Abstract
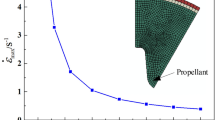
The uniaxial compressive tests at different temperatures (223–298 K) and strain rates (\(0.40\mbox{--}63~\mbox{s}^{-1}\)) are reported to study the properties of hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) propellant at intermediate strain rates, using a new INSTRON testing machine. The experimental results indicate that the compressive properties (mechanical properties and damage) of HTPB propellant are remarkably affected by temperature and strain rate and display significant nonlinear material behaviors at large strains under all the test conditions. Continuously decreasing temperature and increasing strain rate, the characteristics of stress-strain curves and damage for HTPB propellant are more complex and are significantly different from that at room temperature or at lower strain rates. A new constitutive model was developed to describe the compressive behaviors of HTPB propellant at room temperature and intermediate strain rates by simply coupling the effect of strain rate into the conventional hyperelastic model. Based on the compressive behaviors of HTPB propellant and the nonlinear viscoelastic constitutive theories, a new thermovisco-hyperelastic constitutive model with damage was proposed to predict the stress responses of the propellant at low temperatures and intermediate strain rates. In this new model, the damage is related to the viscoelastic properties of the propellant. Meanwhile, the effect of temperature on the hyperelastic properties, viscoelastic properties and damage are all considered by the macroscopical method. The constitutive parameters in the proposed constitutive models were identified by the genetic algorithm (GA)-based optimization method. By comparing the predicted and experimental results, it can be found that the developed constitutive models can correctly describe the uniaxial compressive behaviors of HTPB propellant at intermediate strain rates and different temperatures.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bencher, C.D.: Microstructural damage and fracture processes in a composite solid rocket propellant. J. Spacecr. Rockets 32, 328–334 (1995)
Canga, M.E., Becker, W.B., Özüpek, S.: Constitutive modeling of viscoelastic materials with damage-computational aspects. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 190(15–17), 2207–2226 (2001)
Chang, X., Lai, J., Zhang, X., Hu, K., Qi, W.: High strain-rate viscoelastic constitutive model for HTPB propellant. J. Propuls. Technol. 35(1), 123–127 (2014)
Chen, W.W.: Experimental methods for characterizing dynamic response of soft materials. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2, 2–14 (2016)
Chu, H.T., Chou, J.H.: Effect of cooling load on the safety factor of propellant grains. J. Propuls. Power 29, 27–33 (2013)
Duncan, E.J.S.: Characterization of a glycidylazide polymer composite propellant: strain rate effects and relaxation response. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 56, 365–375 (1995)
Duncan, E.J.S., Margetson, J.: A nonlinear viscoelastic theory for solid rocket propellants based on a cumulative damage approach. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 23(2), 94–104 (1998)
Field, J.E., Walley, S.M., Proud, W.G., Goldrein, H.T., Siviour, C.R.: Review of experimental techniques for high rate deformation and shock studies. Int. J. Impact Eng. 30, 725–775 (2004)
Furmanski, J., Cady, C.M., Brown, E.N.: Time-temperature equivalence and adiabatic heating at large strains in high density polyethylene and ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. Polymer 54(1), 381–390 (2013)
Gent, A.N.: A new constitutive relation for rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 69(1), 59–61 (1996)
Gligorijević, N., Živković, S., Subotić, S., Rodić, V., Gligorijević, I.: Effect of cumulative damage on rocket motor service life. J. Energ. Mater. 33(4), 229–259 (2015)
Gray, G.T. III, Blumenthal, W.R.: Split-Hopkinson pressure bar testing of soft materials. In: Kuhn, H., Medlin, D. (eds.) ASM Handbook: Mechanical Testing and Evaluation, pp. 488–496. ASM International, Materials Park (2000)
Han, L., Chen, X., Xu, J., Zhou, C., Yu, J.: Research on the time-temperature-damage superposition principle of NEPE propellant. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 19(4), 581–599 (2015)
Hinterhoelzl, R.M., Schapery, R.A.: FEM implementation of a three-dimensional viscoelastic constitutive model for particulate composites with damage growth. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 8(1), 65–94 (2004)
Ho, S.Y.: High strain-rate constitutive models for solid rocket propellants. J. Propuls. Power 18, 1106–1111 (2002)
Ho, S.Y., Fong, C.W.: Temperature dependence of high strain-rate impact fracture behaviour in highly filled polymeric composite and plasticized thermoplastic propellants. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 3023–3031 (1987)
Hsiao, R.C.: Structural analyses of solid propellant grains under ignition pressurization using explicit dynamics method. In: AIAA 2013-3959, (2013)
Iwamoto, T., Yokoyama, T.: Effects of radial inertia and end friction in specimen geometry in split Hopkinson pressure bar test: a computational study. Mech. Mater. 51, 97–109 (2012)
Jeremic, R.: Some aspects of time-temperature superposition principle applied for predicting mechanical properties of solid rocket propellants. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 24, 221–223 (1999)
Jiang, S., Rui, X., Hong, J., Wang, G., Rong, B., Wang, Y.: Numerical simulation of impact breakage of gun propellant charge. Granul. Matter 13, 611–622 (2011)
Jordan, J.L., Montaigne, D., Gould, P., Neel, C., Sunny, G., Molek, C.: High strain rate and shock properties of hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) with varying amounts of plasticizer. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2, 91–100 (2016)
Judge, M.D.: An investigation of composite propellant accelerated ageing mechanisms and kinetics. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 28(3), 114–119 (2003)
Kakavas, P.A.: Mechanical properties of propellant composite materials reinforced with ammonium perchlorate particles. Int. J. Solids Struct. 51, 2019–2026 (2014)
Kunz, R.K.: Characterization of solid propellant for linear cumulative damage modeling. In: AIAA-2009-5257 (2009)
Long, B., Chang, X., Hu, K., Zhang, Y.: Effects of temperature and strain rate on the dynamic fracture properties of HTPB propellant. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 40(4), 479–483 (2015)
Matheson, E.R., Nguyen, D.Q.: A rate-dependent viscoelastic damage model for simulation of solid propellant impacts. In: Furnish, E., Rusell, W. (eds.) Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, pp. 913–916. American Institute of Physics, New York (2005)
Ogden, R.W.: Large deformation isotropic elasticity-on the correlation of theory and experiment for incompressible rubberlike solids. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A, Math. Phys. Sci. 326, 565–584 (1972)
Özüpek, Ş., Becker, E.B.: Constitutive modeling of high-elongation solid propellants. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 114, 111–115 (1992)
Park, S.W., Schapery, R.A.: A viscoelastic constitutive model for particulate composites with growing damage. Int. J. Solids Struct. 34(8), 931–947 (1997)
Pouriayevalia, H., Guoa, Y.B., Shim, V.P.W.: A visco-hyperelastic constitutive description of elastomer behaviour at high strain rates. Proc. Eng. 10, 2274–2279 (2011)
Ren, P., Hou, X., He, G., Gao, J., He, T.: Comparative research of tensile and compressive modulus of composite solid propellant for solid rocket motor. J. Astronaut. 31, 2354–2359 (2010)
Rivlin, R.S.: Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials. IV. Further developments of the general theory. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A, Math. Phys. Sci. 241(835), 379–397 (1948)
Rivlin, R.S.: Proceedings of First Symposium on Naval Structural Mechanics. Pergamon, New York (1960)
Shim, V.P.W., Yang, L.M., Lim, C.T., Law, P.H.: A viscohyperelastic constitutive model to characterize both tensile and compressive behavior of rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 92(1), 523–531 (2004)
Siviour, C.R., Jordan, J.L.: High strain rate mechanics of polymers: a review. J. Dyn. Behav. Mater. 2, 15–32 (2016)
Siviour, C.R., Walley, S.M., Proud, W.G., Field, J.E.: The high strain rate compressive behaviour of polycarbonate and polyvinylidene difluoride. Polymer 46(26), 12546–12555 (2005)
Song, B., Chen, W.W., Lu, W.Y.: Mechanical characterization at intermediate strain rates for rate effects on an epoxy syntactic foam. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 49, 1336–1343 (2007)
Sounik, D.F., Gansen, P., Clemons, J.L., Liddle, J.W.: Head-impact testing of polyurethane energy-absorbing (EA) foams. SAE Trans. J. Mater. Manuf. 106, 211–220 (1997)
Sun, C., Xu, J., Chen, X., Zheng, J., Zheng, Y., Wang, W.: Strain rate and temperature dependence of the compressive behavior of a composite modified double-base propellant. Mech. Mater. 89, 35–46 (2015)
Swanson, S.R., Christensen, L.W.: A constitutive formulation for high-elongation propellants. J. Spacecr. Rockets 20, 559–566 (1983)
Wang, P., Wang, Z., Ju, Y., Sun, C., Xu, J.: Experimental research on rate dependent constitutive relation of double-basepropellant under impact load. J. Solid Rocket Technol. 35(1), 69–72 (2012)
Wang, Z., Qiang, H., Wang, G.: Experimental investigation on high strain rate tensile behaviors of HTPB propellant at low temperatures. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 40, 814–820 (2015a)
Wang, Z., Qiang, H., Wang, G., Huang, Q.: Tensile mechanical properties and constitutive model for HTPB propellant at low temperature and high strain rate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132, 42104 (2015b)
Xu, F., Aravas, N., Sofronis, P.: Constitutive modeling of solid propellant materials with evolving microstructural damage. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 2050–2073 (2008)
Xu, J., Ju, Y., Han, Bo., Zhou, C., Zheng, J.: Research on relaxation modulus of viscoelastic materials under unsteady temperature states based on TTSP. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 17(4), 543–556 (2013)
Xu, J., Chen, X., Wang, H., Zheng, J., Zhou, C.: Thermo-damage-viscoelastic constitutive model of HTPB composite propellant. Int. J. Solids Struct. 51, 3209–3217 (2015)
Yang, L.M., Shim, V.P.W., Lim, C.T.: A visco-hyperelastic approach to modelling the constitutive behaviour of rubber. Int. J. Impact Eng. 24(6–7), 545–560 (2000)
Yang, L., Wang, N., Xie, K., Sui, X., Li, S.: Influence of strain rate on the compressive yield stress of CMDB propellant at low, intermediate and high strain rates. Polym. Test. 51, 49–57 (2016)
Yeoh, O.H.: Some forms of the strain energy function for rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 66(5), 754–771 (1993)
Yıldırım, H.C., Özüpek, Ş.: Structural assessment of a solid propellant rocket motor: effects of aging and damage. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 15(8), 635–641 (2011)
Zalewski, R., Wolszakiewicz, T.: Analysis of uniaxial tensile tests for homogeneous solid propellants under various loading conditions. Central Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 8, 223–231 (2011)
Zalewski, R., Pyrz, M., Wolszakiewicz, T.: Modeling of solid propellants viscoplastic behavior using evolutionary algorithms. Central Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 7, 289–300 (2010)
Zhang, X., Chang, X., Lai, J., Hu, K.: Comparative research of tensile and compressive mechanical properties of HTPB propellant at low temperature. J. Solid Rocket Technol. 36(6), 771–774 (2013)
Zhang, J., Zheng, J., Chen, X., Sun, C., Xu, J.: A thermovisco-hyperelastic constitutive model of NEPE propellant over a large range of strain rates. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME 136(3), 1–8 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National 973 Program in China through Grant Nos. 61338 and 613142 and the National Funds in China through Grant 51328050101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Qiang, H., Wang, T. et al. A thermovisco-hyperelastic constitutive model of HTPB propellant with damage at intermediate strain rates. Mech Time-Depend Mater 22, 291–314 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-017-9357-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-017-9357-9