014) Synthesis and characterization of rod-like ZnO decorated with γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles monolayer. J Alloys Compd 586:S476–S482. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.02.118
Bødker F, Hansen MF, Koch CB, Lefmann K, Mørup S (2000) Magnetic properties of hematite nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 61(10):6826–6838. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.61.6826
Chandraiahgari CR, De Bellis G, Ballirano P, Balijepalli SK, Kaciulis S, Caneve L, Sarto F, Sarto MS (2015) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanorods with a narrow size distribution. RSC Adv 5(62):49861–49870. doi:10.1039/C5RA02631H
Chen D, Xu R (1998) Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline γ-Fe2O3 particles. J Solid State Chem 137(9):185–190. doi:10.1006/jssc.1997.7631
Chen C, Ma W, Zhao J (2010a) Semiconductor-mediated photodegradation of pollutants under visible-light irradiation. Chem Soc Rev 39(11):4206–4219. doi:10.1039/b921692h
Chen YJ, Zhang F, Zhao GG, Fang XY, Jin HB, Gao P, Zhu CL, Cao MS, Xiao G (2010b) Synthesis, multi-nonlinear dielectric resonance, and excellent electromagnetic absorption characteristics of Fe3O4/ZnO core/shell nanorods. J Phys Chem C 114(20):9239–9244. doi:10.1021/jp912178q
Chu XY, Hong X, Zhang XT, Zou P, Liu YC (2008) Heterostructures of ZnO microrods coated with iron oxide nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 112(41):15980–15984. doi:10.1021/jp804590y
Farbod M, Kajbafvala M (2013) Effect of nanoparticle surface modification on the adsorption-enhanced photocatalysis of Gd/TiO2 nanocomposite. Powder Technol 239:434–440. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2013.02.027
Fu R, Wang W, Han R, Chen K (2008) Preparation and characterization of γ-Fe2O3/ZnO composite particles. Mater Lett 62(25):4066–4068. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2008.05.006
Guo N, Liang Y, Lan S, Liu L, Zhang J, Ji G, Gan S (2014) Microscale hierarchical three-dimensional flowerlike TiO2/PANI composite: synthesis, characterization, and its remarkable photocatalytic activity on organic dyes under UV-light and sunlight irradiation. J Phys Chem C 118(32):18343–18355. doi:10.1021/jp5044927
Guskos N, Glenis S, Zolnierkiewicz G, Typek J, Sibera D, Kaszewski J, Moszyński D, Łojkowski W, Narkiewicz U (2010) Magnetic study of Fe2O3/ZnO nanocomposites. Phys B Condens Matter 405(18):4054–4058. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2010.06.055
Hernández A, Maya L, Sánchez-Mora E, Sánchez EM (2007) Sol–gel synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of mixed oxide ZnO-Fe2O3. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 42(1):71–78. doi:10.1007/s10971-006-1521-7
Hsu YK, Chen YC, Lin YG (2015) Novel ZnO/Fe2O3 core–shell nanowires for photoelectrochemical water splitting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(25):14157–14162. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b03921
Jayanthi SA, Nathan DMGT, Jayashainy J, Sagayaraj P (2015) A novel hydrothermal approach for synthesizing α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 mesoporous magnetic nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 162:316–325. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.05.073
Jiang R, Yao J, Zhu H, Fu Y, Guan Y, Xiao L, Zeng G (2014) Effective decolorization of congo red in aqueous solution by adsorption and photocatalysis using novel magnetic alginate/γ-Fe2O3/CdS nanocomposite. Desalin Water Treat 52(1–3):238–247. doi:10.1080/19443994.2013.787551
Kaneti YV, Zakaria QMD, Zhang Z, Chen C, Yue J, Liu M, Jiang X, Yu A (2014) Solvothermal synthesis of ZnO-decorated α-Fe2O3 nanorods with highly enhanced gas-sensing performance toward n-butanol. J Mater Chem A 2:13283–13292. doi:10.1039/C4TA01837K
Kishore PNR, Jeevanadam P (2011) Synthesis of silver–iron oxide nanocomposites by thermal decomposition. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11(4):3445–3453. doi:10.1166/jnn.2011.3748
Kishore PNR, Jeevanandam P (2012) A novel thermal decomposition approach for the synthesis of silica-iron oxide core-shell nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd 522(1):51–62. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.01.076
Konstantinou IK, Albanis TA (2004) TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: a review. Appl Catal B Environ 49(1):1–14. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.010
Kumar SG, Rao KSRK (2015) Zinc oxide based photocatalysis: tailoring surface-bulk structure and related interfacial charge carrier dynamics for better environmental applications. RSC Adv 5(5):3306–3351. doi:10.1039/C4RA13299H
Kumar S, Surendar T, Baruah A, Shanker V (2013) Synthesis of a novel and stable g-C3N4–Ag3PO4 hybrid nanocomposite photocatalyst and study of the photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. A 1(17):5333–5340. doi:10.1039/c3ta00186e
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Elst LV, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108(6):2064–2110. doi:10.1021/Cr068445e
Lee YJ, Jun KW, Park JY, Potdar HS, Chikate RC (2008) A simple chemical route for the synthesis of γ-Fe2O3 nano-particles dispersed in organic solvents via an iron–hydroxy oleate precursor. J Ind Eng Chem 14(1):38–44. doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2007.08.009
Li X, Lin H, Chen X, Niu H, Zhang T, Liu J, Qu F (2015) Fabrication of TiO2/porous carbon nanofibers with superior visible photocatalytic activity. New J Chem 39(10):7863–7872. doi:10.1039/C5NJ01189B
Lin CR, Chu YM, Wang SC (2006) Magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles prepared by mechanochemical reaction. Mater Lett 60(4):447–450. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2005.09.009
Lin ST, Thirumavalavan M, Jiang TY, Lee JF (2014) Synthesis of ZnO/Zn nano photocatalyst using modified polysaccharides for photodegradation of dyes. Carbohydr Polym 105(1):1–9. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.017
Liu S, Ma C (2015) Synthesis and characterization of flower-like NiCoP/ZnO composites. New J Chem 39(8):6332–6337. doi:10.1039/C5NJ00992H
Liu Y, Yu L, Hu Y, Guo C, Zhang F, Lou XW (2012) A magnetically separable photocatalyst based on nest-like γ-Fe2O3/ZnO double-shelled hollow structures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Nanoscale 4(1):183–187. doi:10.1039/c1nr11114k
Liu X, Li W, Chen N, Xing X, Dong C, Wang Y (2015a) Ag–ZnO heterostructure nanoparticles with plasmon-enhanced catalytic degradation for Congo red under visible light. RSC Adv 5(43):34456–34465. doi:10.1039/C5RA03143E
Liu Y, Sun L, Wu J, Fang T, Cai R, Wei A (2015b) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of ZnO/Fe2O3 nanotube composites. Mater Sci Eng B 194:9–13. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2014.12.021
Ma J, Wang K, Zhan M (2015) Growth mechanism and electrical and magnetic properties of Ag–Fe3O4 core–shell nanowires. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(29):16027–16039. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b04342
Maiti D, Mukhopadhyay S, Chandra Mohanta S, Saha A, Sujatha Devi P (2015) A multifunctional nanocomposite of magnetic γ-Fe2O3 and mesoporous fluorescent ZnO. J Alloys Compd 653(1):187–194. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.08.230
Maity D, Agrawal DC (2007) Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles under oxidizing environment and their stabilization in aqueous and non-aqueous media. J Magn Magn Mater 308(1):46–55. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.05.001
Mashlan M, Zboril R, Machala L, Vujtek M, Walla J, Nomura K (2004) Mössbauer spectroscopy in study of thermally induced crystallization of amorphous Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J Metastab Nanocryst Mater 20–21:641–647. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/JMNM.20-21.641
Maya-Treviño ML, Guzmán-Mar JL, Hinojosa-Reyes L, Ramos-Delgado NA, Maldonado MI, Hernández-Ramírez A (2014) Activity of the ZnO-Fe2O3 catalyst on the degradation of Dicamba and 2,4-D herbicides using simulated solar light. Ceram Int 40(6):8701–8708. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.088
Mikhaylova M, Kim DK, Bobrysheva N, Osmolowsky M, Semenov V, Tsakalakos T, Muhammed M (2004) Superparamagnetism of magnetite nanoparticles: dependence on surface modification. Langmuir 20(6):2472–2477. doi:10.1021/la035648e
Mo M, Ma T, Jia L, Peng L, Guo X, Ding W (2009) Ferric oxide and ZnFe2O4 nanotubes derived from nano ZnO/FeOx core/shell structures. Mater Lett 63(26):2233–2235. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2009.07.041
Morales MP, Veintemilas-Verdangure S, Montero MI, Serna CJ, Roig A, Casas L, Martinez B, Sandiumenge F (1999) Surface and internal spin canting in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem Mater 11(12):3058–3064. doi:10.1021/cm991018f
Mukherjee S, Pal AK, Bhattacharya S, Chattopadhyay S (2008) Field-induced spin–flop transitions of interacting nanosized α-Fe2O3 particles dispersed in a silica glass matrix. J Phys Condens Matter 20(5):055204/1–055204/12. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/20/05/055204
Nadeem K, Krenn H, Traussnig T, Würschum R, Szabó DV, Letofsky-Papst I (2011) Effect of dipolar and exchange interactions on magnetic blocking of maghemite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 323(15):1998–2004. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.02.041
Narayan H, Alemu H, Macheli L, Thakurdesai M, Rao TKG (2009) Synthesis and characterization of Y3+-doped TiO2 nanocomposites for photocatalytic applications. Nanotechnology 20(25):255601/1–255601/8. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/20/25/255601
Pandey BK, Shahi AK, Shah J, Kotnala RK, Gopal R (2014) Optical and magnetic properties of Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation/fragmentation technique in different liquid media. Appl Surf Sci 289:462–471. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.11.009
Phu ND, Ngo DT, Hoang LH, Luong NH, Chau N, Hai NH (2011) Crystallization process and magnetic properties of amorphous iron oxide nanoparticles. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(34):345002/1–345002/7. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/44/34/345002
Pouretedal HR, Keshavarz MH (2010) Synthesis and characterization of Zn1 − XCuXS and Zn1 − XNiXS nanoparticles and their applications as photocatalyst in congo red degradation. J Alloys Compd 501(1):130–135. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.04.058
Pradhan GK, Martha S, Parida KM (2012) Synthesis of multifunctional nanostructured zinc-iron mixed oxide photocatalyst by a simple solution-combustion technique. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(2):707–713. doi:10.1021/am201326b
Qin L, Zhu Q, Li G, Liu F, Pan Q (2012) Controlled fabrication of flower–like ZnO–Fe2O3 nanostructured films with excellent lithium storage properties through a partly sacrificed template method. J Mater Chem 22(15):7544–7550. doi:10.1039/c2jm30277b
Ramachandra TV, Jain R, Krishnadas G (2011) Hotspots of solar potential in India. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15(6):3178–3186. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2011.04.007
Reda SM (2010) Synthesis of ZnO and Fe2O3 nanoparticles by sol–gel method and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater Sci Semicond Process 13(5–6):417–425. doi:10.1016/j.mssp.2011.09.007
Saffari J, Mir N, Ghanbari D, Khandan-Barani K, Hassanabadi A, Hosseini-Tabatabaei MR (2015) Sonochemical synthesis of Fe3O4/ZnO magnetic nanocomposites and their application in photo-catalytic degradation of various organic dyes. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 26(12):9591–9599. doi:10.1007/s10854-015-3622-y
Schimanke G, Martin M (2000) In situ XRD study of the phase transition of nanocrystalline maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) to hematite (α-Fe2O3). Solid State Ionics 136–137(1):1235–1240. doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00593-2
Si S, Li C, Wang X, Yu D, Peng Q, Li Y (2005) Magnetic monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Cryst Growth Des 5(2):391–393. doi:10.1021/cg0497905
Si S, Li C, Wang X, Peng Q, Li Y (2006) Fe2O3/ZnO core-shell nanorods for gas sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 119(1):52–56. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2005.11.050
Song YB, Song XD, Cheng CJ, Zhao ZG (2015) Poly(4-styrenesulfonic acid-co-maleic acid)-sodium-modified magnetic reduced graphene oxide for enhanced adsorption performance toward cationic dyes. RSC Adv 5(106):87030–87042. doi:10.1039/C5RA18255G
Sreeja V, Joy PA (2007) Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and their magnetic properties. Mater Res Bull 42(8):1570–1576. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2006.11.014
Suresh R, Giribabu K, Manigandan R, Stephen A, Narayanan V (2014) Fabrication of Ni–Fe2O3 magnetic nanorods and application to the detection of uric acid. RSC Adv 4(33):17146–17155. doi:10.1039/c4ra00725e
Teja AS, Koh PY (2009) Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 55(1–2):22–45. doi:10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2008.08.003
Thiripuranthagan S, Raj D, Kannan K (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of congo red on silica supported Ag impregnated TiO2. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15(6):4727–4733. doi:10.1166/jnn.2015.9795
Tsuzuki T, Schäffel F, Muroi M, McCormick PG (2011) Magnetic properties of mechanochemically synthesized γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 509(17):5420–5425. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.02.073
Wang J, Li R, Zhang Z, Sun W, Xu R, Xie Y, Xing Z, Zhang X (2008) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes over titanium dioxide coating upconversion luminescence agent under visible and sunlight irradiation. Appl Catal A Gen 334(1–2):227–233. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2007.10.009
Wang J, Liu P, Fu X, Li Z, Han W, Wang X (2009) Relationship between oxygen defects and the photocatalytic property of ZnO nanocrystals in nafion membranes. Langmuir 25(2):1218–1223. doi:10.1021/la803370z
Wang Y, Deng K, Zhang L (2011) Visible light photocatalysis of BiOI and its photocatalytic activity enhancement by in situ ionic liquid modification. J Phys Chem C 115(29):14300–14308. doi:10.1021/jp2042069
Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhan X, Wang F, Safdar M, He J (2013) Visible light driven type II heterostructures and their enhanced photocatalysis properties: a review. Nanoscale 5(18):8326–8339. doi:10.1039/c3nr01577g
Wilson JL, Poddar P, Frey NA, Srikanth H, Mohomed K, Harmon JP, Kotha S, Wachsmuth J (2004) Synthesis and magnetic properties of polymer nanocomposites with embedded iron nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 95(3):1439–1443. doi:10.1063/1.1637705
Woo K, Hong J, Choi S, Lee H, Ahn J, Kim CS, Lee SW (2004) Easy synthesis and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Mater 16(14):2814–2818. doi:10.1021/cm049552x
Wu H, Wang L (2014) Phase transformation-induced crystal plane effect of iron oxide micropine dendrites on gaseous toluene photocatalytic oxidation. Appl Surf Sci 288(1):398–404. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.046
Wu P, Du N, Zhang H, Jin L, Yang D (2010) Functionalization of ZnO nanorods with γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: layer-by-layer synthesis, optical and magnetic properties. Mater Chem Phys 124(2–3):908–911. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.08.009
Wu W, Zhang S, Xiao X, Zhou J, Ren F, Sun L, Jiang C (2012) Controllable synthesis, magnetic properties, and enhanced photocatalytic activity of spindlelike mesoporous α-Fe2O3/ZnO core-shell heterostructures. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(7):3602–3609. doi:10.1021/am300669a
Wu W, Jiang C, Roy VAL (2015) Recent progress in magnetic iron oxide–semiconductor composite nanomaterials as promising photocatalysts. Nanoscale 7(1):38–58. doi:10.1039/c4nr04244a
Xuan S, Jiang W, Gong X, Hu Y, Chen Z (2009) Magnetically separable Fe3O4/TiO2 hollow spheres: fabrication and photocatalytic activity. J Phys Chem C 113(2):553–558. doi:10.1021/jp8073859
Yang G, Zhang B, Wang J, Xie S, Li X (2015) Preparation of polylysine-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 374:205–208. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.08.040
Yang X, Qian F, Zou G, Li M, Lu J, Li Y, Bao M (2016) Facile fabrication of acidified g-C3N4/g-C3N4 hybrids with enhanced photocatalysis performance under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 193:22–35. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.060
Ye M, Zhang Q, Hu Y, Ge J, Lu Z, He L, Chen Z, Yin Y (2010) Magnetically recoverable core-shell nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem: Eur J 16(21):6243–6250. doi:10.1002/chem.200903516
Yin Q, Qiao R, Zhu L, Li Z, Li M, Wu W (2014) α-Fe2O3 decorated ZnO nanorod-assembled hollow microspheres: synthesis and enhanced visible-light photocatalysis. Mater Lett 135:135–138. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2014.07.149
Yu L, Peng X, Ni F, Li J, Wang D, Luan Z (2013) Arsenite removal from aqueous solutions by γ-Fe2O3-TiO2 magnetic nanoparticles through simultaneous photocatalytic oxidation and adsorption. J Hazard Mater 246–247:10–17. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.12.007
Zhang L, Papaefthymiou GC, Ying JY (1997) Size quantization and interfacial effects on a novel γ-Fe2O3/SiO2 magnetic nanocomposite via sol–gel matrix-mediated synthesis. J Appl Phys 81(10):6892/1–6892/10. doi:10.1063/1.365233
Zhang J, Liu X, Wang L, Yang T, Guo X, Wu S, Wang S, Zhang S (2011) Synthesis and gas sensing properties of α-Fe2O3@ZnO core-shell nanospindles. Nanotechnology 22(18):185501/1–185501/7. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/22/18/185501
Zhang S, Ren F, Wu W, Zhou J, Xiao X, Sun L, Liu Y, Jiang C (2013) Controllable synthesis of recyclable core-shell γ-Fe2O3@SnO2 hollow nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic and gas sensing properties. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(21):8228–8236. doi:10.1039/c3cp50925g
Zhang R, Wang L, Deng J, Zhou T, Lou Z, Zhang T (2015) Hierarchical structure with heterogeneous phase as high performance sensing materials for trimethylamine gas detecting. Sensors Actuators B Chem 220(1):1224–1231. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.07.036
Zhiyong Y, Ruiying Q, Huanrong L, Zhiyin W, Xiaohong M, Chaonan D (2015) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of SnO2. Mater Lett 170(1):25–30. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2015.12.100
Zhou X, Xiao Y, Wang M, Sun P, Liu F, Liang X, Li X, Lu G (2015) Highly enhanced sensing properties for ZnO nanoparticle-decorated round-edged α-Fe2O3 hexahedrons. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(16):8743–8749. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b01071
Zysler RD, Fiorani D, Testa AM (2001) Investigation of magnetic properties of interacting Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 224(1):5–11. doi:10.1016/S0304-8853(00)01328-7
Acknowledgments
P. J thanks the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for the financial support (Project No. 01(2726)/13/EMR-II). The award of Research Fellowship to Mr. Sudheer Kumar Yadav by the University Grants Commission, Government of India, is gratefully acknowledged. The authors are also thankful to the Institute Instrumentation Centre, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee for providing the facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, S.K., Jeevanandam, P. Synthesis of ZnO@γ-Fe2O3 core–shell nanocomposites by a facile thermal decomposition approach and their application in photocatalytic degradation of congo red. J Nanopart Res 18, 195 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3502-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3502-2