Abstract
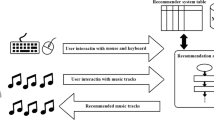
In this paper, we introduce a personalized home audio system that uses IoT technologies to recommend and play music remotely based on a user’s estimated emotion. This system estimates a user’s emotion based on texts on their smartphone collected during outdoor activities. Based on this emotion, our system then searches for music that matches it from a music database. The system automatically detects the user when they return home, and plays the recommended music via a connected audio system. Consequently, personalized emotion-based music recommendation is provided transparently without the user’s awareness.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Android api guide. http://developer.android.com/guide/index.html
Apache tomcat ®;. http://tomcat.apache.org
August home. http://august.com
Bigand E, Vieillard S, Madurell F, Marozeau J, Dacquet A (2005) Multidimensional scaling of emotional responses to music: The effect of musical expertise and of the duration of the excerpts. Cogn Emotion 19(8):1113–1139. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699930500204250
Bradley MM, Lang PJ (1999) Affective norms for english words (anew): instruction manual and affective ratings
Feng Y, Zhuang Y, Pan Y (2003) Music information retrieval by detecting mood via computational media aesthetics. In: Proceedings IEEE/WIC International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI 2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/WI.2003.1241199, pp 235–241
Fernandes E, Jung J, Prakash A (2016) Security analysis of emerging smart home applications. In: 2016 IEEE Symposium on security and privacy (SP). https://doi.org/10.1109/SP.2016.44, pp 636–654
Han BJ, Rho S, Jun S, Hwang E (2010) Music emotion classification and context-based music recommendation. Multimed Tool Appl 47 (3):433–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-009-0332-6
Hello heart. http://helloheart.com
Jun S, Kim D, Jeon M, Rho S, Hwang E (2015) Social mix: automatic music recommendation and mixing scheme based on social network analysis. J Supercomput 71(6):1933–1954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-014-1182-1
Kang D, Shim H, Yoon K (2018) A method for extracting emotion using colors comprise the painting image. Multimed Tool Appl 77(4):4985–5002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4667-0
Kim M, Park SO (2013) Group affinity based social trust model for an intelligent movie recommender system. Multimed Tool Appl 64(2):505–516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-011-0897-8
Kummer M (2017) Review of the ecobee4 smart thermostat with homekit
Lee T, Lim H, Kim D W, Hwang S, Yoon K (2016) System for matching paintings with music based on emotions. In: SIGGRAPH ASIA 2016 Technical briefs, SA ’16. https://doi.org/10.1145/3005358.3005366. ACM, New York, pp 31:1–31:4
Nack F, Dorai C, Venkatesh S (2001) Computational media aesthetics: finding meaning beautiful. IEEE MultiMedia 8(4):10–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/93.959093
Phan D, Siong LY, Pathirana PN, Seneviratne A (2015) Smartwatch: Performance evaluation for long-term heart rate monitoring. In: 2015 International symposium on bioelectronics and bioinformatics (ISBB). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBB.2015.7344944, pp 144–147
Raspberry pi 3 model b. https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-3-model-b/
Rho S, Song S, Nam Y, Hwang E, Kim M (2013) Implementing situation-aware and user-adaptive music recommendation service in semantic web and real-time multimedia computing environment. Multimed Tool Appl 65(2):259–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-011-0803-4
Rho S, Yeo SS (2013) Bridging the semantic gap in multimedia emotion/mood recognition for ubiquitous computing environment. J Supercomputing 65(1):274–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-010-0447-6
Russell JA (1980) A circumplex model of affect. J Person Soc Psychol 39(6):1161
Schimmack U, Grob A. (2000) Dimensional models of core affect: a quantitative comparison by means of structural equation modeling. European J Personal 14 (4):325–345. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-0984(200007/08)14:4<325::AID-PER380>3.0.CO;2-I
Schimmack U, Rainer R (2002) Experiencing activation: energetic arousal and tense arousal are not mixtures of valence and activation. Emotion 2(4):412
Seo S, Kang D (2016) Study on predicting sentiment from images using categorical and sentimental keyword-based image retrieval. J Supercomput 72(9):3478–3488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-015-1510-0
Stojkoska BLR, Trivodaliev KV (2017) A review of internet of things for smart home: Challenges and solutions. J Cleaner Product 140:1454–1464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.006
Thayer RE (1990) The biopsychology of mood and arousal. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Warriner AB, Kuperman V, Brysbaert M (2013) Norms of valence, arousal, and dominance for 13,915 english lemmas. Behav Res Methods 45(4):1191–1207. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-012-0314-x
Yang GZ, Yang G (2006) Body sensor networks, vol 1. Springer, Berlin
Yang YH, Lin YC, Su YF, Chen HH (2008) A regression approach to music emotion recognition. IEEE Trans Audio, Speech, Language Process 16(2):448–457. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASL.2007.911513
Zhang D, Ning H, Xu KS, Lin F, Yang LT (2012) Internet of things. J UCS 18:1069–1071
Acknowledgements
This work has supported by Seoul National University of Science & Technology and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2016R1D1A1B03935378).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, D., Seo, S. Personalized smart home audio system with automatic music selection based on emotion. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 3267–3276 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6733-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6733-7