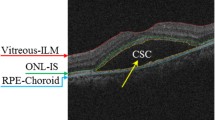
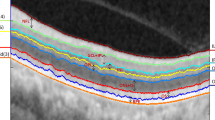
Abstract
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a high-resolution and non-invasive imaging modality that has become one of the most prevalent techniques for ophthalmic diagnosis. Retinal layer segmentation is crucial for doctors to diagnose and analysis retinal diseases. Manual segmentation is often a time-consuming and subjective process. A number of semi-automatic and automatic methods have been proposed for layer segmentation on retinal OCT images, but very few of them are applicable for retinal pathological OCT images. In this work, we propose a new automatic method for segmenting ILM (Inner Limiting Membrane) and OS-RPE (Outer Segment- Retinal Pigment Epithelium) interfaces on pathological OCT images affected by macular hole disease. The proposed method follows shortest path framework, while is enhanced with backtracking and direction consistency. Backtracking can deal with the shortcut problem which occur when classical shortest path algorithm is used to segment deformed linear structure. “Consistency loss” is one kind of soft constraint we defined to limit the propagate direction of modified shortest path algorithm. Besides, the image information after Gabor transform can reflect the layer location to an extent. So, it is considered as one new weight in the weight calculation of the method. Another contribution is that the proposed layer segmentation method is suitable for both normal and pathological retinal OCT images. To quantitate the performance of the proposed method, we did comparative experiments with three state-of-the-art segmentation methods. The experimental result shows that proposed method can achieve better result than other methods and can deal with pathological retinal OCT images.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandello F, Battaglia PM, Lanzetta P, Loewenstein A, Massin P, Menchini F, Veritti D (2014) Diabetic macular edema. Springer, Berlin, pp 989–997
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Yang J, Cao Q, Yang G, Chen J, Shu H, Luo L, Coatrieux JL, Feng Q (2016) Curve-Like Structure Extraction Using Minimal Path Propagation With Backtracking. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(2):988–1003
Chiu SJ, Li XT, Nicholas P, Toth CA, Izatt JA, Farsiu S (2010) Automatic segmentation of seven retinal layers in SDOCT images congruent with expert manual segmentation. Opt Express 18(18):19413–19428
Cootes TF, Edwards GJ, Taylor CJ (2001) Active Appearance Models. Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence IEEE Transactions 23(6):681–685
Cootes TF, Taylor CJ, Cooper DH, Graham J (1995) Active Shape Models-Their Training and Application. Computer Vision & Image Understanding 61(1):38–59
Drexler W, Fujimoto JG (2008) State-of-the-art retinal optical coherence tomography. Prog Retin Eye Res 27(1):45–88
Duan J, Tench C, Gottlob I, Proudlock F, Bai L (2017) Automated Segmentation of Retinal Layers from Optical Coherent Tomography Images Using Geodesic Distance. Pattern Recogn 72
Fang L, Cunefare D, Wang C, Guymer RH, Li S, Farsiu S (2017) Automatic segmentation of nine retinal layer boundaries in OCT images of non-exudative AMD patients using deep learning and graph search. Biomedical Optics Express 8(5):2732–2744
Fu D, Tong H, Shuang Z, Ling L, Gao F, Minar J (2016) Retinal status analysis method based on feature extraction and quantitative grading in OCT images. Biomed Eng Online 15(1):87
Fuller AR, Zawadzki RJ, Choi SS, Wiley DF, Werner JS, Hamann B (2007) Segmentation of Three-dimensional Retinal Image Data. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 13(6):1719–1726
Ghorbel I, Rossant F, Bloch I, Tick S, Paques M (2011) Automated segmentation of macular layers in OCT images and quantitative evaluation of performances. Pattern Recogn 44(8):1590–1603
Hageman GS, Gehrs K, Johnson LV, Anderson D (1995) Age-related macular degeneration (AMD). PubMed, pp. 780–784
Hee MR, Izatt JA, Swanson EA, Huang D, Schuman JS, Lin CP, Puliafito CA, Fujimoto JG (1995) Optical coherence tomography of the human retina. Arch Ophthalmol 113(3):325
Ho AC, Guyer DR, Fine SL (1900) Macular hole. Surv Ophthalmol 42(5):393–416
Hofer B, Hermann B, Považay B, Marshall D, Rosin PL, Kajić V, Drexler W (2010) Robust segmentation of intraretinal layers in the normal human fovea using a novel statistical model based on texture and shape analysis. Opt Express 18(14):14730–14744
Huang G, Liu Z, Maaten LVD, Weinberger KQ (2016) Densely connected convolutional networks
Huang D, Swanson EA, Lin CP, Schuman JS, Stinson WG, Chang W, Hee MR, Flotte T, Gregory K, Puliafito CA (1991) Optical coherence tomography. Science 254(5035):1178
Hussain A, Bhuiyan A, Turpin A, Luu CD, Smith RT, Guymer RH, Kotagiri R (2017) Automatic Identification of Pathology-Distorted Retinal Layer Boundaries Using SD-OCT Imaging. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(7):1638–1649
Ishikawa H, Piette S, Liebmann JM, Ritch R (2002) Detecting the inner and outer borders of the retinal nerve fiber layer using optical coherence tomography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 240(5):362
Ishikawa H, Stein DM, Wollstein G, Beaton S, Fujimoto JG, Schuman JS (2005) Macular segmentation with optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46(6):2012
Izatt JA, Allingham MJ, Mettu PS, Cousins SW, Farsiu S, Chiu SJ (2015) Kernel regression based segmentation of optical coherence tomography images with diabetic macular edema. Biomedical Optics Express 6(4):1172–1194
Jin X, Zhu S, Xiao C, Sun H, Xiaodong LI, Zhao G, Shiming GE (2017) 3D textured model encryption via 3D Lu chaotic mapping. Sci China Inf Sci 60(12):122107
Karri SP, Chakraborthi D, Chatterjee J (2016) Learning layer-specific edges for segmenting retinal layers with large deformations. Biomedical Optics Express 7(7):2888
Keller B, Cunefare D, Grewal DS, Mahmoud TH, Izatt JA, Farsiu S (2016) Length-adaptive graph search for automatic segmentation of pathological features in optical coherence tomography images. J Biomed Opt 21(7):76015
Lang A, Carass A, Hauser M, Sotirchos ES, Calabresi PA, Ying HS, Prince JL (2013) Retinal layer segmentation of macular OCT images using boundary classification. Biomedical Optics Express 4(7):1133–1152
Lebrun M (2012) An Analysis and Implementation of the BM3D Image Denoising Method. Am Soc Mech Eng 2(25):175–213
Li H, Yezzi A (2007) Vessels as 4D Curves: Global Minimal 4D Paths to Extract 3D Tubular Surfaces. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26(9):1213–1223
Liu X, Fu T, Pan Z, Dong L, Wei H, Liu J, Kai Z (2018) Automated layer segmentation of retinal optical coherence tomography images using a deep feature enhanced structured random forests classifier. IEEE Journal of Biomedical & Health Informatics PP(99)
Liu X, Liu D, Fu T, Zhang K, Liu J, Chen L (2018) Shortest path with backtracking based automatic layer segmentation in pathological retinal optical coherence tomography. In: 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2770–2774, IEEE
Liu X, Wang J, Yang Z, Hu W (2016) Automated segmentation of nine retinal layers with layer thickness information on SD-OCT images. In: Eighth International Conference on Digital Image Processing, p. 100331G
Liu X, Yang Z, Hu W, Liu J, Zhang K (2018) Detection of macular diseases in optical coherence tomography image. International Journal of Parallel, Emergent and Distributed Systems, pp. 1–13
Liu X, Yang Z, Wang J, Liu J, Zhang K, Hu W (2017) Patch-based denoising method using low-rank technique and targeted database for optical coherence tomography image. Journal of Medical Imaging 4(1):014002
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2017) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 39(4):640
Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Bowd C, Vessani RM, Susanna R Jr, Weinreb RN (2005) Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer, optic nerve head, and macular thickness measurements for glaucoma detection using optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 139(1):44
Mishra A, Wong A, Bizheva K, Clausi DA (2009) Intra-retinal layer segmentation in optical coherence tomography images. Opt Express 17(26):23719
Na JH, Sung KR, Baek S, Kim YJ, Durbin MK, Lee HJ, Kim HK, Sohn YH (2012) Detection of glaucoma progression by assessment of segmented macular thickness data obtained using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53(7):3817–3826
Niu S, Chen Q, Sisternes LD, Rubin DL, Zhang W, Liu Q (2014) Automated retinal layers segmentation in SD-OCT images using dual-gradient and spatial correlation smoothness constraint. Comput Biol Med 54(C):116–128
Novosel J, Thepass G, Lemij HG, Boer JFD, Vermeer KA, Vliet LJV (2015) Loosely coupled level sets for simultaneous 3D retinal layer segmentation in optical coherence tomography. Med Image Anal 26(1):146–158
Otte S, Otte C, Schlaefer A, Wittig L, Huttmann G, Dromann D, Zell A (2013) OCT A-Scan based lung tumor tissue classification with Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory networks. In: IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, pp. 1–6
Qian S, Chen D (1993) Discrete Gabor transform. IEEE Trans Signal Process 41(7):2429–2438
Rossant F, Bloch I, Ghorbel I, Paques M (2015) Parallel Double Snakes. Application to the segmentation of retinal layers in 2D-OCT for pathological subjects. Pattern Recogn 48(12):3857–3870
Roy AG, Conjeti S, Karri S, Sheet D, Katouzian A, Wachinger C, Navab N (2017) ReLayNet: retinal layer and fluid segmentation of macular optical coherence tomography using fully convolutional networks. Biomedical Optics Express 8(8):3627
Sahu S, Singh HV, Kumar B, Singh AK (2017) De-noising of ultrasound image using Bayesian approached heavy-tailed Cauchy distribution. Multimedia Tools and Applications, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5221-9.
Senthil Kumar T, Helen Prabha K (2018) Geometric mean filter with grayscale morphological method to enhance the RNFL thickness in the SD-OCT images. Multimedia Tools and Applications 77(8):10285–10301
Shahidi M, Wang Z, Zelkha R (2005) Quantitative thickness measurement of retinal layers imaged by optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 139(6):1056–1061
Szkulmowski M, Wojtkowski M, Sikorski BL, Bajraszewski T, Srinivasan VJ, Szkulmowska A, Kaluzny JJ, Fujimoto JG, Kowalczyk A (2007) Analysis of posterior retinal layers in spectral optical coherence tomography images of the normal retina and retinal pathologies. J Biomed Opt 12(4):041207
Tian J, Varga B, Somfai GM, Lee WH, Smiddy WE, Debuc DC (2015) Real-Time Automatic Segmentation of Optical Coherence Tomography Volume Data of the Macular Region. PLoS One 10(8)
Vermeer KA, Der Schoot JV, De Boer J, Lemij HG (2010) Automated Retinal and NFL Segmentation in OCT Volume Scans by Pixel Classification. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(13):219–219
Vermeer KA, Schoot VDJH, Lemij HG, Boer DJF (2011) Automated segmentation by pixel classification of retinal layers in ophthalmic OCT images. Biomedical Optics Express 2(6):1743–1756
Wei L, Worz S, Kang CK, Cho ZH, Rohr K (2017) Progressive Minimal Path Method for Segmentation of 2D and 3D Line Structures. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence PP(99):1
Yang Q, Reisman CA, Wang Z, Fukuma Y, Hangai M, Yoshimura N, Tomidokoro A, Araie M, Raza AS, Hood DC (2010) Automated layer segmentation of macular OCT images using dual-scale gradient information. Opt Express 18(20):21293–21307
Yazdanpanah A, Hamarneh G, Smith B, Sarunic MV (2009) Intra-retinal Layer Segmentation in Optical Coherence Tomography Using an Active Contour Approach. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention 12:649–656
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61403287, No. 61472293, No. 61572381), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2014 M552039) Foundation of Wenzhou Science & Technology Bureau (No. Y20150086), Natural Science foundation of Zhejiang Province (No.LY16F030010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Liu, D., Fu, T. et al. Shortest path with backtracking based automatic layer segmentation in pathological retinal optical coherence tomography images. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 15817–15838 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6979-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6979-0