Abstract
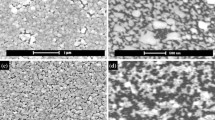
The sintering of a silver (Ag) nanoparticle film by laser beam irradiation was studied using a CW DPSS laser. The laser sintering of the Ag nanoparticle thin film gave a transparent conductive film with a thickness of ca. 10 nm, whereas a thin film sintered by conventional heat treatment using an electronic furnace was an insulator because of the formation of isolated silver grains during the slow heating process. The laser sintering of the Ag nanoparticle thin film gave a unique conductive network structure due to the rapid heating and quenching process caused by laser beam scanning. The influences of the laser sintering conditions such as laser scan speed on the conductivity and the transparency were studied. With the increase of scan speed from 0.50 to 5.00 mm/s, the surface resistivity remarkably decreased from 4.45 × 108 to 6.30 Ω/sq. The addition of copper (Cu) nanoparticles to silver thin film was also studied to improve the homogeneity of the film and the conductivity due to the interaction between the oxidized surface of Cu nanoparticle and a glass substrate. By adding 5 wt% Cu nanoparticles to the Ag thin film, the surface resistivity improved to 2.40 Ω/sq.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminuzzaman M, Watanabe A, Miyashita T (2008a) Fabrication of silver microwiring on a double-decker shaped polysilsesquioxane film by laser direct writing. J Photopolym Sci Technol 21(4):537–540
Aminuzzaman M, Watanabe A, Miyashita T (2008b) Photochemical surface modification and characterization of double-decker-shaped polysilsesquioxane hybrid thin films. J Mater Chem 8:5092–5097
Aminuzzaman M, Watanabe A, Miyashita T (2010) Direct writing of conductive silver micropatterns on flexible polyimide film by laser-induced pyrolysis of silver nanoparticle-dispersed film. J Nanopart Res 12:931–938
Arnold CB, Serra P, Piqué A (2007) Laser direct-write techniques for printing of complex materials. MRS Bull 32(1):23–31
Atsuki T, Hayashi T, Kiyoshima R, Oda M (2004) Metal nanoparticle and method for producing same, liquid dispersion of metal nanoparticle and method for producing same, metal thin line, metal film and method for producing same. PCT/JP2004/012968
Auyeung RCY, Kim H, Birnbaum AJ, Zala-lutidinov M, Mathews SA, Piqué A (2009) Laser decal transfer of free-standing microcantilevers and microbridges. Appl Phys A 97:513–519
Auyeung R, Kim H, Charipar N, Birnbaum A, Mathews S, Piqué A (2011) Laser forward transfer based on a spatial light modulator. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Proc 102(1):21–26
Choi TY, Poulikakos D, Grigoropoulos CP (2004) Fountain-pen-based laser microstructuring with gold nanoparticle inks. Appl Phys Lett 85(1):13–15
Fuller SB, Wilhelm EJ, Jacobson JM (2002) Ink-jet printed nanoparticle microelectromechanical systems. J Microelectromech Syst 11(1):54–60
Gamerith S, Klug A, Scheiber H, Scherf U, Moderegger E, List EJW (2007) Direct ink-jet printing of Ag–Cu nanoparticle and Ag-precursor based electrodes for OFET applications. Adv Func Mater 17(6):3111–3118
Jeong S, Song HC, Lee WW, Lee SS, Choi Y, Son W, Kim ED, Paik CH, Oh SH, Ryu BH (2011) Stable aqueous based Cu nanoparticle ink for printing well-defined highly conductive features on a plastic substrate. Langmuir 27(6):3144–3149
Hamilton JC, Farmer JC, Anderson RJ (1986) In situ raman spectroscopy of anodic films formed on copper and silver in sodium hydroxide solution. J Electrochem Soc 133(4):739–745
Kim H, Kushto GA, Arnold CB, Kafa ZH, Piqué A (2004) Laser processing of nanocrystalline TiO2 flms for dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl Phy Lett 85(3):464–466
Kim H, Auyeung RCY, Piqué A (2007) Laser-printed thick-film electrodes for solid-state rechargeable Li-ion microbatteries. J Power Sources 165(1):413–419
Kim H, Melinger J, Khachatrian A, Charipar N, Auyeung R, Piqué A (2010) Fabrication of terahertz metamaterials by laser printing. Opt Lett 35(23):4039–4041
Ko H, Pan H, Grigoropoulos CP, Luscombe CK, Fréchet JMJ, Poulikakos D (2007a) Air stable high resolution organic transistors by selective laser sintering of ink-jet printed metal nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 90:141103
Ko SH, Park I, Pan H, Grigoropoulos CP, Pisano AP, Luscombe KC, Fréchet JMJ (2007b) Direct nanoimprinting of metal nanoparticles for nanoscale electronics fabrication. Nano Lett 7(7):1869–1877
Ko SW, Chung J, Hotz N, Nam KH, Grigoropoulos CP (2010) Metal nanoparticle direct inkjet printing for low-temperature 3D micro metal structure fabrication. J Micromech Microeng 20:125010
Komatsu H (1991) Interferometry: principles and applications of two-beam and multiple beam interferometry. Nikon Tech Bull. http://www.tecnicaenlaboratorios.com/Nikon/Brochures/Technical%20Bulletin%20Interferometry%201991.pdf
Luechinger NA, Athanassiou EK, Stark WJ (2008) Graphene-stabilized copper nanoparticles as an air-stable substitute for silver and gold in low-cost ink-jet printable electronics. Nanotechnology 19:445201
Maoa Y, Hea J, Suna X, Li W, Lua X, Gana J, Liu Z, Gong L, Chen J, Liu P, Tonga Y (2012) Electrochemical synthesis of hierarchical Cu2O stars with enhanced photoelectrochemical properties. Electrochim. Acta 62:1–7
Murata K, Matsumoto J, Tezuka A, Matsuba Y, Yokoyama H (2005) Super-fine ink-jet printing: toward the minimal manufacturing system. Microsyst Technol 12(1–2):2–7
Oda M, Katsu I, Tsuneizumi M, Fuchita E, Kashu S, Hayashi C (1992) Ultrafine particle films by gas deposition method. MRS Proc 286:121. doi:10.1557/PROC-286-121
Oda M, Abe T, Suzuki T, Saito N, Iwashige H, Kutluk G (2001) Application of dispersed nanoparticles. MRS Proc 704, W3.1.1. doi:10.1557/PROC-704-W3.1.1
Parka BK, Kima D, Jeonga S, Moona J (2007) Direct writing of copper conductive patterns by ink-jet printing. Thin Solid Films 515(19):7706–7711
Perelaer J, de Gans BJ, Schubert US (2006) Ink-jet printing and microwave sintering of conductive silver tracks. Adv Mater 18(16):2101–2104
Piqué A, Chrisey DB, Auyeung RCY, Fitz-Gerald J, Wu HD, McGill RA, Lakeou S, Wu PK, Nyuyen V, Duignan M (1999) A novel laser transfer process for direct writing of electronic and sensor materials. Appl Phys A 69:S279–S284
Piqué A, Auyeung R, Kim H, Metkus K, Mathews S (2008) Digital microfabrication by laser decal transfer. J Laser Micro/Nanoeng 3(3):163–169
Singh M, Haverinen HM, Dhagat P, Jabbour GE (2010) Inkjet printing-process and its applications. Adv Mater 22(6):673–685
Tamai T, Watanabe M, Hatanaka Y, Tsujiwaki H, Nishioka N, Matsukawa K (2008) Formation of metal nanoparticles on the surface of polymer particles incorporating polysilane by UV irradiation. Langmuir 24(24):14203–14208
Wang J, Auyeung R, Kim H, Charipar N, Piqué A (2010) Three-dimensional printing of interconnects by laser direct-write of silver nanopastes. Adv Mater 22(40):4462–4466
Watanabe A (2013) Laser sintering of metal nanoparticle film. J Photopolym Sci Technol 26(2):199–205
Watanabe A, Kobayashi Y, Konno M, Yamada S, Miwa T (2005) Direct drawing of Ag microwiring by laser-induced pyrolysis of film prepared from liquid-dispersed metal nanoparticles. Jpn J Appl Phys 44:L740–L742
Watanabe A, Kobayashi Y, Konno M, Yamada S, Miwa T (2007) Direct drawing of submicron wiring by laser-induced pyrolysis of film prepared from liquid-dispersed metal nanoparticles. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 464:161–167
Watanabe A, Aminuzzaman M, Miyashita T (2009) Submicron writing by laser irradiation on metal nano-particle dispersed films towards flexible electronics. Proc SPIE 7202:6
Watanabe A, Cheng CW, Shen WC, Chu CI (2012) Fabrication of micropatterns by laser direct writing using nanomaterials. J Photopolym Sci Technol 25:679–680
Woo K, Kim D, Kim JS, Lim S, Moon J (2009) Ink-jet printing of Cu–Ag-based highly conductive tracks on a transparent substrate. Langmuir 25(1):429–433
Yonezawa T (2009) In-situ observation of silver nanoparticle ink at high temperature. Biomed Mater Eng 19(1):29–34
ULVAC Inc (2014) Nanometal Ink. http://www.ulvac.co.jp/products_e/materials/nano-metal-ink
Watanabe A, Miyashita T (2007) Formation of copper micro-wiring by laser direct writing. J Photopolym Sci Technol 20(1):115–116
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI under Grant Number 24360301 and also by MEXT KAKENHI under Grant Number 24102004. The authors thank Mr. Masao Ishii for the assistance in the FE-SEM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, G., Watanabe, A. Conductive network structure formed by laser sintering of silver nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 16, 2684 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2684-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2684-8