Abstract
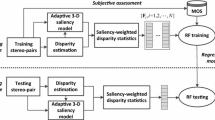
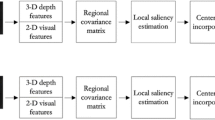
Perceptually salient regions of stereoscopic images significantly affect visual comfort (VC). In this paper, we propose a new objective approach for predicting VC of stereoscopic images according to visual saliency. The proposed approach includes two stages. The first stage involves the extraction of foreground saliency and depth contrast from a disparity map to generate a depth saliency map, which in turn is combined with 2D saliency to obtain a stereoscopic visual saliency map. The second stage involves the extraction of saliency-weighted VC features, and feeding them into a prediction metric to produce VC scores of the stereoscopic images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach compared with the conventional prediction methods on the IVY Lab database, with performance gain ranging from 0.016 to 0.198 in terms of correlation coefficients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bando T, Lijima A, Yano S (2012) Visual fatigue caused by stereoscopic images and the search for the requirement to prevent them: a review. J Display 33(2):76–83
Banitalebi-Dehkordi A, Nasiopoulos E, Pourazad MT, Nasiopoulos P (2016) Benchmark three- dimensional eye-tracking dataset for visual saliency prediction on stereoscopic three-dimensional video. J Electron Imaging 25(1):1–20
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2006) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 2(3):389–396
Cheng MM, Zhang GX, Mitra NJ et al (2015) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):409–416
Choi J, Kim D, Ham B et al (2010) Visual fatigue evaluation and enhancement for 2D-plus-depth video. In: Proc of IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), Hongkong, pp 2981–2984
Ee RV, Bank MS, Backus BT (2001) An analysis of binocular slant contrast. Perception 28(9):1121–1145
Ee RV, Erkelens CJ (2001) Anisotropy in Werner’s binocular depth contrast effect. Vis Res 36(15):2253–2262
Felzenszwalb PF, Huttenlocher DP (2004) Efficient graph-based image segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 59(2):167–181
Ghimire D, Lee J (2011) Nonlinear transfer function-based local approach for color image enhancement. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 57(2):858–865
Gottschalk PG, Dunn JR (2005) The five-parameter logistic: a characterization and comparison with the four-parameter logistic. Anal Biochem 343(1):54–65
Guo C, Zhang L (2010) A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(1):185–188
Haigh SM, Barningham L, Berntsen M et al (2013) Discomfort and the cortical haemodynamic response to coloured gratings. Vis Res 89(5):46–53
Harel J, Koch C, Perona P (2007) Graph-based visual saliency. In: Proc of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 545–552
Hou X, Zhang L (2007) Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach. In: Proc of IEEE conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Minneapolis, USA, pp 1–8
Jiang G, Zhou J, Yu M et al (2015) Binocular vision based objective quality assessment method for stereoscopic images. Multimed Tools Appl 74(18):8197–8218
Jung Y, Sohn h, Lee S, Ro Y (2012) IVY Lab Stereoscopic Image Database [Online]. Available: http://ivylab.kaist.ac.kr/demo/3DVCA/3DVCA.htm
Jung YJ, Sohn, Lee S, Park H (2013) Predicting visual discomfort of stereoscopic images using human attention model. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 23(12):2077–2082
Jung C, Wang S (2015) Visual comfort assessment in stereoscopic 3D images using salient object disparity. Electron Lett 51(6):482–484
Kim D, Sohn K (2011) Visual fatigue prediction for stereoscopic image. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 21(2):231–236
Lambooij M, IJsseltstejin WA, Heynderickx I (2012) Visual discomfort of 3D-TV: assessment methods and modeling. Displays 32(4):209–218
Lina J, Selim O, Peter K (2009) Influence of disparity on fixation and saccades in free viewing of natural scenes. J Vis 9(1):74–76
Niu Y, Geng Y, Li X, Liu F (2012) Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In: 25th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2012), Rhode Island, pp 454–461
Oh C, Ham B, Choi S et al (2015) Visual fatigue relaxation for stereoscopic video via nonlinear disparity remapping. IEEE Trans Broadcast 61(2):142–153
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-scale histograms. IEEE Trans Smc 9:62–66
Park J, Lee S, Bovik AC (2014) 3D visual discomfort prediction: vergence, foveation, and the physiological optics of accommodation. IEEE J Sel Top Sign Process 8(3):415–427
Park J, Oh H, Lee S et al (2015) 3D visual discomfort predictor: analysis of horizontal disparity and neural activity statistics. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(3):1101–1114
Paschos G (2001) Perceptually uniform color spaces for color texture analysis: an empirical evaluation. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(6):932–937
Shao F, Lin W, Gu S et al (2013) Perceptual full-reference quality assessment of stereoscopic images by considering binocular visual characteristics. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(5):1940–1953
Sohn H, Jung YJ, Lee S, Ro YM (2013) Predicting visual discomfort using object size and disparity information in stereoscopic images. IEEE Trans Broadcast 59(1):28–37
Tanimoto M, Fujii T, Suzuki K (2009) Depth estimation reference software (DERS)5.0, ISO/IEC JTCI/SC29/WG11 M16923
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Wang J, Dasilva MP, Lecallet P et al (2013) Computational model of stereoscopic 3D visual saliency. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(6):2151–2165
Zhang Y, Jiang G, Yu M (2010) Stereoscopic visual attention model for 3D video. Advances in Multimedia Modeling, Berlin, Germany: Springer-verlag, pp 324–324
Zhang L, Tong M, Marks T et al (2008) SUN: a Bayesian framework for saliency using natural statistics. J Vis 8(7):1–20
Zhaoqing P, Zhang Y, Kwong S (2015) Efficient motion and disparity estimation optimization for low complexity multiview video coding. IEEE Trans Broadcast 61(2):166–176
Zilly F, Kluger J, Kauff P (2011) Production rules for stereo acquisition. Proc IEEE 99(4):590–606
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the anonymous reviewers whose insightful comments have helped improve the paper. This work was supported in part by Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant Nos. 61401132 and 61471348), in part by Zhejiang Natural Science Funds (Grant No. LY17F020027), in part by Guangdong Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar (Grant No. 2016A030306022) and in part by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2014AA01A302)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., He, Y., Zhang, S. et al. Visual comfort prediction for stereoscopic image using stereoscopic visual saliency. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 23499–23516 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4126-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-4126-3