Abstract
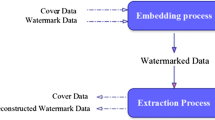
Buyer-seller watermarking protocols, combining digital watermarking and cryptographic tools, have become a feasible technique to guarantee piracy tracing. For securing health information management, watermarking protocols may be introduced to solve the problem of traitor tracing, i.e., tracing the physician who illegally discloses the patient’s health information. As a physician asks the health information system (HIS) for the intended patient’s health information, the relationship between the physician and HIS is similar to that between buyer and seller. By watermarking protocol, it can prevent physician from illegally distributing the patient’s health information over telemedicine environments in case remote physician and local physician exchange the patient’s health information and diagnosis views. While unauthorized health information is found, HIS can trace and accuse some physician who illegally releases the sensitive patient’s health information. However, buyer-seller protocols mentioned above cannot be applied to telemedicine systems directly because there is more than one physician involved. This paper proposes a multi-watermarking protocol to solve this problem, in which a well-defined single watermarking protocol is extended to form a novel multi-watermarking protocol. In addition, the proposed protocol adopts symmetric cryptosystem into watermark embedding so that the computation cost is lower than the protocols based on public key operation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelsbach A, Huber U, Sadeghi AR (2006) Fingercasting-joint fingerprinting and decryption of broadcast messages. In Proceedings of ACISP’06 4058:136–147
Celik M, Lemma A, Katzenbeisser S, van der Veen M (2007) Secure embedding of spread spectrum watermarks using look-up-tables. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing 153–156
Chen TH, Horng G, Tsai D (2005) An anonymous buyer-reseller watermarking protocol. J Chin Inst Eng 28(3):535–538
Cheung SC, Currem H (2002) Rights protection for digital contents redistribution over the internet. In Proceedings of 26th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference 26–29:105–110
Das VV (2008) Buyer-seller watermarking protocol for an anonymous network transaction. in proceedings of first International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Technology 807–812
Deng M, Preneel B (2008) On secure and anonymous buyer-seller watermarking protocol. In proceedings of third International Conference on Internet and Web Applications and Services 524–529
Gritzalis S, Lambrinoudakis C, Lekkas D, Deftereos S (2005) Technical guidelines for enhancing privacy and data protection in modern electronic health environments. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 9(3):413–423
Ibrahim IM, Din SHNE, Hegazy AFA (2007) An effective and secure buyer-seller watermarking protocol. In proceedings of third International Symposium on Information Assurance and Security 21–28
Katzenbeisser S, Lemma A, Celik MU, Veen MVD, Maas M (2008) A buyer-seller watermarking protocol based on secure embedding. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 3(4):783–786
Kundur D (2004) Video fingerprinting and encryption principles for digital rights management. Proc IEEE 92(6):918–932
Lei CL, Pei-Ling Y, Tsai P-L, Chan M-H (2004) An efficient and anonymous buyer-seller watermarking protocol. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(12):1618–1626
Lemma A, Katzenbeisser S, Celik M, van der Veen M (2006) Secure watermark embedding through partial encryption. In Proceedings of IWDW’06 4283:433–445
Li M, Poovendran R, Narayanan S (2005) Protecting patient privacy against unauthorized release of health images in a group communication environment. Comput Health Imaging Graph 29(5):367–383
Memon N, Wong PW (2001) A buyer-seller watermarking protocol. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(4):643–649
RSA Laboratories’ Frequently Asked Questions about Today’s Crypto-graphy, V4.0, available from http://www.rsasecurity.com/rsalabs/faq/.
Yong S, Lee SH (2005) An efficient fingerprinting scheme with symmetric and commutative encryption. In Proceedings of IWDW’05, LNCS 3710:54–66
Zhang J, Kou W, Fan K (2006) Secure buyer-seller watermarking protocol. IEE Proc Inf Sec 153(1)
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported National Science Council, Taiwan, R.O.C., under contract by NSC 102-2221-E-415-014 and NSC 102-2221-E-415-007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeng, FG., Wu, YT. & Chen, TH. A multi-watermarking protocol for health information management. Multimed Tools Appl 75, 8123–8135 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2728-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2728-9