Abstract
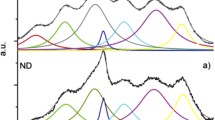
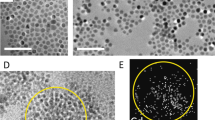
A new type of hybrid nanomaterial composed of magnetic FePt nanoparticles grown on the surface of nanodiamond nanotemplate assemblies is described for the first time. Post annealing in vacuum of the as-made nanomaterial bearing cubic A1 soft magnetic FePt nanoparticles leads to the development of FePt nanoparticles with tetragonal L10 hard, magnetic-phase characteristics, leaving untouched the nanodiamond nanotemplate assemblies. X-ray diffraction, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy including chemical mapping (HRTEM/HAADF), magnetization measurements, and 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy data show that the magnetic FePt nanoparticles, with average sizes of 3 and 8 nm in the as-made and annealed hybrids, respectively, are homogenously distributed within the nanodiamond template in both nanomaterials. As a consequence, their structural, morphological, and magnetic properties differ significantly from the corresponding properties of the nonsupported (free) as-made and annealed FePt nanoparticles with average sizes of 6 and 32 nm, respectively, developed by the same methods. This spatial isolation suppresses the size-growth of the FePt nanoparticles during the post-annealing procedure, triggering superparamagnetic relaxation phenomena, which are exposed as a combination of hard and soft magnetic-phase characteristics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad RK, Parada AC, Jackman RB (2011) Nanodiamond-gated silicon ion-sensitive field effect transistor. Appl Phys Lett 98:153507. doi:10.1063/1.3568887
Bourlinos AB, Panagiotopoulos I, Niarchos D, Petridis D (2004) Hydrophilic Co-Pt alloy nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and perspectives. J Mater Res 19:1227–1233. doi:10.1557/JMR.2004.0159
Bourlinos AB et al (2011) Fabrication of fluorescent nanodiamond@C core-shell hybrids via mild carbonization of sodium cholate-nanodiamond complexes. J Mater Sci 46:7912–7916. doi:10.1007/s10853-011-5911-z
Branson BT, Beauchamp PS, Beam JC, Lukehart CM, Davidson JL (2013) Nanodiamond Nanofluids for Enhanced Thermal Conductivity. ACS Nano 7:3183–3189. doi:10.1021/nn305664x
Buzug TM, Borgert J, Knopp T, Biederer S, Sattel TF, Erbe M, Lüdtke-Buzug K (2010) Magnetic Nanoparticles: Particle Science, Imaging Technology, and Clinical Applications. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore
Chen M, Liu JP, Sun S (2004) One-step synthesis of FePt nanoparticles with tunable size. J Am Chem Soc 126:8394–8395. doi:10.1021/ja047648m
Chen M, Pierstorff ED, Lam R, Li SY, Huang H, Osawa E, Ho D (2009) Nanodiamond-mediated delivery of water-insoluble therapeutics. ACS Nano 3:2016–2022. doi:10.1021/nn900480m
Cheng LC et al (2013) Targeting polymeric fluorescent nanodiamond-gold/silver multi-functional nanoparticles as a light-transforming hyperthermia reagent for cancer cells. Nanoscale 5:3931–3940. doi:10.1039/c3nr34091k
Chepulskii RV, Butler WH (2005) Temperature and particle-size dependence of the equilibrium order parameter of FePt alloys. Phys Rev B 72:134205. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.72.134205
Chepulskii RV, Butler WH, van der Walle A, Curtarolo S (2010) Surface segregation in nanoparticles from first principles: the case of FePt. Scr Mater 62:179–182. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2009.10.019
Colak L, Hadjipanayis GC (2009) Chemically synthesized FePt nanoparticles with controlled particle size, shape and composition. Nanotechnology 20(48):485602. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/20/48/485602
Cullity BD (1956) Elements of X-ray Diffraction. Addison-Wesley, Massachusetts
Cullity BD, Graham CD (2009) Introduction to Magnetic Materials. Wiley, Hoboken
Danilenko VV (2004) On the history of the discovery of nanodiamond synthesis. Phys Solid State 46:595–599
Dormann JL, Fiorani D, Tronc E (1997) Magnetic relaxation in fine-particle systems. Adv Chem Phys 98:283–494
Douvalis AP, Polymeros A, Bakas T (2010) IMSG09: a 57Fe-119Sn Mössbauer spectra computer fitting program with novel interactive user interface. J Phys 217:012014
Douvalis AP, Zboril R, Bourlinos AB, Tucek J, Spyridi S, Bakas T (2012) A facile synthetic route toward air-stable magnetic nanoalloys with Fe-Ni/Fe-Co core and iron oxide shell. J Nanopart Res 14:1130. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1130-z
Fiorani D (2005) Surface effects in magnetic nanoparticles. Springer, New York
Frey NA, Peng S, Cheng K, Sun S (2009) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, functionalization, and applications in bioimaging and magnetic energy storage. Chem Soc Rev 38:2532–2542. doi:10.1039/b815548h
Ganesh P, Kent PRC, Mochalin V (2011) Formation, characterization, and dynamics of onion-like carbon structures for electrical energy storage from nanodiamonds using reactive force fields. J Appl Phys 110:073506. doi:10.1063/1.3641984
Goto T, Utsugi H, Watanabe K (1990) Mössbauer study of permanent magnets Fe-Pt. Hyperfine Interact 54:539–544
Greenwood NN, Gibb TC (1971) Mössbauer spectroscopy. Chapman and Hall Ltd, London
Gubin SP (2009) Magnetic Nanoparticles. Wiley, Weinheim
Guo S, Sun S (2012) FePt nanoparticles assembled on graphene as enhanced catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. J Am Chem Soc 134:2492–2495. doi:10.1021/ja2104334
Ho D (2010) Nanodiamonds: applications in biology and nanoscale medicine. Springer, New York
Hoinville J et al (2003) High density magnetic recording on protein-derived nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 93:7187–7189. doi:10.1063/1.1555896
Hsu SH, Kang WP, Davidson JL, Huang JH, Kerns DV (2013) Nanodiamond vacuum field emission integrated differential amplifier. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 60:487–493. doi:10.1109/TED.2012.2228485
Hu Q et al (2012) Self-assembly of colloidal γ-Fe2O3 and FePt nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes by dip-coating process. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12:1709–1712. doi:10.1166/jnn.2012.4684
Hu XC, Agostinelli E, Ni C, Hadjipanayis GC, Capobianchi A (2014) A low temperature and solvent-free direct chemical synthesis of L1 0 FePt nanoparticles with size tailoring. Green Chem 16:2292–2297. doi:10.1039/c3gc42186d
In PC, Kuo CH, Chiang CS (2008) Preparation of fluorescent magnetic nanodiamonds and cellular imaging. J Am Chem Soc 130:15476–15481. doi:10.1021/ja804253y
Kavan L (2014) Exploiting nanocarbons in dye-sensitized solar cells. Top Curr Chem 348:53–94. doi:10.1007/128-2013-447
Kockrick E, Krawiec P, Schnelle W, Geiger D, Schappacher FM, Pöttgen R, Kaskel S (2007) Space-confined formation of fept nanoparticles in ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15. Adv Mater 19:3021–3026. doi:10.1002/adma.200601367
Kostopoulou A et al (2014) Assembly-mediated interplay of dipolar interactions and surface spin disorder in colloidal maghemite nanoclusters. Nanoscale 6:3764–3776. doi:10.1039/c3nr06103e
Kumar A, Ann Lin P, Xue A, Hao B, Khin Yap Y, Sankaran RM (2013) Formation of nanodiamonds at near-ambient conditions via microplasma dissociation of ethanol vapour. Nat Commun 4:2618. doi:10.1038/ncomms3618
La-Torre-Riveros L, Abel-Tatis E, Méndez-Torres AE, Tryk DA, Prelas M, Cabrera CR (2011) Synthesis of platinum and platinum-ruthenium-modified diamond nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 13:2997–3009. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0196-8
Lewis RS, Ming T, Wacker JF, Anders E, Steel E (1987) Interstellar diamonds in meteorites. Nature 326:160–162
Lin CR, Wei DH, Bendao MK, Chang HM, Chen WE, Lee JA (2014) Effects of surface modification of nanodiamond particles for nucleation enhancement during its film growth by microwave plasma jet chemical vapour deposition technique. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2014:937159. doi:10.1155/2014/937159
Liu YL, Sun KW (2011) Plasmon-enhanced photoluminescence from bioconjugated gold nanoparticle and nanodiamond assembly. Appl Phys Lett 98:153702. doi:10.1063/1.3576852
Liu H et al (2014a) A nanodiamond/CNT-SiC monolith as a novel metal free catalyst for ethylbenzene direct dehydrogenation to styrene. Chem Commun 50:7810–7812. doi:10.1039/c4cc01693a
Liu Y et al (2014b) Structural and magnetic properties of the ordered FePt3, FePt and Fe3Pt nanoparticles. J Solid State Chem 209:69–73. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2013.10.027
Lyubina J, Rellinghaus B, Gutfleisch O, Albrecht M (2011) Structure and Magnetic Properties of L10-Ordered Fe–Pt Alloys and Nanoparticles. In: Buschow KHJ (ed) Handbook of Magnetic Materials, vol 19. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 291–407
Manus LM et al (2010) Gd(III)-nanodiamond conjugates for MRI contrast enhancement. Nano Lett 10:484–489. doi:10.1021/nl903264h
Mermoux M, Crisci A, Petit T, Girard HA, Arnault JC (2014) Surface modifications of detonation nanodiamonds probed by multiwavelength raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 118:23415–23425. doi:10.1021/jp507377z
Miyazaki T et al (2005) Size effect on the ordering of L10 FePt nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 72:144419
Mochalin VN, Shenderova O, Ho D, Gogotsi Y (2011) The properties and applications of nanodiamonds. Nat Nanotechnol 7:11–23. doi:10.1038/nnano.2011.209
Mørup S (1983) Magnetic hyperfine splitting in Mössbauer spectra of microcrystals. J Magn Magn Mater 37:39
Mørup S (1990) Mössbauer effect in small particles. Hyperfine Interact 60:959
Mørup S, Hansen M (2007) Superparamagnetic Particles. In: Kronmüller H, Parkin S (eds) Handbook of magnetism and advanced magnetic materials, novel materials. Wiley, Chichester
Nekhaev AI, Bagrii EI, Maximov AL (2011) Petroleum nanodiamonds: new in diamondoid naphthenes. Pet Chem 51:86–95. doi:10.1134/S0965544111020095
Paci JT, Man HB, Saha B, Ho D, Schatz GC (2013) Understanding the surfaces of nanodiamonds. J Phys Chem C 117:17256–17267. doi:10.1021/jp404311a
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D 36:R167–R181
Papagiannouli I, Bourlinos AB, Bakandritsos A, Couris S (2014) Nonlinear optical properties of colloidal carbon nanoparticles: nanodiamonds and carbon dots. RSC Adv 4:40152–40160. doi:10.1039/c4ra04714a
Ram MK, Gomez H, Alvi F, Stefanakos E, Goswami Y, Kumar A (2011) Novel nanohybrid structured regioregular polyhexylthiophene blend films for photoelectrochemical energy applications. J Phys Chem C 115:21987–21995. doi:10.1021/jp205297n
Raty JY, Galli G, Bostedt C, Van Buuren TW, Terminello LJ (2003) Quantum confinement and fullerenelike surface reconstructions in nanodiamonds. Physical Review Letters 90:037401/037401–037401/037404
Rong CB et al (2006) Size-dependent chemical and magnetic ordering in L10-FePt nanoparticles. Adv Mater 18:2984–2988. doi:10.1002/adma.200601904
Shenderova OA, Gruen DM (2012) Ultrananocrystalline diamond: synthesis, properties and applications, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Oxford
Shiryaev AA, Fisenko AV, Vlasov II, Semjonova LF, Nagel P, Schuppler S (2011) Spectroscopic study of impurities and associated defects in nanodiamonds from Efremovka (CV3) and Orgueil (CI) meteorites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75:3155–3165. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2011.03.004
Spada FE, Parker FT, Platt CL, Howard JK (2003) X-ray diffraction and Mössbauer studies of structural changes and L10 ordering kinetics during annealing of polycrystalline Fe51Pt49 thin films. J Appl Phys 94:5123–5134. doi:10.1063/1.1606522
Su Z, Zhou W, Zhang Y (2011) New insight into the soot nanoparticles in a candle flame. Chem Commun 47:4700–4702. doi:10.1039/c0cc05785a
Subramanian K, Kang WP, Davidson JL, Choi BK, Howell M (2006) Nanodiamond lateral comb array field emission diode for high current applications. Diam Relat Mater 15:1994–1997. doi:10.1016/j.diamond.2006.09.016
Sun S (2006) Recent advances in chemical synthesis, self-assembly, and applications of FePt nanoparticles. Adv Mater 18:393–403. doi:10.1002/adma.200501464
Sundar LS, Singh MK, Ramana EV, Singh B, Grácio J, Sousa ACM (2014) Enhanced Thermal Conductivity and Viscosity of Nanodiamond-Nickel Nanocomposite Nanofluids. Sci Rep 4:4039. doi:10.1038/srep04039
Taha-Tijerina JJ, Narayanan TN, Tiwary CS, Lozano K, Chipara M, Ajayan PM (2014) Nanodiamond-Based Thermal Fluids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:4778–4785. doi:10.1021/am405575t
Takahashi YK, Koyama T, Ohnuma M, Ohkubo T, Mono K (2004) Size dependence of ordering in FePt nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 95:2690–2696. doi:10.1063/1.1643187
Thanh NTK (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles: from fabrication to clinical applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Tsoufis T et al (2008) Novel nanohybrids derived from the attachment of FePt nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:5942–5951
Tsoufis T, Douvalis AP, Lekka CE, Trikalitis PN, Bakas T, Gournis D (2013) Controlled preparation of carbon nanotube–iron oxide nanoparticle hybrid materials by a modified wet impregnation method. J Nanopart Res 15:1924–1927
Vargas JM, Zysler RD, Socolovsky LM, Knobel M, Zanchet D (2007) Size dependence on the ordering process in colloidal FePt nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 101:023903. doi:10.1063/1.2409620
Vul’ A, Shenderova O (2013) Detonation Nanodiamonds: Science and Applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wang HL, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Hadjipanayis GC, Weller D, Simopoulos A (2007) Effects of annealing on the magnetic and structural properties of FePt nanoparticles prepared by chemical synthesis. J Magn Magn Mater 310:22–27
Wang Y, Gao L, Sun J, Liu Y (2009) Synthesis and characterization of FePt nanoparticle/single walled carbon nanotube composites. Mater Sci Forum 620–622:505–508. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.620-622.505
Wang Y, Jaiswal M, Lin M, Saha S, Özyilmaz B, Loh KP (2012) Electronic properties of nanodiamond decorated graphene. ACS Nano 6:1018–1025. doi:10.1021/nn204362p
Wang DH, Fillery SP, Durstock MF, Dai LM, Vaia RA, Tan LS (2013) Nanodiamond/polyimide high temperature dielectric films for energy storage applications. Adv Mater Res 785–786:410–416. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.785-786.410
Williams OA (2011) Nanocrystalline diamond. Diam Relat Mater 20:621–640. doi:10.1016/j.diamond.2011.02.015
Williams O (2014) Nanodiamond. RSC Nanoscience & Nanotechnology, vol 31. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Yang B, Asta M, Mryasov ON, Klemmer TJ, Chantrell RW (2005) Equilibrium Monte Carlo simulations of A1–L10 ordering in FePt nanoparticles. Scr Mater 53:417–422
Yang B, Asta M, Mryasov ON, Klemmer TJ, Chantrell RW (2006) The nature of A1–L10 ordering transitions in alloy nanoparticles: a Monte Carlo study. Acta Mater 54:4201–4211
Zeng H, Li J, Liu JP, Wang ZL, Sun S (2002) Exchange-coupled nanocomposite magnets by nanoparticle self-assembly. Nature 420:395–398. doi:10.1038/nature01208
Zhang YJ et al (2011) A novel approach to the synthesis of CoPt magnetic nanoparticles. J Phys D 44:295003. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/44/29/295003
Zhao L et al (2014) Platinum on nanodiamond: a promising prodrug conjugated with stealth polyglycerol, targeting peptide and acid-responsive antitumor drug. Adv Funct Mater 24:5348–5357. doi:10.1002/adfm.201304298
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support from the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic (LO1305). The authors also acknowledge the assistance provided by the Research Infrastructure NanoEnviCz, supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic under Project No. LM2015073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11051_2016_3424_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Additional TEM images of the as-made and annealed free FePt and hybrid FePt/NDs samples; ZFC and FC magnetic susceptibility versus temperature measurements of all samples under an applied magnetic field of 0.10 T (DOCX 1390 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douvalis, A.P., Bourlinos, A.B., Tucek, J. et al. Development of novel FePt/nanodiamond hybrid nanostructures: L10 phase size-growth suppression and magnetic properties. J Nanopart Res 18, 115 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3424-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3424-z