Abstract
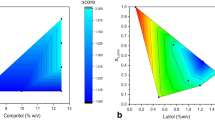
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are a promising carrier for all administration routes due to their safety, small size, and high loading of lipophilic compounds. Among the LNP production techniques, the easy scale-up, lack of organic solvents, and short production times of the high-pressure homogenization technique (HPH) make this method stand out. In this study, a statistical analysis was applied to the production of LNP by HPH. Spherical LNPs with mean size ranging from 65 nm to 11.623 μm, negative zeta potential under –30 mV, and smooth surface were produced. Manageable equations based on commonly used parameters in the pharmaceutical field were obtained. The lipid to emulsifier ratio (R L/S) was proved to statistically explain the influence of oil phase and surfactant concentration on final nanoparticles size. Besides, the homogenization pressure was found to ultimately determine LNP size for a given R L/S, while the number of passes applied mainly determined polydispersion. α-Tocopherol was used as a model drug to illustrate release properties of LNP as a function of particle size, which was optimized by the regression models. This study is intended as a first step to optimize production conditions prior to LNP production at both laboratory and industrial scale from an eminently practical approach, based on parameters extensively used in formulation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo J, Gonzalez-Mira E, Egea MA, Garcia ML, Souto EB (2010) Optimization and physicochemical characterization of a triamcinolone acetonide-loaded NLC for ocular antiangiogenic applications. Int J Pharm 393:167–175
Biasutti M, Venir E, Marchesini G, Innocente N (2010) Rheological properties of model dairy emulsions as affected by high pressure homogenization. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 11:580–586
Bondì ML, Craparo EF, Giammona G, Drago F (2010) Brain-targeted solid lipid nanoparticles containing riluzole: preparation, characterization and biodistribution. Nanomedicine (Lond, Engl) 5:25–32
Charcosset C, El-Harati A, Fessi H (2005) Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles using a membrane contactor. J Control Release 108:112–120
Chattopadhyay P, Shekunov BY, Yim D, Cipolla D, Boyd B, Farr S (2007) Production of solid lipid nanoparticle suspensions using supercritical fluid extraction of emulsions (SFEE) for pulmonary delivery using the AERx system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:444–453
Das S, Chaudhury A (2011) Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 12:62–76
El-Harati AA, Charcosset C, Fessi H (2006) Influence of the formulation for solid lipid nanoparticles prepared with a membrane contactor. Pharm Dev Technol 11:153–157
Floury J, Desrumaux A, Lardières J (2000) Effect of high-pressure homogenization on droplet size distributions and rheological properties of model oil-in-water emulsions. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 1:127–134
García-Fuentes M, Torres D, Alonso MJ (2002) Design of lipid nanoparticles for the oral delivery of hydrophilic macromolecules. Colloid Surf B 27:159–168
Gasco MR (1997) Solid lipid nanospheres from warm microemulsion. Pharm Technol Eur 9:32–42
Håkansson A, Fuchs L, Innings F, Revstedt J, Trägårdh C (2011) On flow-fields in a high pressure homogenizer and its implication on drop fragmentation. Procedia Food Sci 1:1353–1358
Heurtault B, Saulnier P, Pech B, Proust JE, Benoit JP (2002) A novel phase inversion-based process for the preparation of lipid nanocarriers. Pharm Res 19:875–880
Hu FQ, Yuan H, Zhang HH, Fang M (2002) Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles with clobetasol propionate by a novel solvent diffusion method in aqueous system and physicochemical characterization. Int J Pharm 239:121–128
Innocente N, Biasutti M, Venir E, Spaziani M, Marchesini E (2009) Effect of high-pressure homogenization on droplet size distribution and rheological properties of ice cream mixes. J Dairy Sci 92:1864–1875
Jafari S, Assadpoor E, He Y, Bhandari B (2008) Re-coalescence of emulsion droplets during high-energy emulsification. Food Hydrocoll 22:1191–1202
Kluge J, Muhrer G, Mazzotti M (2012) High pressure homogenization of pharmaceutical solids. J Supercrit Fluids 66:380–388
Liedtke S, Wissing S, Müller RH, Mäder K (2000) Influence of high pressure homogenisation equipment on nanodispersions characteristics. Int J Pharm 196:183–185
Liu J, Hu W, Chen H, Ni Q, Xu H, Yang X (2007) Isotretinoin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles with skin targeting for topical delivery. Int J Pharm 328:191–195
Maindarkar SN, Raikar NB, Bongers P, Henson MA (2012) Incorporating emulsion drop coalescence into population balance equation models of high pressure homogenization. Colloids Surf A 396:63–73
McClements DJ (2005) Food emulsions principles, practices, and techniques, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Mehnert W, Mäder K (2001) Solid lipid nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47:165–196
Mishra DK, Dhote V, Bhatnagar P, Mishra PK (2012) Engineering solid lipid nanoparticles for improved drug delivery: promises and challenges of translational research. Drug Deliv Transl Res 2:238–253
Mohr K-H (1987a) High-pressure homogenization. Part I. Liquid–liquid dispersion in turbulence fields of high energy density. J Food Eng 6:177–186
Mohr K-H (1987b) The influence of cavitation on liquid–liquid dispersion in turbulence fields of high energy density. J Food Eng 6:311–324
Mucho M, Maincent P, Müller RH (2008) Lipid nanoparticles with a solid matrix (LNP, NLC, LDC) for oral drug delivery. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34:1394–1405
Müller RH, Schwarz C, Zur Mühlen A, Mehnert W (1994) Incorporation of lipophilic drugs and drug release profiles of solid lipid nanoparticles (LNP). Proc Int Symp Control Release Bioact Mater 21:146
Müller RH, Maassen S, Schwarz C, Mehnert W (1997) Solid lipid nanoparticles (LNP) as potential carrier for human use: interaction with human granulocytes. J Control Release 47:261–269
Müller RH, Dingler A, Schneppe T, Gohla S (2000a) Large scale production of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanosuspensions (DissoCubes). In: Wise D (ed) Handbook of pharmaceutical controlled release technology [e-book]. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 359–376
Müller RH, Mäder K, Gohla S (2000b) Solid lipid nanoparticles (LNP) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:161–177
Pardeike J, Hommoss A, Müller RH (2009) Lipid nanoparticles (LNP, NLC) in cosmetic and pharmaceutical dermal products. Int J Pharm 366:170–184
Priano L, Esposti D, Castagna G, De Medici C, Fraschini F, Gasco MR, Mauro A (2007) Solid lipid nanoparticles incorporating melatonin as new model for sustained oral and transdermal delivery systems. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:3596–3601
Puglia C, Blasi P, Rizza L, Schoubben A, Bonina F, Rossi C, Ricci M (2008) Lipid nanoparticles for prolonged topical delivery: an in vitro and in vivo investigation. Int J Pharm 357:295–304
Qian C, McClements DJ (2010) Formation of nanoemulsions stabilized by model food-grade emulsifiers using high-pressure homogenization: factors affecting particle size. Food Hydrocoll 25:1000–1008
Saheki A, Seki J, Nakanishi T, Tamai I (2012) Effect of back pressure on emulsification of lipid nanodispersions in a high-pressure homogenizer. Int J Pharm 422:489–494
Salmaso S, Elvassore N, Bertucco A, Caliceti P (2009) Production of solid lipid submicron particles for protein delivery using a novel supercritical gas-assisted melting atomization process. J Pharm Sci 98:640–650
Schäfer-Korting M, Mehnert W, Korting HC (2007) Lipid nanoparticles for improved topical application of drugs for skin diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:427–443
Schubert MA, Müller-Goymann CC (2003) Solvent injection as a new approach for manufacturing lipid nanoparticles—evaluation of the method and process parameters. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 55:125–131
Sebti T, Amighi K (2006) Preparation and in vitro evaluation of lipidic carriers and fillers for inhalation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 63:51–58
Severino P, Santana MHA, Souto EB (2012) Optimizing LNP and NLC by 22 full factorial design: effect of homogenization technique. Mater Eng C 32:1375–1379
Sinha VR, Srivastava S, Goel H, Jindal V (2010) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN’S)—trends and implications in drug targeting. Int J Adv Pharm Sci 1:212–238
Sjöstrom B, Bergenstahl B (1992) Preparation of submicron drug particles in lecithin-stabilized o/w emulsions: I. Model studies of the precipitation of cholesteryl acetate. Int J Pharm 84:107–116
Souto EB, Müller RH (2006) Investigation of the factors influencing the incorporation of clotrimazole in LNP and NLC prepared by hot high-pressure homogenization. J Microencapsul 23:377–388
Trombino S, Cassano R, Muzzalupo R, Pingitore A, Cione E, Picci N (2009) Stearyl ferulate-based solid lipid nanoparticles for the encapsulation and stabilization beta-carotene and alpha-tocopherol. Colloids Surf B 72:181–187
Trotta M, Debernardi F, Caputo O (2003) Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles by a solvent emulsification–diffusion technique. Int J Pharm 257:153–160
Varshosaz J, Ghaffari S, Khoshayand MR, Atyabi F, Azarmi S, Kobarfard F (2010) Development and optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles of amikacin by central composite design. J Liposome Res 20:97–104
Vitorino C, Carvalho FA, Almeida AJ, Sousa JJ, Pais AACC (2011) The size of solid lipid nanoparticles: an interpretation from experimental design. Colloids Surf B 84:117–130
Walstra P (1993) Principles of emulsion formation. Chem Eng Sci 48:333–349
Wooster TJ, Golding M, Sanguansri P (2008) Impact of oil type on nanoemulsion formation and Ostwald ripening stability. Langmuir 24:12758–12765
Zur Mühlen A, Mehnert W (1998) Drug release and release mechanism of prednisolone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Pharmazie 53:552–555
Zur Mühlen A, Schwarz C, Mehnert W (1998) Solid lipid nanoparticles (LNP) for controlled drug delivery–drug release and release mechanism. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 45:149–155
Acknowledgments
M. D. L. thanks University of Seville for a Grant from IV Research Plan of University of Seville. L. M. B. is especially grateful to Junta de Andalucía (Spain) for financial support (Project No. P09-CTS5029). Microscopy Services (Centro de Investigación, Tecnología e Innovación de la Universidad de Sevilla, CITIUS) technical support is also grateful. Authors also thank Dr. Álvarez-Fuentes for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durán-Lobato, M., Enguix-González, A., Fernández-Arévalo, M. et al. Statistical analysis of solid lipid nanoparticles produced by high-pressure homogenization: a practical prediction approach. J Nanopart Res 15, 1443 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1443-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1443-6