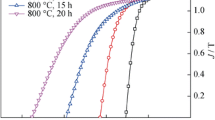
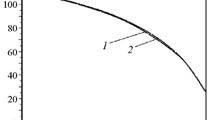
Sm – Co – Fe – Cu – Zr sintered high-temperature permanent magnets (HTPM) produced by the “POZ-Progress” Company are studied. The microstructure of the magnets is determined by scanning electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction analysis. The Curie temperature and the magnetic properties of the materials are described. The hysteresis loops of the magnets are measured in strong pulsed fields at room and elevated temperatures. The temperature dependence of the magnetic susceptibility is plotted using the method of compensated transformer in a variable magnetic field.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. G. Popov, “Temperature dependence of H c of Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)7.3 alloys,” in: Theses of Reports of VIII All-Union Conference of Permanent Magnets [in Russian], Suzdal (1988), p. 4.
A. G. Popov, A. V. Korolev, and N. N. Shchegoleva, “Temperature dependence of the coercivity of Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)7.3 alloys,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., No. 3, 100 – 105, (1990).
J. F. Liu, T. Chui, D. Dimitrov, and G. C. Hadjipanayis, “Abnormal temperature dependence of intrinsic coercivity in Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)z powder materials,” Appl. Phys. Lett., 73, 3007 – 3009 (1998).
H. Chen, M. S. Walmer, M. H. Walmer, et al., “Sm2(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)17 magnets for use at temperature > 400°C,” J. Appl. Phys., 83, 6706 – 6708 (1998).
J. F. Liu, Y. Ding, Y. Zhang, et al., “New rare-earth permanent magnets with an intrinsic coercivity of 10 kOe at 500°C,” J. Appl. Phys., 85, 5660 – 5662 (1999).
C. H. Chen, M. S.Walmer,M. H.Walmer, et al., “Magnetic pinning strength for the new Sm-TM magnetic materials for use up to 550°C,” J. App. Phys., 87, 6719 – 6721 (2000).
Y. Zhang, M. Corte-Real, G. C. Hadjipanayis, “Magnetic hardening studies in sintered Sm(Co, Cu, Fe, Zr)z 2:17 high temperature magnets,” J. Appl. Phys., 87, 6722 – 6724 (2000).
G. C. Hadjipanayis, W. Tang, Y. Zhang, et al., “High temperature 2:17 magnets: relationship of magnetic properties to microstructure and processing,” IEEE Trans. Magn., 36, 3382 – 3387 (2000).
W. Tang, A. M. Gabay, Y. Zhang, et al., “Temperature dependence of coercivity and magnetization reversal mechanism in Sm(CobalFe0.1CuyZr0.04)7.0 magnets,” IEEE Trans. Magn., 37, 2515 – 2517 (2001).
W. Tang, Y. Zhang, A. M. Gabay, and G. C. Hadjipanayis, “Anomalous temperature dependence of coercivity in rare earth cobalt magnets,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 242, 1335 – 1337 (2002).
Walmer, et al., High Temperature Permanent Magnets, Patent US 06451132, Publ. 17.09.2002.
J. F. Liu and M. S.Walmer, “Design with high performance rare earth permanent magnets,” in: Proc. 18th Int. Workshop on High Performance Magnets and their Applications, Annecy, France (2004), pp. 630 – 636.
R. K. Mishra, G. Thomas, T. Yoneyama, et al., “Microstructure and properties of step aged rare earth alloy magnets,” J. Appl. Phys., 52, 1517 – 2519 (1981).
R. M. W. Strnat, S. Liu, and K. J. Strnat, “Thermal stability and temperature coefficients of four rare-earth-cobalt matrix magnets heated in dry air,” J. Appl. Phys., 53, 2380 – 2382 (1982).
S. Liu, H. F. Mildrum, and K. J. Strnat, “Demagnetization curves of four rare-earth-cobalt magnet types at temperatures 300 – 1000 K,” J. Appl. Phys., 53, 2383 – 2385 (1982).
L. Rabenberg, R. K. Mishra, and G. Thomas, “Microstructure of precipitation-hardened SmCo permanent magnets,” Appl. Phys., 53(3), 2389 – 2391 (1982).
P. Fidler and J. Skalicky, “Microstructure of precipitation-hardened cobalt-rare earth permanent magnets,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 27(2), 127 – 131 (1982).
E. I. Teytel, A. G. Popov, V. G. Maykov, et al., “A study of the phase composition, structure and magnetic properties of alloy Sm2Co10Cu3.2Fe1.2Zr0.4,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 55(2), 349 – 357 (1983).
K.-D. Durst, H. Kronmuller, and W. Ervens, “Investigation of the magnetic properties and demagnetization processes of extremely high coercive Sm(Co, Cu, Fe, Zr)7.6 permanent magnet. 1. Determination of intrinsic magnetic material parameters,” Phys. Slat. Sol. (a), 108(1), 403 – 416 (1988).
R. Gopalan, T. Ohkubo, and K. Hono, “Identification of the cell boundary phase in the isothermally aged commercial Sm(Co0.725Fe0.1Cu0.12Zr0.04)7.4 sintered magnet,” Scr. Mater., 54, 1345 – 1349 (2006).
B. N. Beketov, V. N. Moskalev, A. V. Ogurtsov, et al., “SmCoFeCuZr permanent magnets with elevated service temperature from 400 to 600°C,” in: Theses of Reports of XIX International Conference of Permanent Magnets [in Russian], Suzdal (2013), p. 132.
V. N. Beketov, V. N. Moskalev, A. V. Ogurtsov, et al., in: Theses of Reports of XX International Conference of Permanent Magnets [in Russian], Suzdal (2015), p. 116.
A. G. Popov, D. Yu. Vasilenko, T. Z. Puzanova, et al., “Effect of the size of powder particles and concentration of adsorbed oxygen on microstructure and magnetic hysteresis properties of sintered Sm – Co – Fe – Cu – Zr magnets,” Zh. Funkts. Mater., 1(12), 449 – 455 (2007).
H. Sepehri-Amin, J. Thielsch, J. Fischbacher, et al., “Correlation of microchemistry of cell boundary phase and interface structure to the coercivity of Sm(Co0.784Fe0.100Cu0.088Zr0.028)7.19 sintered magnets,” Acta Mater., 126, 1 – 10 (2017).
N. Yu, M. Zhu, Y. Fang, et al., “The microstructure and magnetic characteristics of Sm(CobalFe0.1Cu0.09Zr0.03)7.24 high temperature permanent magnets,” Scr. Mater., 132, 44 – 48 (2017).
Acknowledgments
The work has been performed within a State Assignment of the Federal Agency of Scientific Organizations of Russia (Topic “Magnet” No. AAAA-A18118020290129-5) with partial support of a grant of the Fustian Foundation for Basic Research (Project No. 17-52-80072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 8, pp. 13 – 18, August, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beketov, V.N., Moskalev, V.N., Taranov, D.V. et al. Structure and Properties of Sm – Co – Fe – Cu – Zr Magnets for High-Temperature Applications. Met Sci Heat Treat 60, 498–503 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-018-0308-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-018-0308-0