Abstract
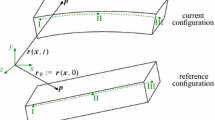
The absolute nodal coordinate formulation (ANCF) is often used for the large rotation and deformation analysis. In the ANCF, absolute nodal coordinates and global slopes are utilized as the element nodal coordinates. Accordingly, it gives a constant and symmetric mass matrix. On the other hand, elastic forces are generally expressed by highly nonlinear terms. Therefore, one of the important topics in the implementation of the ANCF is to derive mathematical descriptions of the elastic forces which can be calculated efficiently. This study focuses on development of efficient calculation procedures for the ANCF beam element under the assumption of the Euler–Bernoulli beam theory. In particular, we focus on the fact that the elastic forces can be described in simpler forms with the element coordinates. It implies that appropriate choices of the coordinate systems for the inertia and the elastic forces could contribute to the development of efficient calculation procedures. In the present formulation, the strain and the kinetic energies are expressed as functions of the element and the global coordinates, respectively. Then algebraic constraints regarding the relations between the global and the element coordinate systems are introduced by means of the Lagrange method of undetermined multipliers. These constraints are used for eliminating the redundant degrees of freedom from a standpoint of consistency in the formulation. Therefore, this method can be categorized as an augmented formulation technique. The equations of motions of this constrained system are derived by the method for constrained Hamiltonian system, namely Dirac’s method with the Poisson bracket formalism. In order to evaluate the proposed method, it is applied to the large deformation problem in the plane case. The equivalence of the previous approach and the proposed method is discussed by a comparison of the two. In addition, its computational performance is investigated.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shabana, A.A.: Dynamics of Multibody Systems, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998)
Shabana, A.A., Hussien, H.A., Escalona, J.L.: Application of the absolute nodal coordinate formulation to large rotation and large deformation problems. Trans. AMSE, J. Mech. Des. 120, 188–195 (1998)
Shabana, A.A., Schwertassek, R.: Equivalence of the floating frame of reference approach and finite element formulations. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 33(3), 417–432 (1998)
Shabana, A.A., Yakoub, R.Y.: Three dimensional absolute nodal coordinate formulation for beam elements: theory. Trans. AMSE, J. Mech. Des. 123, 606–613 (2001)
Yakoub, R.Y., Shabana, A.A.: Three dimensional absolute nodal coordinate formulation for beam elements: implementation and applications. Trans. AMSE, J. Mech. Des. 123, 614–621 (2001)
Omar, M.A., Shabana, A.A.: A two-dimensional shear deformable beam for large rotation and deformation problems. J. Sound Vib. 243(3), 565–576 (2001)
Sugiyama, H., Mikkola, A.M., Shabana, A.A.: A non-incremental nonlinear finite element solution for cable problems. Trans. AMSE, J. Mech. Des. 125, 746–756 (2003)
Mikkola, A.M., Shabana, A.A.: A non-incremental finite element procedure for the analysis of large deformation of plates and shells in mechanical system applications. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 9, 289–309 (2003)
Dmitrochenko, O.N., Pogorelov, D.Y.U.: Generalization of plate finite elements for absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 10, 17–43 (2003)
Berzeri, M., Shabana, A.A.: Development of simple models for the elastic force in the absolute nodal co-ordinate formulation to multibody system dynamics. J. Sound Vib. 235, 539–565 (2000)
Gerstmayr, J.: Strain tensors in the absolute nodal coordinate and the floating frame of reference formulation. Nonlinear Dyn. 34, 133–145 (2003)
Gerstmayr, J., Ambrósio, J.A.C.: Component mode synthesis with constant mass and stiffness matrices applied to flexible multibody systems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 73, 1518–1546 (2008)
Kobayashi, N., Wago, T., Sugawara, Y.: Reduction of system matrices of planar beam in ancf by component mode synthesis method. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 26, 265–281 (2011)
Dufva, K.E., Sopanen, J.T., Mikkola, A.M.: A two-dimensional shear deformable beam element based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. J. Sound Vib. 280, 719–738 (2005)
Kerkkänen, K.S., Sopanen, J.T., Mikkola, A.M.: A linear beam finite element based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. J. Mech. Des. 127, 621–630 (2005)
Sugiyama, H., Suda, Y.: A curved beam element in the analysis of flexible multi-body systems using the absolute nodal coordinates. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Proc., Part K, J. Multi-Body Dyn. 221, 219–231 (2007)
García-Vallejo, D., Mikkola, A.M., Escalona, J.L.: A new locking-free shear deformable finite element based on absolute nodal coordinates. Nonlinear Dyn. 50, 249–264 (2007)
Gerstmayr, J., Mikkola, A.M.: A geometrically exact beam element based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 20, 359–384 (2008)
Gerstmayr, J., Irschik, H.: On the correct representation of bending and axial deformation in the absolute nodal coordinate formulation with an elastic line approach. J. Sound Vib. 318, 461–487 (2008)
Schwab, A.L., Meijaard, J.P.: Comparison of three-dimensional flexible beam elements for dynamic analysis: classical finite element formulation and absolute nodal coordinate formulation. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 5, 011010 (2010)
Sugiyama, H., Koyama, H., Yamashita, H.: Gradient deficient curved beam element using the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 5, 021001 (2010)
Nachbagauer, K., Pechstein, A.S., Irschik, H., Gerstmayr, J.: A new locking-free formulation for planar, shear deformable, linear and quadratic beam finite elements based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 26, 245–263 (2011)
Nachbagauer, K., Gruber, P., Gerstmayr, J.: Structural and continuum mechanics approaches for a 3D shear deformable ancf beam finite element: application to static and linearized dynamic examples. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 8, 021004 (2013)
Nachbagauer, K., Gruber, P., Gerstmayr, J.: Structural and continuum mechanics approaches for a 3D shear deformable ANCF beam finite element: application to buckling and nonlinear dynamic examples. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 9, 011013 (2014)
Dirac, P.A.M.: Lectures on Quantum Mechanics. Yeshiva University Press, New York (1964)
Berzeri, M., Campanelli, M., Shabana, A.A.: Definition of the elastic forces in the finite-element absolute nodal coordinate formulation and the floating frame of reference formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 5, 21–54 (2001)
Wu, S.C., Haug, E.J.: Geometric non-linear substructuring for dynamics of flexible mechanical systems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 26, 2211–2226 (1988)
Berzeri, M., Shabana, A.A.: Study of the centrifugal stiffening effect using the finite element absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 7, 357–387 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 24760190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, K., Watanabe, M. Development of an efficient calculation procedure for elastic forces in the ANCF beam element by using a constrained formulation. Multibody Syst Dyn 43, 369–386 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-017-9594-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-017-9594-3