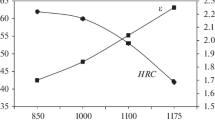
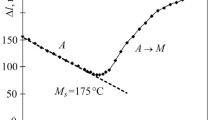
The effect of different kinds of quenching, i.e., laser, vacuum, and induction ones, on the mechanical properties and wear and corrosion resistances of stainless steel AISI 420 is studied. It is shown that all the three kinds of heat treatment raise considerably the wear resistance of the steel due to growth in the hardness. Laser and vacuum quenching also increases the corrosion resistance. After induction quenching the resistance to corrosion is lower than in untreated steel.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Post-discharge treatment involves surface engineering in a chamber spatially separated from the chamber of formation of high-frequency plasma discharge. In the volume where the treatment is conducted the charged particles are chiefly recombined to neutral ones (Ed. note).
References
D. Siva Rama Krishna and Y. Sun, Surf. Coat. Technol., 198, 447 (2005).
P. A. Dearnley and G. Aldrich-Smith, Wear, 256, 491 (2004).
S. Ganesh Sundara Raman and M. Jayaprakash, Surf. Coat. Technol., 201, 5906 (2007).
S. Mukherjee, M. F. Maitz, M. T. Pham, et al., Surf. Coat. Technol., 196, 312 (2005).
K. Hussain, A. Tauqir, A. ul Haq, and A. Q. Khan, Int. J. Fatigue, 21, 163 (1999).
Y. Sun, T. Bell, Z. Kolosvary, and J. Flis, Heat Treat. Met., 26, 9 (1999).
C. X. Li and T. Bell, Wear, 256, 1144 (2004).
K. Bordji, J. Jouzeau, D. Mainard, et al., Biomaterials, 17, 491 (1996).
M. P. Fewell, J. M. Priest, N. J. Baldwin, et al., Surf. Coat. Technol., 131, 284 (2000).
Z. Cheng, C. X. Li, H. Dong, and T. Bell, Surf. Coat. Technol., 191, 195 (2005).
F. B. Pickering, “Physical metallurgy of stainless steel developments,” Int. Met. Rev., 211, 228–241 (1976).
C. Garcia de Andres, G. Caruana, and L. F. Alvarez, Mater. Sci. Eng., A241, 211–215 (1998).
L. F. Alvarez, C. Garcia, and V. Lopez, ISIJ Int., 34, 516–521 (1994).
K. H. Prabhudev, Handbook of Heat Treatment of Steels, McGraw-Hill, New Delhi (1988), pp. 24–27, 702–704.
F. Meng, K. Tagashira, R. Azuma, and H. Sohma, ISIJ Int., 34, 205–210 (1994).
L. Qingbin and L. Hong, J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 88, 77–82 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 12, pp. 30 – 33, December, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sola, R., Giovanardi, R., Veronesi, P. et al. Effect of quenching method on the wear and corrosion resistance of stainless steel AISI 420 (TYPE 30Kh13). Met Sci Heat Treat 54, 644–647 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-013-9564-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-013-9564-1