Abstract
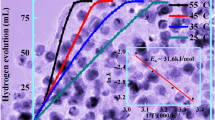
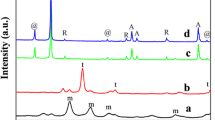
A series of Ni–B catalysts were prepared by mixing nickel acetate in 50% ethanol/water or methanol/water solution. The solution of sodium borohydride (1 M) in excess amount to nickel was then added dropwise into the mixture to ensure full reduction of nickel cations. The mol ratio of boron to nickel in mother solution was 3 to 1. The effects of preparation conditions such as temperature, stirring speed, and sheltering gas on the particle size, surface compositions, electronic states of surface atoms and catalytic activities of the Ni–B catalysts were studied. Ranel nickel catalyst was included for comparison. These catalysts were characterized by N2 sorption, X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The catalysts were tested for liquid phase hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene. All of the catalysts prepared in this study had nanosized particles. The preparation condition has significant influence on the particle size and surface compositions of the catalyst. The Ni–B catalyst was passivated by boron; therefore it was more stable than Raney nickel and did not catch fire after exposure to air. The catalysts prepared under N2 flow could suppress the oxidation of Ni by the dissolved oxygen in water and had metallic state of nickel. The catalyst prepared with vigorous stirring at 25°C under N2 stream yielded the smallest particles and resulted in the highest activity. It was much more active than the Raney nickel catalyst. The reaction condition also has pronounced effect on the hydrogenation activity. Using methanol as the reaction solvent increased p-chloronitrobenzene conversion to a large extent, compared to that using ethanol as the reaction medium. The selectivity of main product (p-chloroaniline) was greater than 99% on all of the Ni–B catalysts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltzly R. and Phillips A.P. (1946). The catalytic hydrogenolysis of halogen compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 68: 261–268
Brown H.C. and Brown C.A. (1963). The reaction of sodium borohydride with nickel acetate in aqueous solution-A convenient synthesis of an active nickel hydrogenation catalyst of low isomerizing tendency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85: 1003
Carberry J.J. (1987). Physico-chemical aspects of mass and heat transfer in heterogeneous catalysis. In: Anderson, J.R. and Boudart, M. (eds) Catalysis, Science and Technology, pp 131–134. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Coq B., Tijani A., Dutartre R. and Figuéras F. (1993). Catalysis by Rh/B system. Part 2: Higly regioselective vapour phase hydroformylation of propene at atmospheric pressure on Rh/B on silica and silica–alumina. J. Mol. Catal. 79: 243–252
Coq B., Tijani A. and Figuéras F. (1991). Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalytic membranes vs. Pt on γ-Al3 powders in the selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene. J. Mol. Catal. 2(68): 331–338
Coq B., Tijani A. and Figuéras F. (1992). Reaction pathways and the role of solvent in the hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes. J. Mol. Catal. 71: 317–323
Deng J.F., Yang J., Sheng S.H., Chen H. and Xing G. (1994). The study of ultrafine Ni–B and Ni–P amorphous alloy powders as catalysts. J. Catal. 150: 434
Fang Z.G., Shen B.R., Lu J., Fan K.N. and Deng J.F. (1999). DFT study of electron transfer between B and Ni in Ni–B amorphous alloy. Acta Chimica Sinia 57: 894
Fogler H.S. (1992). Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering. Prentice-Hall Englewood Cliffs, US, 670
Greenfield H. and Dovell F.S. (1967). Metal sulfide catalysts for hydrogenation of halonitrobenzenes to haloanilines. J. Org. Chem. 32: 3670
Han X., Zhou R., Lai G., Yue B. and Zheng X. (2003). Influence of rare earth (Ce, Sm, Nd, La, and Pr) on the hydrogenation properties of chloronitrobenzene over Pt/ZrO2 catalyst. Catal. Lett. 89: 255
Hu S.C. and Chen Y.W. (1997). Partial hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexene on ruthenium catalysts supported on La2O3–ZnO binary oxides. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 36: 5153–5160
Hutchinson C.R., Heckendorf A.H., Straughn J.L., Daddona P.E. and Cane D.E. (1979). Biosynthesis of camptothecin. 3. Definition of strictosamide as the penultimate biosynthetic precursor assisted by carbon-13 and deuterium NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 101: 3358–3364
Lee S.P. and Chen Y.W. (2000). Catalytic properties of Ni–B and Ni–P ultrafine materials. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 75: 1073–1097
Lee S.P. and Chen Y.W. (2001). Effects of preparation on the catalytic properties of Ni–P–B ultrafine materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 40: 1495
Li C., Chen W. and Wang W.J. (1994). Nitrobenzene hydrogenation over aluminum borate-supported platinum catalyst. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 119: 185–190
Li H., Li H.X., Dai W.L., Wang W., Fang Z. and Deng J.F. (1999). XPS studies on surface electronic characteristics of Ni–B and Ni–P amorphous alloy and its correlation on their catalytic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 152: 25–32
Liao, S., Z. Yu, Y. Xu, B. Yang & D. Yu, 1995. A remarkable synergic effect of polymer-anchored bimetallic palladium–ruthenium catalysts in the selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1155
Liu W., Tu H. and Tang Y. (2000). The metal complex effect on the selective hydrogenation of m- and p-chloronitrobenzene over PVP-stabilized platinum colloidal catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 159: 115–120
Ma A., W. Lu & E. Min, 2000. Amorphous alloy catalyst containing phosphorus, its preparation and use, U.S. Patent 6,051,528
Midland M.M. and Lee P.E. (1985). Efficient asymmetric reduction of acyl cyanides with B-3-pinanyl 9-BBN (Alpine-borane). J. Org. Chem. 50: 3237–3242
Nitta Y., Okamoto Y., Imanaka T. and Teranishi S. (1980). Surface state and catalytic activity and selectivity of nickel catalysts in hydrogenation reactions III electronic and catalytic properties of nickel catalysts. J. Catal. 64: 397–408
Okamoto Y., Fukino K. and Imanaka T. (1982). Surface state and catalytic activity and selectivity of nickel catalysts in hydrogenation reactions IV. Electronic effects on the selectivity in the hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene. J. Catal. 74: 173–180
Okamoto Y., Nitta Y., Imanaka T. and Teranishi S. (1979). Surface characterisation of nickel boride and nickel phosphide catalysts by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 75: 2027–2038
Okamoto Y., Nitta Y., Imanaka T. and Teranishi S. (1980). Surface state, catalytic activity and selectivity of nickel catalysts in hydrogenation reactions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 76: 998–1002
Osby J.O., Heinzman S.W. and Ganem B. (1986). Studies on the mechanism of transition-metal-assisted sodium borohydride and lithium aluminum hydride reductions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 108: 67–72
Paul R., Buisson P. and Joseph N. (1952). Catalytic activity of nickel borides. Ind. Eng. Chem. 44: 1006–1012
Pelavin M., Hendrickson D.N., Hollander J.M. and Jolly W.L. (1970). Phosphorus 2p electron binding energies correlation with extended huckel charges. J. Phys. Chem. 74: 1116
Rajadhyaksha R.A. and Karwa S.L. (1986). Solvent effects in catalytic hydrogenation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 41: 1765–1770
Ramachandran P.A. and Chaudhari R.V. (1983). Three Phase Catalytic Reactors. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York, 15
Rei M.H., Sheu L.L. and Chen Y.Z. (1986). Nickel boride catalysts in organic synthesis. Appl. Catal. 23: 281–290
Schlesinger H.I. and Brown H.C. (1953). New developments in the chemistry of diborane and borohydrides, I. General summary. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75: 186–192
Seo G. and Chon H. (1981). Hydrogenation of furfural over copper-containning catalysts. J. Catal. 67: 424–430
Shen J., Hu Z., Zhang Q., Zhang L. and Chen Y. (1992). Investigation of Ni–P–B ultrafine amorphous alloy particles produced by chemical reduction. J. Appl. Phys. 71: 5217–5221
Tijani A., Coq B. and Figueras F. (1991). Hydrogenation of para-chloronitrobenzene over supported ruthenium-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. 76: 255–266
Weisz P.B. and Prater D.C. (1954). Interpretation of Measurements in Experimental Catalysis. In Advances in Catalysis . New York, Academic Press, 143
Wheeler A. (1951). Reaction Rates and Selectivity in Catalyst Pores. In Advances in Catalysis. New York, Academic Press, 249
Yan X., Liu M., Liu H. and Liew K.Y. (2001). Role of boron species in the hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene over polymer-stabilized ruthenium colloidal catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 169: 225–233
Yao H.C. and Emmett P.H. (1962). Kinetics of liquid phase hydrogenation. IV. Hydrogenation of nitrocompounds over Raney nickel and nickel powder catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 84: 1086–1094
Yu Z.B., Qiao M.H., Li H.X. and Deng J.F. (1997). Preparation of amorphous Ni–Co–B alloys and the effect of cobalt on their hydrogenation activity. Appl. Catal. A 163: 1–13
Zhou R., Han X., Zheng X. and Jiang H. (2003). Effect of rare earths on the hydrogenation properties of p-chloronitrobenzene over polymer-anchored platinum catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 193: 103–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, YC., Huang, CY. & Chen, YW. Hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene on Ni–B Nanometal Catalysts. J Nanopart Res 8, 223–234 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-005-5944-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-005-5944-9