Abstract
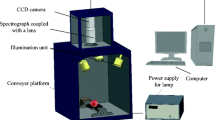
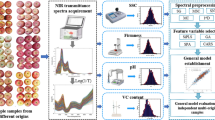
In this paper, a hybrid approach, which combines back propagation neural network (BPNN), generalized regression neural network (GRNN) and particle swarm optimization (PSO), is proposed to determine internal qualities in apples by using NIR diffuse reflectance spectra in the wavelength range of 400-1022 nm. The essence of the hybrid approach incorporates six phases. Firstly, the original spectral data should be submitted to Savitzky-Golay smoothing method to reduce noise. Secondly, using multiplicative scatter correction (MSC) on de-noised spectral data to modify additive and multiplicative effects. Thirdly, principal component analysis (PCA) is used to extract main features from the pretreated spectral data. Fourthly, obtaining forecasting results by using BPNN. Fifthly, obtaining forecasting results by using GRNN. Finally, these respective results are combined into the final forecasting results by using the principle of PSO. The hybrid model is examined by determining soluble solid content (SSC) and total acid content (TAC) of Green apples. Experimental results illustrate that the hybrid model shows great potential for internal quality control of apple fruits based on NIR spectroscopy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes RJ, Dhanoa MS, Lister SJ (1989) Standard normal variate transformation and de-trending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Appl Spectrosc 43:772–777. https://doi.org/10.1366/0003702894202201 https://doi.org/10.1366/0003702894202201
Butz P, Hofmann C, Tauscher B (2005) Recent developments in noninvasive techniques for fresh fruit and vegetable internal quality analysis. J Food Sci 70:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2005.tb08328.x https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2005.tb08328.x
Carlomagno G, Capozzo L, Attolico G, Distante A (2004) Non-destructive grading of peaches by near-infrared spectrometry. Infrared Phys Techn 46:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2004.03.004
Cavaco AM, Pinto P, Antunes MD, da Silva JM, Guerra R (2009) ’rocha’pear firmness predicted by a vis/nir segmented model. Postharvest Biol Tec 51:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2008.08.013 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2008.08.013
Cen H, He Y, Huang M (2006) Measurement of soluble solids contents and pH in orange juice using chemometrics and vis−NIRS. J Agr Food Chem 54:7437–7443. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf061689f
Ciosek P, Brzózka Z, Wróblewski W (2006) Electronic tongue for flow-through analysis of beverages. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 118:454–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2006.04.051
Clark CJ, McGlone VA, De Silva HN, Manning MA, Burdon J, Mowat AD (2004) Prediction of storage disorders of kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis) based on visible-NIR spectral characteristics at harvest. Postharvest Biol Tec 32:147–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2003.11.004
Cui J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhao H, Zha H (2013) Tracking generic human motion via fusion of low-and high-dimensional approaches. IEEE T Syst Man Cy-S 43:996–1002. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCA.2012.2223670 https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCA.2012.2223670
Fan HY, Wei-Zhen Lu J, Xu ZB (2000) An empirical comparison of three novel genetic algorithms. Eng Comput 17:981–1002. https://doi.org/10.1108/02644400010360901
Fan HY, Lu WZ, Xi G, Wang SJ (2003) An improved neural-network-based calibration method for aerodynamic pressure probes. J Fluids Eng 125:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1523063
Fu XP, Ying Y, Liu YD, Lu HS (2006) Detection of pear firmness using near infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Spectrosc Spect Anal 26:1038–1041
Garrido-Novell C, Pérez-Marin D, Amigo JM, Fernández-Novales J, Guerrero JE, Garrido-Varo A (2012) Grading and color evolution of apples using RGB and hyperspectral imaging vision cameras. J Food Eng 113:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.05.038
Geladi P, MacDougall D, Martens H (1985) Linearization and scatter-correction for near-infrared reflectance spectra of meat. Appl Spectrosc 39:491–500. https://doi.org/10.1366/0003702854248656
Gomez AH, He Y, Pereira AG (2006) Non-destructive measurement of acidity, soluble solids and firmness of Satsuma mandarin using vis/NIR-spectroscopy techniques. J Food Eng 77:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.06.036
Harker R (2001) Consumer response to apples. In: Washington Tree Fruit Postharvest Conference, Wenatchee, pp 13–14
Harker FR, Gunson FA, Jaeger SR (2003) The case for fruit quality: an interpretive review of consumer attitudes, and preferences for apples. Postharvest Biol Tec 28:333–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(02)00215-6 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(02)00215-6
Huang Y, Kangas LJ, Rasco BA (2007) Applications of artificial neural networks (ANNs) in food science. Crit Rev Food Sci 47:113–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390600626453
Huishan L, Yibin Y, Huanyu J, Yande L, Xiaping F, Wang J (2005) Application Fourier transform near infrared spectrometer in rapid estimation of soluble solids content of intact citrus fruits. In: American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers Annual Meeting, Tampa, p 1
Jha SN, Narsaiah K, Jaiswal P, Bhardwaj R, Gupta M, Kumar R, Sharma R (2014) Nondestructive prediction of maturity of mango using near infrared spectroscopy. J Food Eng 124:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.10.012
Lammertyn J, Peirs A, De Baerdemaeker J, Nicolaï B M (2000) Light penetration properties of NIR radiation in fruit with respect to non-destructive quality assessment. Postharvest Biol Tec 18:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(99)00071-X
Lau C (1991) Neural networks: theoretical foundations and analysis. IEEE press, Piscataway
Li M, Pullanagari RR, Pranamornkith T, Yule IJ, East AR (2017) Quantitative prediction of post storage ’Hayward’kiwifruit attributes using at harvest vis-NIR spectroscopy. J Food Eng 202:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.01.002
Liu L, Peng Y, Liu M, Huang Z (2015) Sensor-based human activity recognition system with a multilayered model using time series shapelets. Knowl-Based Syst 90:138–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.09.024 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.09.024
Liu L, Chen X, Liu M, Jia Y, Zhong J, Gao R, Zhao Y (2016) An influence power-based clustering approach with PageRank-like model. Appl Soft Comput 40:17–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.050 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.050
Liu L, Cheng L, Liu Y, Jia Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Recognizing complex activities by a probabilistic interval-based model. In: AAAI, Phoenix, pp 1266–1272
Liu L, Peng Y, Wang S, Liu M, Huang Z (2016) Complex activity recognition using time series pattern dictionary learned from ubiquitous sensors. Inform Sci 340:41–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.020 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.020
Liu L, Sun L, Chen S, Liu M, Zhong J (2016) K-PRSCAN: A clustering method based on PageRank. Neurocomputing 175:65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.020
Liu L, Wang Q, Wang J, Liu M (2016) A rolling grey model optimized by particle swarm optimization in economic prediction. Comput Intell-US 32:391–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/coin.12059
Liu L, Wang S, Peng Y, Huang Z, Liu M, Hu B (2016) Mining intricate temporal rules for recognizing complex activities of daily living under uncertainty. Pattern Recogn 60:1015–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.04.022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.04.022
Liu L, Wang S, Su G, Huang ZG, Liu M (2017) Towards complex activity recognition using a Bayesian network-based probabilistic generative framework. Pattern Recogn 68:295–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.02.028 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.02.028
Liu Y, Ying Y (2005) Use of FT-NIR spectrometry in non-invasive measurements of internal quality of ’Fuji’ apples. Postharvest Biol Tec 37:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2005.02.013
Liu Y, Ying Y, Fu X (2005) Prediction of valid acidity in intact apples with Fourier transform near infrared spectroscopy. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B 6:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0158
Liu Y, Chen X, Ouyang A (2008) Nondestructive determination of pear internal quality indices by visible and near-infrared spectrometry. LWT-Food Sci Technol 41:1720–1725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2007.10.017 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2007.10.017
Liu Y, Zhang X, Cui J, Wu C, Aghajan H, Zha H (2010) Visual analysis of child-adult interactive behaviors in video sequences. In: IEEE International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia, Seoul, pp 26–33
Liu Y, Cui J, Zhao H, Zha H (2012) Fusion of low-and high-dimensional approaches by trackers sampling for generic human motion tracking. In: IEEE ICPR, Tsukuba Science City, pp 898–901
Liu Y, Nie L, Han L, Zhang L, Rosenblum DS (2015) Action2activity: recognizing complex activities from sensor data. In: IJCAI, Buenos Aires, pp 1617–1623
Liu Y, Liang Y, Liu S, Rosenblum DS, Zheng Y (2016) Predicting urban water quality with ubiquitous data. arXiv:http://arXiv.org/abs/1610.09462
Liu Y, Nie L, Liu L, Rosenblum DS (2016) From action to activity: Sensor-based activity recognition. Neurocomputing 181:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.08.096
Liu Y, Zhang L, Nie L, Yan Y, Rosenblum DS (2016) Fortune teller: predicting your career path. In: AAAI, Phoenix, pp 201–207
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Liang Y, Liu S, Rosenblum DS (2016) Urban water quality prediction based on multi-task multi-view learning. In: IJCAI, New York City, pp 2576–2581
Lorente D, Escandell-Montero P, Cubero S, Gómez-Sanchis J, Blasco J (2015) Visible-NIR reflectance spectroscopy and manifold learning methods applied to the detection of fungal infections on citrus fruit. J Food Eng 163:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2015.04.010
Lu Y, Wei Y, Liu L, Zhong J, Sun L, Liu Y (2017) Towards unsupervised physical activity recognition using smartphone accelerometers. Multimed Tools Appl 76:10701–10719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3188-y https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3188-y
Lu Y, Wei Y, Liu L, Zhong J, Sun L, Liu Y (2017) Towards unsupervised physical activity recognition using smartphone accelerometers. Multimed Tools Appl 76:10701–10719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3188-y https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3188-y
Maier HR, Dandy GC (2000) Neural networks for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variables: a review of modelling issues and applications. Environ Modell Softw 15:101–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-8152(99)00007-9 https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-8152(99)00007-9
McGlone VA, Jordan RB, Martinsen PJ (2002) Vis/NIR estimation at harvest of pre-and post-storage quality indices for ’Royal Gala’apple. Postharvest Biol Tec 25:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(01)00180-6 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(01)00180-6
Nascimento PAM, de Carvalho LC, Júnior L C C, Pereira FMV, de Almeida Teixeira GH (2016) Robust PLS models for soluble solids content and firmness determination in low chilling peach using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR). Postharvest Biol Tec 111:345–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.08.006 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.08.006
Nicolaï B M, Lötze E, Peirs A, Scheerlinck N, Theron KI (2006) Non-destructive measurement of bitter pit in apple fruit using NIR hyperspectral imaging. Postharvest Biol Tec 40:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2005.12.006 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2005.12.006
Nicolai BM, Beullens K, Bobelyn E, Peirs A, Saeys W, Theron KI, Lammertyn J (2007) Nondestructive measurement of fruit and vegetable quality by means of NIR spectroscopy: A review. Postharvest Biol Tec 46:99–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2007.06.024
Oliveri P, Casolino MC, Casale M, Medini L, Mare F, Lanteri S (2013) A spectral transfer procedure for application of a single class-model to spectra recorded by different near-infrared spectrometers for authentication of olives in brine. Anal Chim Acta 761:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.11.020
Pearson K (1901) LIII. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond Edinb Dublin Philos Mag J Sci 2:559–572. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440109462720
Preoţiuc-Pietro D, Liu Y, Hopkins D, Ungar L (2017) Beyond binary labels: political ideology prediction of Twitter users. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, pp 729–740
Schmilovitch ZE, Mizrach A, Hoffman A, Egozi H, Fuchs Y (2000) Determination of mango physiological indices by near-infrared spectrometry. Postharvest Biol Tec 19:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(00)00102-2 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(00)00102-2
Song W, Wang H, Maguire P, Nibouche O (2016) Differentiation of organic and non-organic apples using near infrared reflectance spectroscopya pattern recognition approach. In: IEEE Sensors, Orlando, pp 1–3
Specht DF (1991) A general regression neural network. IEEE T Neural Networ 2:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.97934
Sun T, Huang K, Xu H, Ying Y (2010) Research advances in nondestructive determination of internal quality in watermelon/melon: A review. J Food Eng 100:569–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.05.019 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.05.019
Urbano-Cuadrado M, De Castro ML, Pérez-Juan P M, García-Olmo J, Gómez-Nieto M A (2004) Near infrared reflectance spectroscopy and multivariate analysis in enology: Determination or screening of fifteen parameters in different types of wines. Anal Chim Acta 527:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.07.057 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.07.057
Wang Q, Liu L, Wang S, Wang JZ, Liu M (2017) Predicting Beijing’s tertiary industry with an improved grey model. Appl Soft Comput 57:482–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.04.022
Ying YB, Liu YD, Wang JP, Fu XP, Li YB (2005) Fourier transform near-infrared determination of total soluble solids and available acid in intact peaches. T ASAE 48:229–234. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.17922 https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.17922
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by Gansu Povincial Science & Technology Department (Grant No. 1506RJZA107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Li, L., Liu, L. et al. Nondestructive measurement of internal quality attributes of apple fruit by using NIR spectroscopy. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 4179–4195 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5388-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-5388-0