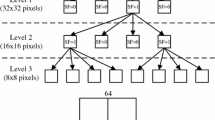
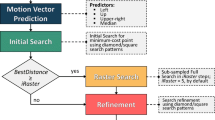
Abstract
Computational load of motion estimation in advanced video coding (AVC) standard is significantly high and its more true for HDTV sequences. In this paper, video processing algorithm is mapped onto a learning method to improve machine to machine (M2M) architecture, namely, the parallel reconfigurable computing (PRC) architecture, which consists of multiple units, First, we construct a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to represent the video coding algorithms comprising motion estimation. In the future trillions of devices are connected (M2M) together to provide services and that time power management would be a challenge. Computation aware scheme for different machine is reduced by dynamically scheduling usage of multi-core processing environment for video sequence depending up complexity of the video. And different video coding algorithm is selected depending upon the nature of the video. Simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed method.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benini L, Paleologo G, Bogliolo A, De Micheli G (1999) Policy optimization for dynamic power management. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Des 18(6):813–833
Chen Y-K (2012) Challenges and opportunities of internet of things. ASP-DAC, 2012, 17th Asia-South Pacific Conference Proceedings, Page 383–388, Jan 30th–Feb 2nd 2012
Chen LF, Lai YK (2004) VLSI architecture of the reconfigurable computing engine for digital signal processing applications. IEEE Circuits and Systems Conference, ISCAS ’04. pp 937–40
Chung E, Benini L, De Micheli G (1999) Dynamic power management for nonstationary service requests. Design, Automation and Test in Europe, pp 77–81
Johnson RA (2001) Probability and statistics for engineers. Prentice hall of India
Joint Video Team of ITU-T and ISODEC JTC I (2003) Draft ITU-T recommendation and final draft international standard of joint video specification. (ITU-T Kec. H.264 ISO/IEC 14496.10 AVC) JVT of ISO/IEC MPEG and ITU-T VCEG , JVT – GO05
Kortuem G, Kawar F, Fitton D, Sundramoorty V (2010) Smart object as building blocks for the internet of things. IEEE Internet Comput 44–51
Lu Y, Chung E, Simuníc T, Benini L, De Micheli G (2000) Quantitative comparison of PM algorithms. Design, Automation and Test in Europe, pp 20–26
Lu Y-H, De Micheli G (2001) Comparing system-level power management policies. Stanford University, IEEE
Maestre R, Kurdahi FJ, Fernández M, Hermida R, Bagherzadeh N, Singh H (2001) Kernel scheduling techniques for efficient solution space exploration in reconfigurable computing. Special issue on modern methods and tools in digital system design. J Syst Archit 47:277–292
Paul A (2013) High performance for adaptive deblocking filter in H.264/AVC system. IETE Tech Rev
Paul A, Bharanitharan K, Wu J (2013) Algorithm and architecture for adaptive motion estimation in video processing. IETE Tech Rev 30(1):24–30
Paul A, Chen B-W, Bharanitharan K, Wang J-F (2013) Video search and indexing with reinforcement agent for interactive multimedia services. ACM Trans Embed Comput Syst 12(2)
Paul A, Jiang YC, Wang JF, Yang JF (2012) Parallel reconfigurable computing based mapping algorithm for motion estimation in advanced video coding. ACM Trans Embed Comput Syst 11(S2)
Paul A, Wu J, Yang J-F, Jeong J (2011) Gradient-based edge detection for motion estimation in H.264/AVC. IET Image Process 323–327
Qiu Q, Pedram M (1999) Dynamic power management based on continuous-time Markov decision processes. Design Automation Conference
Schmit H et al (2002) PipeRench: a virtualized programmable datapath in 0.18 micron technology. IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, pp 63–66
Singh H, Lu G, Lee M, Kurdahi FJ, Bagherzadeh N, Filho E, Maestre R (2000) MorphoSys: case study of a reconfigurable computing system targeting multimedia applications. Proceedings Design Automation Conference (DAC’00), pp 573–578, Los Angeles, California
Stallings W (2003) Computer organization and architecture: designing for performance. Pearson Education
Sutton RS, Barto AG (1998) Reinforcement learning—an introduction. MITPress, Cambridge, A Bradford Book
Tsai PL, Huang SY, Liu CT, Wang JS (2003) Computationaware scheme for software-based block motion estimation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 13(9):901–913
Vissers KA (2003) Parallel processing architectures for reconfigurable systems. Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition, pp 396–397
Wiegand T, Sullivan GJ, Bjontegaard G, Luthra A (2003) Overview of the H.264/AVC video coding standard. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 13(7):560–576
Acknowledgments
This research is support by Kyungpook National University Research Fund 2012. This work was partially supported by URP-CEST 2013 [Undergraduate Research Program - Center for Embedded Software Technology], Kyungpook National University, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, A., Rho, S. & Bharnitharan, K. Interactive scheduling for mobile multimedia service in M2M environment. Multimed Tools Appl 71, 235–246 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1490-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1490-0